1. Introduction
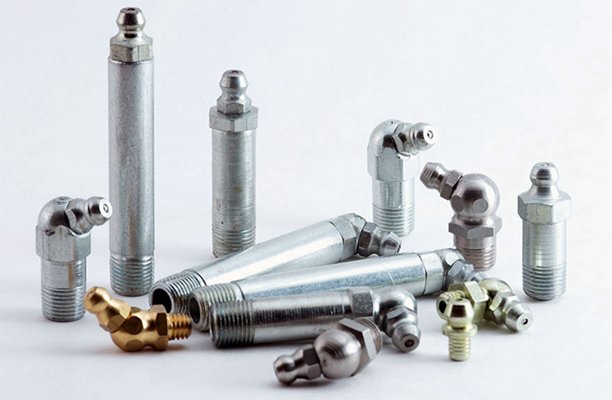
Grease fittings, also known as Zerk fittings, play a vital role in ensuring the proper lubrication of mechanical systems. Whether you’re working with automotive, manufacturing, or agricultural machinery, grease fittings are essential components that help reduce friction and prevent wear and tear on critical parts. This guide will delve into the importance of grease fittings, the different types available, how to select the correct size, and best practices for maintenance.
2. What Are Grease Fittings?
Definition and Function
Grease fittings are small components that are installed into machinery to enable the easy application of grease or lubrication to specific parts. These fittings are designed to accept grease from a grease gun, which is then directed to the bearings, joints, or other moving parts that require lubrication. By ensuring proper lubrication, grease fittings help prevent friction, reduce the risk of overheating, and extend the lifespan of machinery.
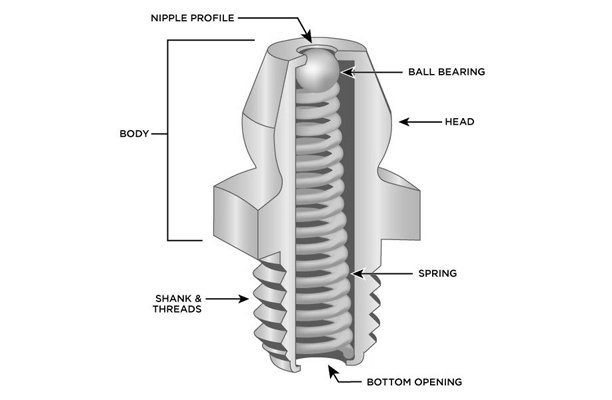
Types of Grease Fittings
There are several types of grease fittings, each designed to meet specific lubrication needs. Some of the most common types include:
- Standard Grease Fittings: The most commonly used type, these fittings are used in a wide variety of machinery and vehicles.
- Button Head Grease Fittings: These fittings have a flat, rounded head that allows for easier application of grease, typically used in low-clearance areas.
- Flush-type Grease Fittings: Designed to sit flush with the surface of the machine, these fittings prevent accumulation of dirt and debris.
- 90-degree Grease Fittings: These fittings have a right-angle design, making them ideal for tight spaces or when straight fittings are difficult to access.
- Hydraulic Grease Fittings: Used in hydraulic systems to ensure lubrication under high pressure.
3. How Do Grease Fittings Work?
Grease fittings function by allowing the application of lubrication directly into parts of machinery that require it. The grease is pumped into the fitting using a grease gun, which then forces the grease into the internal components of the machine, such as bearings or bushings. This process helps reduce friction, wear, and heat, contributing to smoother operation and extended machine life. Grease fittings are often used in areas where machinery parts are under heavy load or require regular lubrication.
Proper grease fitting maintenance is crucial for their functionality. Over time, grease fittings can become clogged, leading to reduced lubrication flow and potential damage to the machinery. Regular inspection and cleaning are recommended to ensure they remain functional and free from blockages.
4. Standard Grease Fitting Sizes
Metric vs Imperial Sizes
Grease fittings come in two primary measurement systems: metric and imperial. Understanding the difference between these two systems is essential when selecting the right grease fitting for your application. In general, the imperial system uses inches to measure dimensions, while the metric system uses millimeters. Choosing the correct measurement system is vital to ensure compatibility with your machinery and prevent issues during installation or operation.
