JIC fittings are key components used in high-pressure hydraulic systems and mechanical applications. Whether you’re working in the automotive, aerospace, or construction industries, knowing about JIC fittings can help you create safer, more efficient systems. These fittings form leak-proof connections, making them essential for fluid lines and machinery that operate under high pressure.
In this guide, we will cover everything you need to know about JIC fittings, including the types available, their applications, how to install them, and how to choose the best fitting for your system. Let’s dive in!
What Are JIC Fittings?
JIC stands for Joint Industry Council, the group that standardized these fittings in the 1940s. Engineers designed them for use in hydraulic and pneumatic systems, and they have since become one of the most common types of fittings used in industrial systems worldwide.
The primary function of JIC fittings is to connect tubes, hoses, and pipes in a way that prevents leaks, even under high pressure. They are commonly used in fluid systems, including oil and gas, automotive, aerospace, and agriculture, where safety and efficiency are critical.
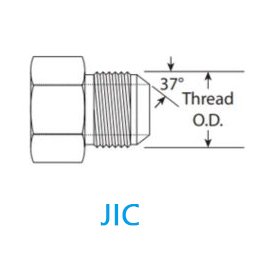
JIC fittings are easily recognizable by their 37-degree flare at the end of the tube or hose, which helps create a tight, secure connection.
Key Characteristics of JIC Fittings
JIC fittings are known for their strong, leak-proof connections. Here are some key characteristics:
- Flared Design: The tube or hose has a flared end at a 37-degree angle. This flare fits tightly into the fitting, creating a secure seal when the two parts are tightened.
- High Pressure Resistance: JIC fittings handle high-pressure systems, making them ideal for hydraulic systems that transfer fluid under extreme pressure.
- Durability: These fittings use corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel, brass, or carbon steel and perform well in harsh environments.
- Leak-Proof Seal: The 37-degree flare provides a tight, leak-proof seal that prevents fluid or gas from escaping, even at high pressures.
Types of JIC Fittings
JIC fittings come in various shapes and sizes, each designed for different applications. The most common types include:
- Straight JIC Fittings: These fittings connect two pipes or hoses in a straight line, typically used to assemble hoses or connect equipment in one direction.
- Elbow JIC Fittings: Elbow fittings create a 45-degree or 90-degree bend, allowing pipes or hoses to change direction. This is useful when space is limited or when you need to re-route a line.
- Tee JIC Fittings: Tee fittings have three connections and branch a single pipe into two separate pipes or hoses, allowing fluid to divide or combine in a hydraulic system.
- Cross JIC Fittings: Cross fittings are similar to tee fittings, but they have four connections. They are used when you need to connect multiple pipes or hoses in a cross configuration.
Each of these types plays a unique role in ensuring that fluid and gas systems function smoothly, even in complex setups.
JIC Fitting Thread Standards
JIC fittings use SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) threads. These threads have a 37-degree flare angle, which ensures that the tube and fitting form a tight seal when joined. The correct thread pitch and size are crucial for compatibility and to prevent leaks.
If the threads don’t match, the connection could fail, leading to leaks or even system failure. It’s important to always verify the size and type of threads when choosing or installing JIC fittings.
How JIC Fittings Work in Hydraulic Systems
In hydraulic systems, JIC fittings provide a critical function. They connect tubes and hoses in such a way that fluid can flow through the system without leakage, even under high pressure.
When you tighten the fitting, the flared end of the tube or hose pushes against the matching surface inside the fitting. This creates a tight seal, ensuring that the fluid is securely contained within the system. The 37-degree flare angle is key to ensuring that the connection remains leak-free even under demanding conditions.
Many systems that require tight sealing, such as fuel systems, brake systems, or hydraulic machinery, often use these fittings.
Applications
Many industries use JIC fittings because they handle high pressure and are reliable in demanding environments. Some of the most common applications include:
- Automotive: In fuel lines, brake systems, power steering, and other hydraulic systems found in vehicles. JIC fittings prevent fluid leakage and maintain pressure throughout the system.
- Aerospace: JIC fittings are used in aircraft hydraulic systems to transfer fluids. In aerospace applications, a reliable, leak-proof connection is critical for safety.
- Agriculture: Agricultural machinery, such as tractors and harvesters, often uses JIC fittings to connect hydraulic lines that power various equipment. These fittings ensure the hydraulic system works properly under pressure.
- Oil & Gas: The oil and gas industry commonly uses JIC fittings to connect pipes and hoses that carry high-pressure fluids, from drilling equipment to pipelines.
