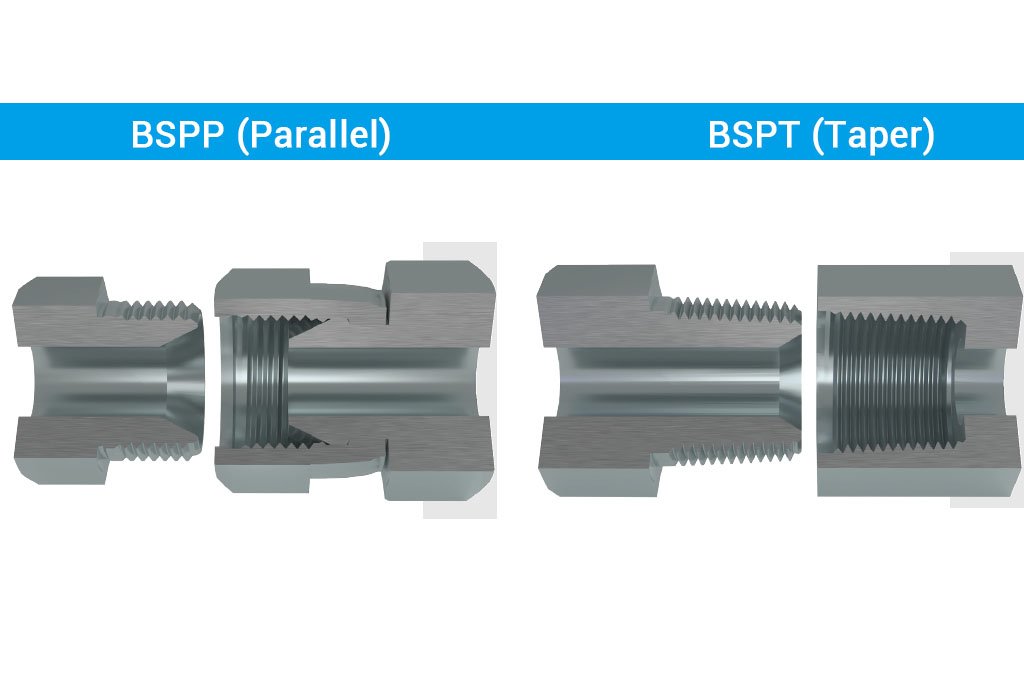
BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel) and BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper) are two prevalent thread standards used in hydraulic systems. Understanding BSPP and BSPT is crucial for ensuring compatibility, sealing, and functionality of hydraulic connections.
Importance of Thread Standards in Hydraulic Systems
Thread standards like BSPP and BSPT are vital in hydraulic systems for achieving leak-free connections and maintaining system integrity under pressure. Proper selection and application of BSPP and BSPT threads prevent operational failures and enhance system reliability.
Purpose and Scope of This Guide
At Taske, a leading manufacturer of hydraulic fittings and control valves, we understand the importance of using the correct thread standards in hydraulic systems. This guide aims to provide an exhaustive understanding of BSPP and BSPT, covering their specifications, differences, applications, and best practices for installation and maintenance. We also address common issues and future trends in thread standards to help you make informed decisions for your hydraulic systems.
For more information on our products and services, visit our contact page. Our experts are ready to assist you.
Basics of BSPP and BSPT
What is BSPP?
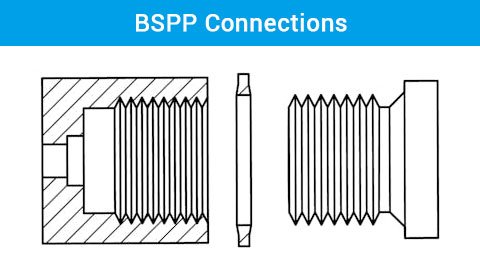
BSPP stands for British Standard Pipe Parallel. Specifically, BSPP thread refers to a type of threading where the threads run parallel to the axis of the pipe. Consequently, this creates a consistent diameter throughout the length of the thread.
BSPP threads were developed in the United Kingdom as part of the British Standard for pipe threads, primarily used in low-pressure applications where a gasket or O-ring provides the seal.
What is BSPT?