In the United States, imperial sizes are more common, while many international and European manufacturers prefer metric sizes. For example, common imperial sizes include 1/4″ and 1/8″, while metric sizes might include M6 and M8. Always verify the system used by your machinery to avoid choosing the wrong size grease fitting.
Grease Fitting Size Chart & Standard Dimensions
To assist in selecting the right size grease fitting, a standard size chart can be used. The chart outlines common sizes for both imperial and metric fittings, including dimensions for both the fitting and the corresponding hole in the machine component. Here is an example of a typical size chart:
| Fitting Type | Thread Size (Imperial) | Thread Size (Metric) | Recommended Hole Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Grease Fitting | 1/4″-28 | M6x1.0 | 5.5mm |
| 90-Degree Grease Fitting | 1/4″-28 | M6x1.0 | 5.5mm |
| Button Head Grease Fitting | 1/8″-27 | M5x0.8 | 3.5mm |
5. Factors to Consider When Choosing Grease Fitting Sizes
Choosing the right grease fitting size involves several factors to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with your machinery. Below are the key considerations:
Equipment Requirements
Different machines have varying lubrication needs. For instance, industrial machinery might require heavy-duty grease fittings, while automotive applications might use more compact ones. The equipment’s design and the lubrication points’ location can determine the type and size of the grease fitting needed.
Operational Environment
The operating conditions of your machinery should also play a crucial role in your grease fitting selection. For example, equipment exposed to high temperatures or harsh environmental conditions (like dust, dirt, or water) might need specialized fittings, such as flush-type fittings that prevent debris from entering the grease flow.
Type of Grease Used
The type of grease used in the machinery can influence the grease fitting selection. For high-pressure applications, heavier-duty grease fittings that can withstand the pressure are necessary. Similarly, if using a grease with a high viscosity, ensure the fitting can accommodate it without clogging.
6. Measuring and Identifying Grease Fitting Sizes
To ensure that you select the correct grease fitting, accurate measurement is essential. Using the right tools and techniques can help you identify the proper size for your application. This section provides a guide on how to measure grease fittings and identify the correct size for your needs.
Tools and Techniques for Accurate Measurement
Several tools can be used to measure grease fittings accurately:
- Calipers: A caliper is one of the most precise tools for measuring the outer diameter and thread size of grease fittings. It helps in measuring both internal and external dimensions.
- Micrometers: For more precise measurements, a micrometer can measure the diameter of the fitting to within thousandths of an inch.
- Grease Fitting Gauge: A grease fitting gauge is specifically designed to help identify the thread size of a grease fitting quickly.
Make sure to use the appropriate tool for the measurements you need, and double-check your readings to avoid mistakes. If you’re measuring the hole where the fitting is installed, a hole gauge can also be beneficial.
Step-by-Step Measurement Process
Follow these steps to measure a grease fitting accurately:
- Step 1: Clean the grease fitting to ensure you get an accurate measurement without dirt or grease interfering with your readings.
- Step 2: Use a caliper or micrometer to measure the outer diameter of the fitting, ensuring to check the thread size and pitch.
- Step 3: If using a grease fitting gauge, insert it into the threads of the fitting to identify the exact size and type.
- Step 4: Compare your measurements with the corresponding size charts to ensure compatibility with your equipment.
7. Selecting the Right Grease Fitting for Your Needs
Choosing the correct grease fitting is crucial for ensuring the proper function of your machinery. This section outlines the process of selecting the best grease fitting based on your specific requirements.
Step-by-Step Selection Process
The selection process for grease fittings involves several steps. Here’s a simple guide to help you:
- Step 1: Assess the machine’s lubrication requirements. Identify the lubrication points and pressure ratings.
- Step 2: Determine the fitting size based on the equipment specifications and measurement guidelines.
- Step 3: Choose the material of the fitting that suits the environmental and operational conditions (e.g., stainless steel for corrosion resistance).
- Step 4: Select the appropriate fitting type (e.g., flush-type or 90-degree) based on accessibility and space constraints.