The ability to withstand high pressure and resist corrosion makes JIC fittings a popular choice in any system where fluid needs to flow under pressure without leaks.
Advantages
JIC fittings offer several advantages, making them widely used across different industries. These include:
- Leak-Proof Connections: The 37-degree flare ensures that the fitting forms a secure, leak-proof seal even under high pressure. This is especially important in critical systems where leaks could lead to system failure or accidents.
- Durability: JIC fittings are made from tough materials like stainless steel, brass, or carbon steel. This makes them resistant to corrosion and wear, which extends their lifespan.
- Versatility: JIC fittings are used in a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, and oil and gas. Their ability to handle high pressure and provide secure connections makes them useful for a variety of applications.
- Ease of Use: JIC fittings are easy to install and maintain. Unlike other fittings, they require fewer tools, making installation quicker and simpler.
Common Materials for JIC Fittings
JIC fittings are made from different materials depending on the specific application and operating environment. Some of the most common materials include:
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel offers high strength, corrosion resistance, and durability, making it ideal for critical systems where safety is a priority, such as aerospace or medical applications.
- Brass: Brass is a popular choice for lower-pressure systems or applications where weight is a concern. It is corrosion-resistant and easy to machine, making it a versatile option.
- Carbon Steel: Carbon steel is often used for industrial applications where cost is a major consideration. It is strong but may not be as resistant to corrosion as stainless steel.
Each material has strengths and weaknesses, so you must choose the right one for your application based on factors like pressure rating, environment, and fluid type.
JIC Fittings vs. Other Fitting Types
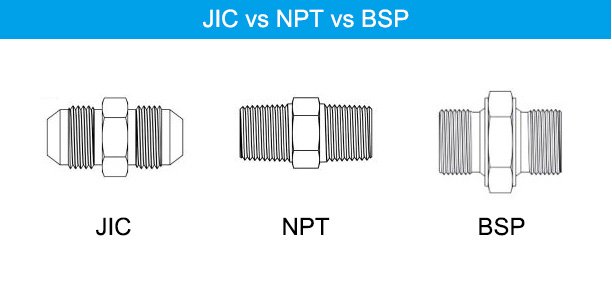
When choosing a fitting for your system, it’s important to consider how JIC fittings compare to other common types, such as NPT and BSP fittings. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | JIC Fittings | NPT Fittings | BSP Fittings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure Resistance | High | Moderate | Low to Moderate |
| Leak-Proof Seal | 37-degree flare | Tapered threads with O-ring | Compression seals |
| Compatibility | Universal across industries | More specialized | Primarily used in Europe |
JIC fittings offer superior leak-proof performance under high pressure, making them ideal for hydraulic systems, whereas NPT and BSP fittings are more specialized for certain regions or systems.
Choosing the Right JIC Fitting for Your System
Selecting the correct JIC fitting for your system is critical to ensuring that your hydraulic system functions properly. When making your choice, consider these factors:
- Pressure Rating: Always ensure that the fitting can handle the pressure in your system. Each fitting has a specific pressure rating, and using one rated too low can cause leaks or failure.
- Size Compatibility: Ensure the fitting size matches the diameter of the hose or pipe it will attach to. JIC fittings are sized by their dash number (e.g., -4, -6), which corresponds to the tube’s inside diameter.
- Material: Choose a fitting material that can withstand the conditions of your system. For example, stainless steel is ideal for corrosive environments, while carbon steel is a cost-effective option for general industrial use.
How to Measure JIC Fittings
Measuring JIC fittings accurately is crucial to ensuring compatibility with other components in your hydraulic or pneumatic system. Improperly sized fittings can lead to leaks, system failure, or unsafe operating conditions. Fortunately, measuring JIC fittings is a straightforward process when you know the key measurements to focus on. Below, we outline the essential steps for measuring JIC fittings.
1. Understanding the Dash Size and Thread Measurement
The “dash size” typically identifies JIC fittings, representing the nominal inside diameter (ID) of the tube the fitting connects to. The dash size is expressed in sixteenths of an inch, such as -4, -6, -8, -10, etc. To measure the dash size:
- Dash Size Example: A -6 JIC fitting refers to a fitting that is designed for a tube with an inside diameter of 3/8 inch (6/16 of an inch).
- Step 1: Measure the inside diameter (ID) of the tube or hose that the fitting will be connected to. If it’s a hydraulic line, ensure you’re measuring the ID accurately, using a caliper or micrometer.
