Ball valves play a crucial role in fluid control systems, serving as reliable components that manage the flow of liquids and gases in various industries. Understanding the fundamentals of ball valves is essential for engineers, technicians, and anyone involved in fluid management. This article will provide you with the basic knowledge necessary to understand how ball valves function and their significance in fluid control applications.
What is a Ball Valve?
A ball valve is a type of quarter-turn valve that uses a spherical disc (the ball) to control fluid flow. When you open the valve, the ball rotates to allow fluid to pass through; when you close it, the ball blocks the flow. This simple mechanism allows for quick and efficient operation, making ball valves a popular choice in various applications.
Compared to other types of valves, such as gate or globe valves, ball valves offer several advantages, including minimal pressure drop, ease of operation, and excellent sealing capabilities. Their design makes them particularly suitable for on/off control in high-flow applications.
Components of a Ball Valve
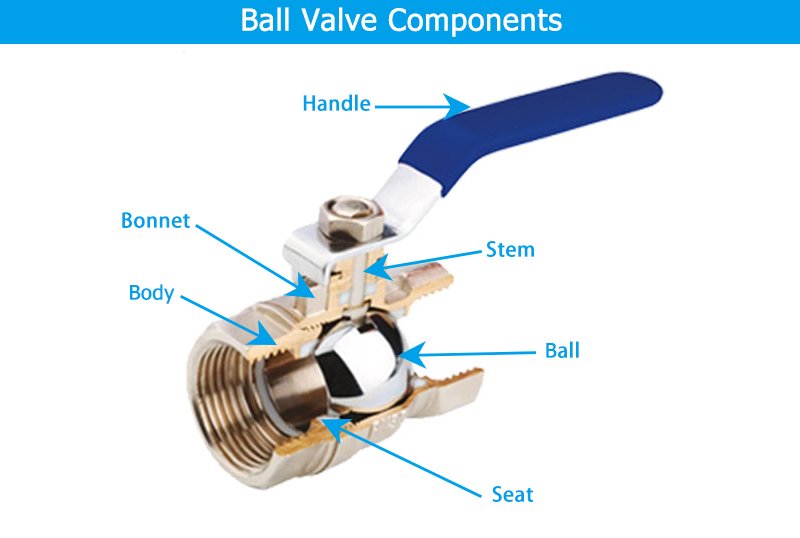
Understanding the components of a ball valve is key to appreciating its functionality. A typical ball valve consists of the following main parts:
- Ball: The core component that controls the flow. It has a hole in the center that aligns with the flow path when open.
- Body: The outer shell that houses the ball and other internal components.
- Seats: The surfaces that create a seal when the valve is closed, preventing leakage.
- Stem: Connects the ball to the handle, allowing for rotation.
- Handle: The external part used to operate the valve.
You can make ball valves from various materials, including brass, stainless steel, and plastic, depending on the specific requirements of the application. Each material offers distinct benefits, such as corrosion resistance or weight savings.
How Ball Valves Work
Ball valves operate using a simple quarter-turn mechanism.When you turn the handle 90 degrees, the ball rotates within the valve body. If the hole in the ball aligns with the flow path, the valve opens, allowing fluid to flow through. Conversely, when you turn the ball so the hole is perpendicular to the flow path, the valve closes and blocks the fluid.
This straightforward operation is one of the reasons ball valves are favored in many applications. They provide quick, reliable shut-off capabilities, making them ideal for situations where immediate control is essential. Furthermore, ball valves offer low friction during operation, which contributes to their longevity and minimal wear.
Understanding Fluid Control
Controlling fluid is critical in many industrial and commercial processes, as it ensures effective management of liquids and gases to maintain system efficiency, safety, and reliability. Fluid control involves the regulation of flow rate, pressure, and temperature within piping systems, and it plays a vital role in a variety of applications ranging from water supply and wastewater treatment to chemical processing and HVAC systems.
Importance of Fluid Control
The importance of fluid control cannot be overstated. Proper management of fluids is essential for:
- Safety: Controlling fluid flow helps prevent leaks and spills, which can lead to hazardous situations in many industries, including oil and gas, chemicals, and food processing.
- Efficiency: Efficient fluid control systems minimize energy consumption and reduce operational costs. By maintaining optimal flow rates and pressures, businesses can enhance productivity and reduce waste.
- Quality: In manufacturing processes, maintaining the correct flow of fluids is crucial for product quality. Variations in flow can affect the properties of finished products, making consistent fluid control vital.
Principles of Fluid Control
Fluid control involves several key principles that help ensure effective management of liquid and gas systems:
- Flow Rate: This refers to the volume of fluid that passes through a given point in a system over a specific period. Accurate measurement and control of flow rate are essential for maintaining system performance.
- Pressure Management: Pressure control is critical for preventing equipment failure and ensuring the safe operation of fluid systems. Valves, including ball valves, are often used to maintain desired pressure levels within a system.