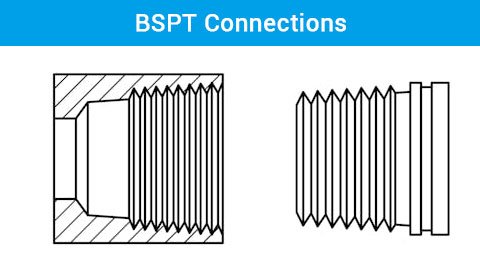
BSPT stands for British Standard Pipe Taper. Unlike BSPP, BSPT threads taper along their length, meaning the diameter decreases from the start of the thread to the end, creating a wedge effect.
BSPT threads were also established in the UK, designed to create a seal through the wedging action of the tapered threads, typically used in high-pressure applications without the need for additional sealing materials.
Technical Specifications
BSPP Specifications
- Thread Angle: BSPP threads have a 55-degree thread angle, consistent with the British Standard Whitworth form.
- Thread Shape: The threads are parallel, with a constant diameter and a rounded crest and root.
BSPT Specifications
- Thread Angle: BSPT threads also have a 55-degree angle but feature a taper of 1:16.
- Thread Shape: The tapering shape of BSPT threads ensures a tighter fit as the thread engagement increases, aiding in sealing.
Major Differences Between BSPP and BSPT
Understanding the differences between BSPP and BSPT threads is crucial for selecting the appropriate type for your application. The table below summarizes the key features, advantages, and disadvantages of BSPP and BSPT threads.
| BSPT (Tapered) | BSPP (Parallel) | Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Tapered | Straight, Cylindrical | Thread Profile |
| Threads and Sealant (PTFE tape recommended) | Primarily Threads | Sealing Mechanism |
| Broader Range of Pressures (Hydraulics, Pneumatics, High-Pressure Water Lines, Oil & Gas) | Low-Pressure Systems (Plumbing, Air Conditioning, Instrumentation) | Applications |
| More Secure Seal, Wider Pressure Range | Simple Design, Easy Assembly, No Sealant (low pressure) | Advantages |
| Requires Proper Tightening, Needs Sealant (extra step) | Not Suitable for High Pressure | Disadvantages |
| Pressure in Application (Moderate to High Pressure) | Pressure in Application (Low Pressure) | Choosing Factor |
| Prioritize for safety in high-pressure applications | Cost-effective for low pressure | Additional Notes |
- Thread Type
BSPP threads are parallel, while BSPT threads are tapered. This fundamental difference affects how each type of thread seals and is used in various applications.
- Sealing Method
BSPP threads typically use an additional sealing mechanism, such as an O-ring or gasket, to ensure a leak-free connection. In contrast, BSPT threads achieve sealing through the wedging action of the tapered threads.
- Application Differences
BSPP is generally used in low-pressure systems where a gasket or O-ring can provide the necessary seal. BSPT is preferred for high-pressure applications where the tapered threads themselves provide the seal.
Applications of BSPP
- Common Industries: BSPP threads are widely used in various industries, including automotive, manufacturing, and plumbing.
- Typical Use Cases: Common applications include connecting pipes and hoses in low-pressure hydraulic and pneumatic systems, as well as in general plumbing tasks.
- Advantages of Using BSPP: The primary advantages of BSPP threads are their ease of installation and the ability to create a reliable seal with the addition of an O-ring or gasket.
Applications of BSPT
- Common Industries: BSPT threads are commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, high-pressure hydraulics, and heavy machinery.
- Typical Use Cases: Typical uses include high-pressure hydraulic systems, steam piping, and natural gas systems.
- Advantages of Using BSPT: BSPT threads provide a strong, self-sealing connection that is ideal for high-pressure applications, reducing the need for additional sealing components.
BSPP vs BSPT: Which One to Choose?
- Factors to Consider
When choosing between BSPP and BSPT, consider factors such as system pressure, the need for sealing, and the specific requirements of the application.
- Industry-Specific Recommendations
For low-pressure systems and applications requiring easy disassembly, BSPP is recommended. For high-pressure systems and applications where a strong seal is critical, BSPT is the better choice.
- Cost Implications
Consider the cost of additional sealing materials for BSPP and the potential for higher initial costs for BSPT fittings, balanced against the long-term reliability and maintenance needs.