Matching Fittings to Specific Needs
Different machines may require different types of grease fittings. For example:
- High-pressure applications: Choose heavy-duty fittings capable of withstanding higher grease pressures.
- Space constraints: In tight spaces, 90-degree or button-head fittings are ideal, as they allow for easier installation in hard-to-reach areas.
- Environmental factors: If the machinery is exposed to harsh weather, corrosive substances, or extreme temperatures, opt for fittings made from durable, corrosion-resistant materials.
Evaluating Pressure Requirements
When selecting a grease fitting, it’s crucial to evaluate the pressure requirements of your machinery. Some systems, such as hydraulic machinery, may require fittings that can handle higher pressures. Make sure to match the grease fitting’s pressure rating with the equipment’s needs to ensure smooth operation and prevent fitting failure.
8. Best Practices for Installing Grease Fittings
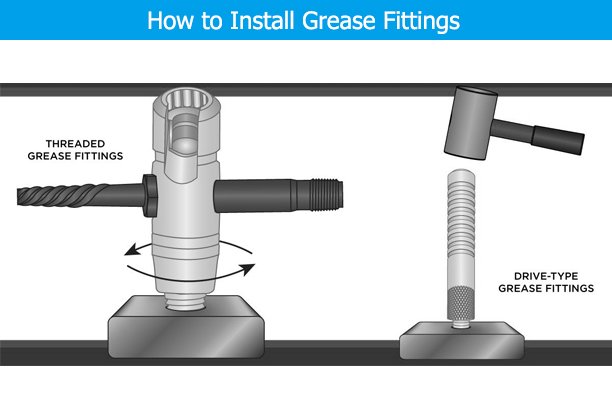
Proper installation of grease fittings is crucial to ensuring their long-term functionality and preventing potential issues like leakage or clogging. This section highlights the best practices to follow when installing grease fittings.
Tools Needed for Installation
To install grease fittings effectively, you will need a few basic tools:
- Grease Fitting Tool: A special grease fitting tool helps you easily install the fittings into the machine.
- Torque Wrench: Using a torque wrench ensures the fitting is installed with the correct amount of force, preventing over-tightening or under-tightening.
- Sealing Compound: For preventing leakage, a sealing compound or thread sealant may be necessary, especially when working in high-pressure environments.
Proper Torque and Sealing Techniques
When installing grease fittings, it’s essential to follow proper torque specifications. Over-tightening can damage the fitting or cause the threads to strip, while under-tightening can result in leaks. Always check the torque specification in the manufacturer’s manual for both the fitting and the equipment. Additionally, applying a thin layer of thread sealant on the fitting threads helps create a secure seal, preventing grease leakage during operation.
Avoiding Contamination During Installation
Contaminants like dirt, dust, or moisture can enter the grease system and compromise the effectiveness of lubrication. To prevent contamination during installation, ensure the fitting and surrounding areas are clean before installing the new grease fitting. Use clean cloths to wipe away debris, and consider using a protective cover over the fitting to keep it clean until it’s ready for use.
9. Maintenance and Troubleshooting Grease Fittings
Grease fittings require periodic maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Neglecting proper maintenance can lead to clogging, leakage, and ultimately, equipment failure. This section explains how to maintain your grease fittings and troubleshoot common issues.
How to Keep Your Grease Fittings in Top Condition
Routine maintenance is key to extending the lifespan of grease fittings. Here are some tips for proper maintenance:
- Regular Lubrication: Ensure that grease fittings are regularly lubricated to maintain their function and prevent wear.
- Inspect for Wear: Check fittings periodically for signs of wear or damage, and replace any that show signs of excessive use.
- Clean Fittings: Clean grease fittings regularly to avoid the buildup of dirt, which can clog the fitting and prevent grease from flowing effectively.
How to Fix Clogged or Damaged Grease Fittings
If a grease fitting becomes clogged or damaged, it may prevent proper lubrication. To fix a clogged fitting, follow these steps:
- Step 1: Remove the fitting and inspect it for blockages.
- Step 2: Use a cleaning tool or compressed air to clear out any grease or debris blocking the fitting.
