Introduction
BSP (British Standard Pipe) threads are widely used in hydraulic systems, but they are not always the best fit for every application. Due to regional preferences, compatibility issues, and advancements in hydraulic technology, many industries seek alternatives to BSP threads. Choosing the right thread type is crucial to ensuring leak-proof connections, high-pressure resistance, and overall system efficiency.
In this article, we’ll explore why BSP threads may not always be the best choice, the alternatives available, and how to choose the right one for your hydraulic system.
Understanding BSP Threads in Hydraulics
What is BSP (British Standard Pipe)?
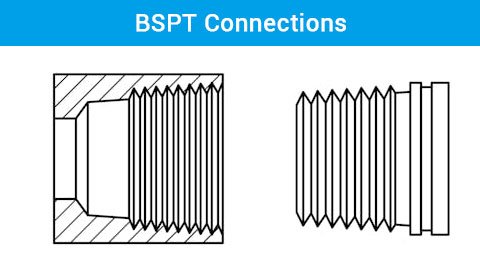
BSP is a thread standard commonly used in hydraulic and pneumatic applications, particularly in Europe, Asia, and Australia. It is divided into two types:
- BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel) – A parallel-threaded connection that relies on an O-ring or washer for sealing.
- BSPT (British Standard Pipe Tapered) – A tapered-thread connection that seals by thread interference.
Common Applications of BSP in Hydraulics
BSP threads are widely used in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and construction. They are favored due to their simplicity and historical standardization in many regions.
Limitations and Challenges with BSP Threads
Despite their widespread use, BSP threads come with certain challenges:
- Regional Compatibility Issues: Many countries, including the U.S., prefer NPT or metric threads.
- Sealing Limitations: BSPP requires an additional sealing washer, while BSPT can have leak risks due to thread taper.
- Pressure Constraints: Some BSP connections may not handle extremely high-pressure applications as efficiently as other alternatives.
Common Alternatives to BSP Threads
To address these limitations, several alternative thread standards are used in hydraulic systems. The most common alternatives include:
- NPT (National Pipe Thread): Popular in North America, NPT is a tapered-thread connection that offers strong sealing properties.
- Metric Threads: Common in Europe and Asia, metric threads follow ISO and DIN standards, providing compatibility with modern hydraulic equipment.
- JIC (Joint Industry Council): A flare-fitting thread that provides a leak-free seal and high-pressure tolerance.
- ORFS (O-Ring Face Seal): Designed for high-pressure applications, ORFS uses an O-ring for superior sealing performance.
- SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers): A thread standard commonly used in the automotive and industrial sectors.
Each of these alternatives has specific advantages and limitations, making them suitable for different applications. In the next sections, we will explore these options in more detail.
NPT (National Pipe Thread) as an Alternative
What is NPT?
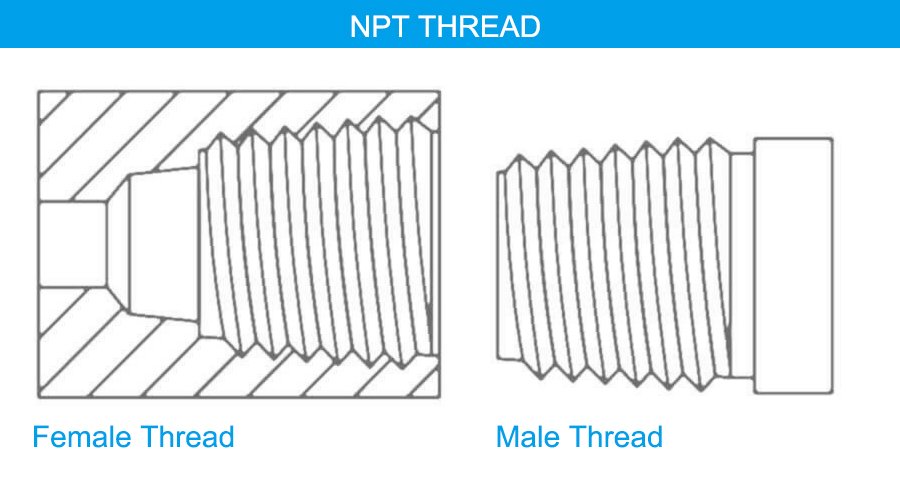
NPT (National Pipe Thread) is the standard pipe threading system used primarily in the United States. It features a tapered design, which allows the threads to create a mechanical seal by wedging together tightly. This differs from BSPP, which requires a separate sealing element.
Key Differences Between NPT and BSP
While both BSPT and NPT have tapered threads, they are not interchangeable due to their differing thread angles:
- Thread Angle: NPT threads have a 60-degree thread angle, whereas BSPT threads have a 55-degree angle.
- Sealing Method: NPT forms a seal through thread interference, while BSPT may require thread sealant.
- Regional Use: NPT is the standard in North America, while BSP is common in Europe and Asia.
Pros and Cons of Using NPT in Hydraulics
Advantages:
- Good sealing performance due to tapered design.
- Widely available in North America.