- Step 2: Convert the measurement into a dash size, remembering that each dash size corresponds to 1/16th of an inch (e.g., a 1/4″ ID would be a dash -4, a 3/8″ ID would be a dash -6, and so on).
2. Measuring the Thread Size
JIC fittings also have threads that need to be measured for proper fitment. JIC uses SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) threads, which are 37-degree flare fittings. To measure the thread size:
- Step 1: Use a thread gauge or caliper to measure the external threads of the male fitting or the internal threads of the female fitting.
- Step 2: Measure the major diameter (the outermost diameter of the thread) and the pitch (the distance between thread peaks).
- Step 3: Confirm the fitting’s thread standard is SAE J514, and ensure that the thread pitch and the number of threads per inch (TPI) match the specifications for JIC fittings.
3. Measuring the Flare Angle
The 37-degree flare angle is one of the defining features of a JIC fitting. To measure this:
- Step 1: Use a protractor or a flare gauge to measure the angle of the flare on the tube or fitting.
- Step 2: The standard angle for JIC fittings is precisely 37 degrees, so be sure that your measurement matches this specification.
The flare angle ensures that when the fitting is tightened, the tube’s flared end creates a tight, leak-proof seal against the fitting’s seat.
4. Determining the Length of the Fitting
Measuring the length of a JIC fitting is essential to ensure it will fit into your system without interfering with other components or hoses. To measure the length:
- Step 1: Use a ruler or caliper to measure the length of the fitting from the base of the threads (where it connects to the component) to the end of the fitting. For elbows, tees, or crosses, measure along the centerline of the fitting.
- Step 2: Ensure that you’re measuring to the correct part of the fitting—don’t include additional lengths such as the nut or washer if they’re not part of the fitting.
5. Using a Digital Caliper or Micrometer
For precise measurements, using a digital caliper or micrometer is highly recommended. These tools allow you to accurately measure the outside and inside diameters of tubes, as well as the thread size and flare angle. Digital calipers provide a precise reading to within thousandths of an inch, which is especially helpful for smaller fittings.
6. Double-Check the Material Compatibility
When selecting and measuring a JIC fitting, it’s also important to ensure that the material of the fitting is compatible with your system’s requirements. If you’re using the fitting in a system that operates under extreme temperatures, high pressures, or aggressive chemicals, make sure the material—typically stainless steel, brass, or carbon steel—can withstand the conditions.
Installation of JIC Fittings: A Step-by-Step Guide
Installing JIC fittings is a straightforward process if done correctly. Here are the basic steps:
- Prepare the Tube or Hose: Cut the tube or hose to the required length. Be sure to smooth out the edges to avoid damaging the flare.
- Flare the Tube End: Use a flaring tool to create the 37-degree flare at the end of the tube.
- Insert the Tube into the Fitting: Push the flared tube into the fitting, ensuring it sits securely.
- Tighten the Fitting: Use the appropriate tool to tighten the fitting, ensuring a leak-proof connection. Avoid over-tightening.
Maintenance & Troubleshooting for JIC Fittings
To keep your JIC fittings in good condition, follow these maintenance tips:
- Inspect Regularly: Look for signs of wear, corrosion, or leaks. Replace any fittings that appear damaged.
- Tighten as Needed: Over time, fittings can loosen. Tighten them periodically to maintain a secure connection.
- Keep Clean: Dirt and debris can interfere with the fitting’s seal. Clean fittings regularly to ensure proper function.
Common Problems:
- Leaks: This can happen if the fitting is not tightened properly or if the flare is damaged.
- Corrosion: Occurs in harsh environments or when fittings are exposed to moisture or chemicals.
Conclusion
JIC fittings are essential components for creating high-pressure, leak-proof hydraulic systems. Their versatility, durability, and ease of use make them a go-to choice for a variety of industries, from automotive to aerospace. By understanding the different types, materials, and applications, you can select the right JIC fitting to ensure your system operates smoothly and safely.
FAQs
- What’s the difference between JIC and NPT fittings? JIC fittings use a 37-degree flare for a leak-proof seal, while NPT fittings rely on tapered threads.
- Can I reuse JIC fittings? Yes, as long as they are in good condition and the sealing surface is not damaged.
- How do I maintain JIC fittings? Regularly check for wear, tighten as necessary, and clean them to avoid debris buildup.
- What materials are JIC fittings made from? JIC fittings are usually made from stainless steel, brass, or carbon steel.
- Can JIC fittings be used for fuel lines? Yes, JIC fittings are perfect for high-pressure fuel lines where a secure, leak-proof connection is essential.