- Temperature Regulation: Temperature control is crucial in many applications, especially in chemical processing and HVAC systems. Maintaining the correct temperature helps ensure optimal fluid properties and system efficiency.
Role of Ball Valves in Fluid Control
Ball valves play a significant role in fluid control due to their unique design and operational advantages:
- Rapid Operation: The quarter-turn design allows for quick opening and closing, enabling immediate control over fluid flow.
- Leak Prevention: With their tight sealing capabilities, ball valves help prevent leaks in high-pressure applications, enhancing safety and reliability.
- Versatility: Ball valves are suitable for various applications, including on/off control in water systems, gas distribution, and chemical processing, making them an essential component in fluid management.
By understanding the principles of fluid control and the integral role that ball valves play, industries can optimize their operations, improve safety, and enhance the quality of their products.
Ball Valves in Fluid Control Applications
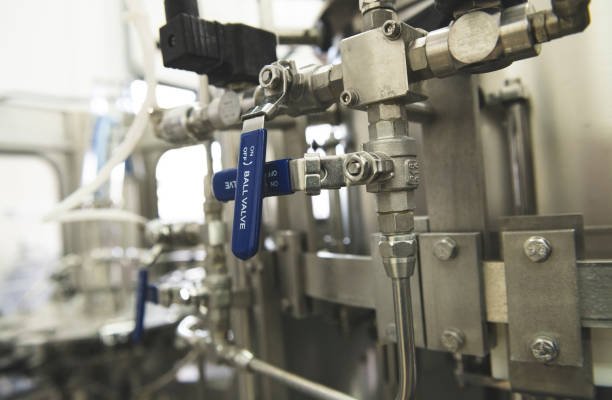

Many industries widely utilize ball valves because of their efficiency and reliability in fluid control. Here are some key applications:
- Oil and Gas: Used for controlling the flow of crude oil and natural gas, ball valves are essential in extraction and transportation processes.
- Water Treatment: In municipal water systems, ball valves help regulate water flow and maintain system pressure, ensuring safe and efficient distribution.
- HVAC Systems: Ball valves manage the flow of refrigerants and water in heating and cooling systems, optimizing energy efficiency and comfort.
- Chemical Processing: Their ability to handle corrosive fluids makes ball valves ideal for chemical plants, where precise flow control is critical.
These examples illustrate how versatile and vital ball valves are in maintaining effective fluid control across diverse sectors.
Sizing and Selection of Ball Valves for Fluid Control
Choosing the right ball valve for a specific application is crucial for ensuring optimal performance. You should consider several factors during the selection process:
- Pressure Rating: Ensure the valve can withstand the maximum pressure in the system. Different ball valves have varying pressure ratings based on their design and materials.
- Temperature: The selected valve must operate effectively at the expected temperature range of the application.
- Flow Rate: Consider the required flow rate and size the valve appropriately to maintain system efficiency without excessive pressure loss.
- Media Compatibility: Ensure the valve materials match the fluids being handled to prevent degradation or failure.
Proper sizing and selection of ball valves not only enhance system efficiency but also prolong the lifespan of the valve and reduce the need for maintenance.
Advantages of Ball Valves in Fluid Control
Ball valves offer numerous advantages that make them a preferred choice in fluid control systems:
- Durability and Reliability: Manufacturers design ball valves to withstand harsh conditions, making them less prone to wear and tear compared to other valve types. Their robust construction ensures a long service life, even in demanding environments.
- Low Maintenance Requirements: With fewer moving parts and a simple design, ball valves require minimal maintenance. Regular inspections are usually sufficient to ensure their functionality.
- Leak-tight Sealing: Ball valves provide excellent sealing capabilities, which help prevent leaks in high-pressure applications. This feature is crucial for maintaining system integrity and safety.
- Quick Operation: The quarter-turn operation allows for rapid opening and closing, making ball valves ideal for situations that require immediate flow control.
These benefits contribute to the efficiency and reliability of fluid control systems across various applications.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding ball valves and their operation is essential for effective fluid control. Their simple mechanism, durability, and versatility make them indispensable in numerous industries, from oil and gas to water treatment. By selecting the right ball valve for specific applications and understanding its advantages, users can ensure optimal performance and reliability in fluid management.
FAQs
What is the difference between a ball valve and a gate valve?
Ball valves provide quick shut-off and are suitable for on/off control, while gate valves are better for throttling flow and have a higher pressure drop.
Can ball valves be used for throttling?
Although you can use ball valves for throttling, they are not the best choice for precise flow control. They primarily serve on/off applications.
What materials are ball valves made from?
You can make ball valves from various materials, including brass, stainless steel, plastic, and carbon steel, depending on the application requirements.
How do you know if a ball valve is suitable for your application?
Consider factors like pressure rating, temperature range, media compatibility, and flow rate when selecting a ball valve for your application.
What are the common causes of ball valve failure?
Common causes include wear and tear from improper use, exposure to incompatible media, and insufficient maintenance.