- Reliable for medium to high-pressure applications.
Disadvantages:
- Not compatible with BSP threads without adapters.
- Thread wear over time can lead to leaks.
- Requires proper torqueing to prevent damage.
Metric Threads in Hydraulic Systems
Introduction to Metric Threads
Metric threads are widely used in Europe and Asia for hydraulic applications. Unlike BSP and NPT, metric threads follow standardized ISO and DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung) specifications.
Common Metric Thread Standards
- ISO 6149: Designed for high-pressure hydraulic applications, using an O-ring for sealing.
- DIN 3852: A common metric thread standard for hydraulic fittings.
- ISO 9974: Another widely used hydraulic metric thread standard.
Benefits of Metric Threads Over BSP
Advantages:
- More precise thread specifications compared to BSP.
- Better sealing performance when using O-ring face seals.
- Globally recognized standard in modern hydraulic systems.
Disadvantages:
- Less common in North America compared to NPT.
- Requires proper identification to avoid mismatches.
JIC (Joint Industry Council) Threads
What is JIC Threading?
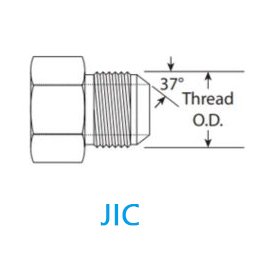
JIC (Joint Industry Council) threads are a popular hydraulic fitting standard based on a 37-degree flare design. These fittings use metal-to-metal contact to create a secure, leak-proof connection.
Why JIC is Widely Used in Hydraulic Applications
- High Pressure Handling: JIC threads are commonly used in high-pressure hydraulic systems due to their secure seal.
- Interchangeability: They are widely used in industrial, automotive, and aerospace applications.
- Reusable Connections: Unlike BSP or NPT, JIC fittings can be disassembled and reused without damaging the thread.
Comparison of JIC vs. BSP
While BSP threads rely on a washer or thread taper for sealing, JIC threads use a 37-degree flare, offering superior resistance to leaks.
Advantages of JIC:
- Leak-proof connections even under high pressure.
- Easier to assemble and disassemble without damage.
- More widely used in North America and globally.
Disadvantages of JIC:
- Requires flaring tools for proper installation.
- Higher initial cost than BSP fittings.
ORFS (O-Ring Face Seal) Threads
What is ORFS?
O-Ring Face Seal (ORFS) threads are a highly reliable alternative to BSP, particularly in high-pressure hydraulic systems. These fittings feature a flat sealing surface with an O-ring, ensuring a leak-free connection.
Advantages of ORFS for High-Pressure Systems
- Superior Sealing: The O-ring face seal design prevents leaks, making it ideal for high-pressure applications.
- Vibration Resistance: ORFS fittings are highly resistant to loosening due to system vibrations.
- Long-Term Durability: The design reduces wear and tear, extending the life of the connection.
Why ORFS is a Reliable Replacement for BSP
ORFS fittings offer significant benefits over BSP, including:
- Better high-pressure sealing without thread interference.
- No additional sealant or washer required.
- Used extensively in heavy machinery, aerospace, and industrial hydraulics.
SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) Threads
Overview of SAE Thread Standard
SAE threads are commonly used in hydraulic applications, particularly in North America. These fittings follow a standard set by the Society of Automotive Engineers, ensuring compatibility across various hydraulic systems.
Benefits of SAE in Hydraulic Applications
- Standardized Design: SAE threads ensure easy replacement and compatibility.
- Leak Prevention: Many SAE fittings use O-rings to improve sealing performance.
- Widely Used in North America: Ideal for industries that follow U.S. engineering standards.
How SAE Compares to BSP
While BSP relies on thread engagement for sealing, SAE fittings often use O-rings, providing a more secure connection. Additionally, SAE threads are easier to integrate into North American hydraulic systems without the need for adapters.
UN/UNF (Unified National Fine) Threads
Introduction to UN/UNF Threads
Unified National (UN) and Unified National Fine (UNF) threads are widely used in hydraulic and fluid power systems. These threads follow a straight-thread design and typically require an O-ring for sealing.
Key Differences Between UN/UNF and BSP
- Thread Design: UN/UNF threads are straight, whereas BSPT threads are tapered.
- Sealing Method: UN/UNF fittings rely on O-rings instead of thread engagement.
- Regional Usage: UNF threads are more common in North America, whereas BSP is used in Europe and Asia.
Applications in Hydraulics
UN/UNF threads are frequently used in:
- Hydraulic hose fittings.
- Industrial machinery.
- Aircraft hydraulic systems.
Due to their precise sealing capabilities, UN/UNF threads are often preferred in high-performance hydraulic applications.
BSPT vs. BSPP: Internal Alternatives
What are BSPT and BSPP?
BSP (British Standard Pipe) threads are divided into two main types: BSPT (tapered) and BSPP (parallel). Understanding the differences between these two internal alternatives can help in choosing the right connection.
- BSPT (British Standard Pipe Tapered): A tapered-thread connection that seals by thread interference, often requiring a thread sealant.
- BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel): A parallel-thread connection that relies on a washer or O-ring for sealing.
Differences Between BSPT and BSPP
- Sealing Mechanism: BSPT relies on metal-to-metal contact, while BSPP uses an additional sealing washer.
- Application: BSPT is often used in high-pressure hydraulic systems, whereas BSPP is more common in low-pressure applications.
- Thread Compatibility: BSPP and BSPT are not interchangeable without adapters.
When to Use Each Type
Choosing between BSPT and BSPP depends on the hydraulic system’s requirements:
- Use BSPT for high-pressure applications where thread interference sealing is preferred.
- Use BSPP when a leak-proof seal with an O-ring or washer is necessary.
Choosing the Right Alternative for Your System
Factors to Consider
Selecting the right thread alternative to BSP requires evaluating various factors:
- Pressure Rating: Ensure the thread type can handle the required system pressure.
- Sealing Method: Decide whether an O-ring, thread interference, or metal-to-metal sealing is preferable.
- Material Compatibility: Check for compatibility with hydraulic fluid and environmental conditions.
- Regional Standards: Ensure the chosen thread type aligns with industry and geographic standards.
How to Determine the Best Thread Alternative
To find the most suitable BSP replacement:
- Compare the sealing effectiveness of BSP, NPT, JIC, ORFS, and metric threads.
- Ensure compatibility with existing hydraulic fittings and hoses.
- Consult manufacturer specifications and industry standards.
Adapter Solutions for BSP Alternatives
When Adapters are Needed
Adapters are useful when transitioning from BSP to other thread types without replacing the entire hydraulic system. They allow connections between incompatible thread types while maintaining a leak-free seal.
Common Adapter Types
- BSP to NPT Adapters: Converts British Standard Pipe to National Pipe Thread.
- BSP to JIC Adapters: Allows connection between BSP and 37-degree JIC flare fittings.
- BSP to Metric Adapters: Facilitates connections between BSP and ISO metric threads.
Best Practices for Using Adapters in Hydraulic Systems
- Choose high-quality, pressure-rated adapters to prevent leaks.
- Ensure proper installation and torqueing to avoid thread damage.
- Use thread sealant if necessary to enhance sealing effectiveness.
Global Standards and Regional Preferences
How Different Regions Prefer Different Thread Standards
Hydraulic thread preferences vary by region due to industry standards and historical use:
- North America: Primarily uses NPT, JIC, ORFS, and SAE threads.
- Europe: Commonly uses BSP, metric threads (DIN, ISO), and ORFS.
- Asia: Uses a mix of BSP, metric, and JIS (Japanese Industrial Standard) threads.
Key Industry-Specific Requirements
Different industries also have specific thread preferences based on performance needs:
- Automotive & Aerospace: SAE, JIC, and ORFS for high-performance sealing.
- Heavy Machinery: Metric and ORFS for durability and pressure resistance.
- Oil & Gas: NPT and BSPT for high-pressure fluid transport.
Future Trends in Hydraulic Thread Technology
Innovations in Hydraulic Fittings
The hydraulic industry is moving toward advanced sealing and connection technologies:
- Push-to-Connect Fittings: Tool-free hydraulic connections for faster assembly.
- Standardized Global Threading: Efforts to unify thread types across regions.
- Improved O-Ring Seals: Development of high-pressure O-ring materials for better performance.
The Shift Towards Standardization
As industries globalize, there is a push to reduce thread variations and adopt universal standards such as ISO metric threads and ORFS.
Conclusion
Choosing the right alternative for BSP threads in hydraulics depends on factors like pressure rating, sealing method, and regional compatibility. While BSP remains widely used, alternatives like NPT, JIC, ORFS, metric, and SAE threads offer improved sealing and performance for different applications.
Key Takeaways:
- NPT: Good alternative for North American systems but requires thread sealant.
- Metric: Ideal for European and global hydraulic applications.
- JIC & ORFS: Excellent high-pressure, leak-proof alternatives.
- SAE & UNF: Reliable options for automotive and industrial applications.
For seamless BSP thread replacements, consider adapter solutions and always verify system requirements before making a switch.
FAQs
1. What is the best alternative to BSP threads in hydraulics?
The best alternative depends on your system’s needs. NPT is ideal for North America, while metric threads and ORFS provide better sealing and high-pressure performance.
2. Can I use NPT threads instead of BSP?
Not directly, as NPT and BSP have different thread angles and sealing methods. An adapter is required for compatibility.
3. Why is ORFS considered a better alternative for high-pressure hydraulics?
ORFS fittings use an O-ring face seal, which prevents leaks and improves durability under high-pressure conditions.
4. Are BSPP and BSPT interchangeable?
No, BSPP (parallel) requires a washer for sealing, whereas BSPT (tapered) seals through thread interference.
5. What are the advantages of using metric threads over BSP?
Metric threads follow global ISO standards, offer better sealing with O-rings, and provide more precise specifications than BSP threads.