BSPP and BSPT Compatibility
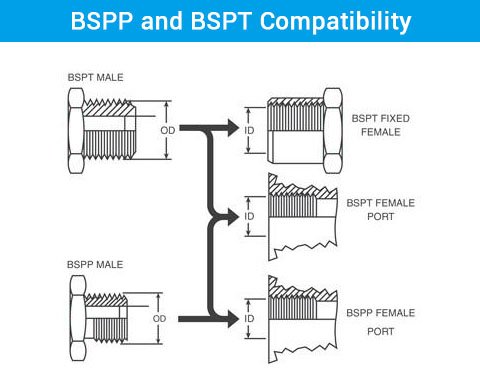
Understanding the compatibility between BSPP and BSPT threads is crucial for ensuring leak-free connections and system integrity.
A useful rule to remember is that a tapered male thread can fit both tapered and parallel female threads. Specifically, a BSPT (tapered) male thread can engage with both BSPT (tapered) and BSPP (parallel) female threads because the taper of the male thread allows it to fit snugly into a cylindrical thread.
- BSPT Male to BSPT Female: This combination is optimal for high-pressure situations as the tapered threads create a secure, self-sealing connection.
- BSPT Male to BSPP Female: This combination is feasible because the BSPT male’s taper can mate with the BSPP female’s parallel threads, forming a solid connection when using proper sealing techniques such as thread sealant.
Potential Issues with Interchangeability
While some compatibility exists, mixing BSPP and BSPT threads can lead to potential problems:
- Poor Sealing: Without using the correct sealing materials, the connection may not be fully leak-proof. Always apply suitable thread sealant or use O-rings.
- Mechanical Stress: Mismatched threads can cause mechanical stress, potentially leading to thread damage or failure.
- Cross-Threading: Misalignment during installation can cause cross-threading, damaging the threads and compromising the connection.
To ensure the best performance and avoid issues, always match threads correctly or use the appropriate sealing methods when combining BSPP and BSPT threads.
Installation and Maintenance
- Installation Guidelines for BSPP
When installing BSPP threads, ensure the use of appropriate sealing materials, such as O-rings or gaskets, and avoid over-tightening to prevent damage.
- Installation Guidelines for BSPT
For BSPT threads, ensure proper alignment and gradually tighten to achieve a secure seal, avoiding over-tightening which can damage the threads and compromise the seal.
- Maintenance Best Practices
Regularly inspect threaded connections for signs of wear, leaks, and mechanical damage. Replace any damaged components promptly to maintain system integrity.
Common Problems and Solutions
- Leaks
Leaks can occur due to improper sealing, damage to threads, or wear and tear. Ensure proper installation and regular maintenance to prevent leaks.
- Cross-Threading
Cross-threading happens when threads are not properly aligned during installation. To avoid this, ensure careful alignment and use appropriate tools.
- Wear and Tear
Over time, threads can wear out, leading to leaks and mechanical failures. Regular inspections and timely replacements are crucial to maintaining system performance.
Industry Standards and Regulations
Overview of Relevant Standards
BSPP and BSPT threads conform to standards set by organizations such as ISO, ANSI, and BSI, ensuring global compatibility and reliability.
Key Regulatory Bodies
Key regulatory bodies include the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), American National Standards Institute (ANSI), and British Standards Institution (BSI).
BSPP and BSPT in Different Regions
- North America: In North America, BSPP and BSPT threads are used alongside NPT threads, with specific applications in various industries.
- Europe: Europe predominantly uses BSPP and BSPT threads, adhering to British and ISO standards.
- Asia-Pacific: The Asia-Pacific region utilizes a mix of BSPP, BSPT, and other international thread standards, depending on the industry and application.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the main difference between BSPP and BSPT?
The main difference lies in the thread type: BSPP threads are parallel, while BSPT threads are tapered.
Q2. Can BSPP and BSPT be used interchangeably?
While they can sometimes be used together with appropriate sealing solutions, it is generally not recommended due to the risk of leaks and mechanical failure.
Q3. What are the advantages of using BSPP threads?
BSPP threads are easy to install and create a reliable seal with the addition of an O-ring or gasket.
Q4. What are the common issues faced with BSPT threads?
Common issues include cross-threading and damage from over-tightening, which can compromise the seal and system integrity.
Q5. How do I choose between BSPP and BSPT for my application?
Consider factors such as system pressure, sealing needs, and specific application requirements when choosing between BSPP and BSPT threads.
At Taske, we manufacture both BSPP and BSPT threaded hydraulic fittings to meet international standards and various application needs.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of BSPP and BSPT threads is crucial for anyone involved in hydraulic systems. By following best practices for selection, installation, and maintenance, you can ensure optimal performance and longevity of your hydraulic connections. For further reading and resources, consult industry standards and technical manuals.