- Step 3: If cleaning doesn’t resolve the issue, replace the fitting with a new one to restore proper lubrication.
For damaged fittings, always replace them with high-quality replacements to prevent further issues.
10. Grease Fittings vs Other Lubrication Methods
While grease fittings are widely used for lubrication in machinery, they are not the only option available. This section compares grease fittings with other lubrication methods to help you understand their advantages and disadvantages.
Grease Fittings vs Oil Lubrication
Grease fittings and oil lubrication systems both serve to reduce friction and wear in machinery, but they operate differently. Grease is typically thicker and stays in place longer, making it ideal for high-pressure or slow-moving components. Oil, on the other hand, is more fluid and can be used for faster-moving parts or systems requiring constant lubrication.
Here are some key differences:
- Grease: Ideal for high-load, low-speed applications and for areas where lubrication must stay in place for long periods.
- Oil: Suitable for high-speed components that require constant lubrication and cooling, such as engines and motors.
Best Lubrication Method for Different Applications
Choosing the right lubrication method depends on the specific needs of the equipment. Grease fittings are commonly used in machinery with moving parts under high pressure, such as agricultural equipment and automotive systems. Oil lubrication is better suited for high-speed applications like motors and turbines. Understanding the requirements of your machinery will help you select the optimal lubrication method for better performance and longevity.
11. Recommended Grease Fitting Brands & Manufacturers
Not all grease fittings are created equal. When choosing grease fittings, it’s essential to select reputable brands and manufacturers to ensure quality, durability, and compatibility with your equipment. Here are some of the top brands and manufacturers to consider:
11.1. Top-rated Grease Fitting Manufacturers
- SKF: SKF is known for its high-quality bearings and lubrication systems, including grease fittings that ensure optimal performance in a variety of industries.
- Lincoln Industrial: A leading manufacturer of lubrication equipment, including grease fittings, Lincoln Industrial provides products designed for reliability in harsh environments.
- Timken: Timken is recognized for its precision-engineered lubrication components, including durable grease fittings for heavy-duty applications.
11.2. How to Choose High-Quality Grease Fittings
When selecting grease fittings, look for these qualities:
- Material Quality: Choose fittings made from corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel or brass.
- Precision: Ensure the fitting is manufactured with tight tolerances for leak-free operation.
- Durability: Look for fittings that are designed for heavy-duty applications and can withstand harsh operating conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, grease fittings are essential components that ensure the smooth operation of various types of machinery by reducing friction and wear. Choosing the right grease fitting size, understanding the different types, and maintaining them properly can significantly extend the lifespan of your equipment. By following the guidelines in this guide, you can make informed decisions when selecting grease fittings and ensure optimal lubrication for your machinery.
Regular maintenance, proper installation, and the use of high-quality grease fittings will help you avoid costly repairs and downtime, ultimately improving the efficiency and longevity of your equipment. Whether you’re working with heavy machinery, automotive systems, or agricultural equipment, grease fittings are indispensable for maintaining smooth and reliable operation.
FAQs
1. What is the lifespan of a grease fitting?
The lifespan of a grease fitting depends on factors like the quality of the fitting, the operating conditions, and the maintenance schedule. Typically, with proper care, a grease fitting can last several years before needing replacement.
2. Can grease fittings be reused?
Grease fittings can often be reused as long as they are not damaged or clogged. However, it is essential to inspect them regularly for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion, as worn-out fittings can lead to lubrication issues.
3. How do you know if a grease fitting is bad?
A grease fitting can be considered bad if it shows signs of leakage, is clogged, or fails to accept grease properly. Difficulty greasing or a noticeable lack of lubrication could also indicate a malfunctioning fitting.
4. What happens if you over-grease a fitting?
Over-greasing a fitting can lead to the accumulation of excess grease, which can cause the fitting to become clogged or leak. This can result in ineffective lubrication, potential damage to components, and a messy work environment.
5. Are grease fittings universal?
Grease fittings are not always universal. Different machines may require different fitting types and sizes, so it’s crucial to choose the right fitting based on your equipment’s specifications to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.





