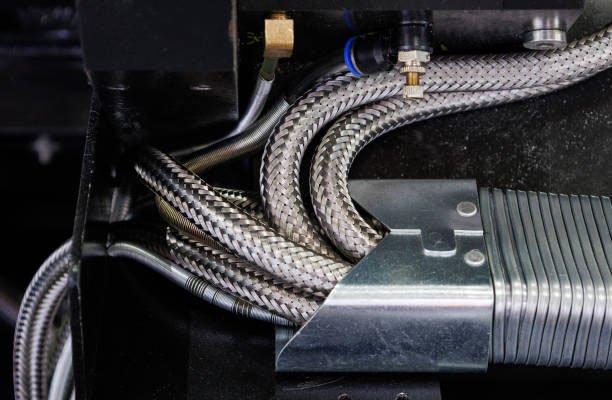
Introduction to Hydraulic Hoses
Hydraulic hoses are critical components in modern fluid power systems, serving as conduits for transferring pressurized hydraulic fluid between various components such as pumps, cylinders, valves, and actuators. They are designed to operate under extreme pressures and temperatures, enabling the efficient transmission of power in mobile and industrial hydraulic systems.
The role of hydraulic hoses extends beyond mere connectivity—they are engineered for flexibility, durability, and high-performance, tailored to meet the specific needs of different mechanical environments. With industries demanding ever-more robust and reliable fluid power systems, the choice of hose material becomes paramount, particularly in harsh or high-risk operating conditions.
Overview of Metal Hydraulic Hoses
Manufacturers construct metal hydraulic hoses entirely or partially from metal—typically stainless steel or galvanized steel—unlike their rubber or thermoplastic counterparts. They design these hoses specifically to withstand the most challenging operating environments, where traditional hoses might degrade or fail due to heat, pressure, or corrosive materials.
The term “metal hydraulic hose” often refers to a composite structure involving corrugated metal tubes, which provide the hose with superior flexibility and strength. The metallic construction allows them to perform reliably in environments involving high temperatures, high pressures, and aggressive chemicals.
Metal hydraulic hoses are a preferred choice for applications where rubber hoses are prone to wear and fatigue, particularly in permanent installations or dynamic applications where movement and vibration are frequent.
Construction and Design

The construction of a metal hydraulic hose is a sophisticated process, combining precision engineering and high-performance materials. These hoses typically consist of three main layers:
1. Inner Core
This is the innermost layer made from a seamless or welded metal tube—commonly stainless steel. It is responsible for containing the fluid and withstanding internal pressure. The inner core is often corrugated to enhance flexibility and ease of movement.
2. Reinforcement Layer
Manufacturers wrap or braid metal wires around the hose to reinforce it and provide additional strength and pressure resistance. They apply single or double braiding depending on the pressure requirements. This layer helps prevent deformation and rupture under load.
3. Outer Cover (Optional)
Although users often leave metal hoses unjacketed, some applications require them to add a protective outer cover to guard against abrasion, chemicals, or mechanical damage. This can be a polymer coating or an additional metal braid.
Two primary design variations are:
- Braided Metal Hoses: Offer excellent flexibility and pressure resistance. Suitable for dynamic applications involving frequent motion or vibration.
- Corrugated Metal Hoses: Provide flexibility and are ideal for high-temperature and high-pressure static applications.
End fittings, which include flanges, threaded ends, or quick-release couplings, are welded or mechanically attached to the hose ends, ensuring a secure and leak-proof connection to the hydraulic system.
Key Features and Properties
Metal hydraulic hoses are prized for their robust engineering and ability to endure extreme conditions. Below are some of the most notable features and properties that distinguish them from other hose types:
Flexibility vs Rigidity
Although metal may seem inherently rigid, metal hydraulic hoses—especially those with corrugated or braided structures—offer considerable flexibility. This design enables the hose to bend and adapt to confined spaces while maintaining structural integrity. However, they are generally less flexible than rubber hoses and require careful installation to avoid overbending or fatigue.
Temperature and Pressure Tolerance
One of the most critical advantages of metal hoses is their exceptional tolerance to both high and low temperatures, often ranging from -325°F (-198°C) to 1500°F (815°C), depending on the material. Their ability to withstand high internal pressures also makes them suitable for heavy-duty applications where failure is not an option.
Resistance to Abrasion, Corrosion, and Vibration
Metal hoses are naturally resistant to external abrasions and corrosive substances, particularly when made from stainless steel. This makes them ideal for chemical plants, offshore drilling rigs, and environments where exposure to salts, acids, or bases is common. Furthermore, they can absorb vibration and dampen noise, enhancing overall system performance and safety.
Types of Metal Hydraulic Hoses
Metal hydraulic hoses come in several variations, each designed to meet specific operational needs. The main types include:
Annular Corrugated Hoses
These hoses feature circular corrugations perpendicular to the hose axis, offering greater flexibility and pressure resistance. They are commonly used in high-pressure and high-vibration applications.
Helical Corrugated Hoses
Featuring spiral-shaped corrugations, helical hoses are slightly more rigid but provide a smoother flow path for certain fluids. These are often used where directional flow and minimal pressure drop are desired.
Braided Metal Hoses
These consist of a corrugated metal inner hose surrounded by one or more layers of metal braid. The braid adds strength, pressure capability, and abrasion resistance, making them suitable for dynamic and mobile applications.
Interlocked Hoses
Interlocked hoses are made from helically wound, interlocked metal strips. While not leak-tight, they are excellent for applications involving the conveyance of solids, exhaust gases, or where high mechanical strength is required.
Comparison: Metal vs. Rubber Hydraulic Hoses
Choosing between metal and rubber hydraulic hoses depends on application-specific requirements such as pressure, temperature, environment, and cost. Here’s how they compare:
Durability and Longevity
Metal hoses typically last longer than rubber hoses, especially in harsh environments. They resist wear, corrosion, and temperature-related degradation better than rubber, making them a long-term investment.
Flexibility and Weight
Rubber hoses are generally more flexible and lighter, making them easier to handle and install. However, this flexibility often comes at the cost of reduced durability and temperature resistance.
Cost and Maintenance
Rubber hoses are less expensive upfront but may require more frequent replacement. Metal hoses cost more initially but reduce downtime and maintenance costs over time due to their longevity and reliability.
Ultimately, the choice depends on the operational needs—metal hoses for high-performance, extreme conditions; rubber hoses for everyday, lower-stress environments.
Common Applications

Engineers design metal hydraulic hoses for reliability in challenging environments, making them indispensable in industries where performance, safety, and durability are essential. Below are the most common sectors that utilize metal hydraulic hoses:
Industrial Machinery
Manufacturing and production facilities use metal hoses to handle high-pressure hydraulic systems and high-temperature fluids. Their resistance to wear and tear makes them ideal for continuous, high-duty cycles found in presses, injection molding machines, and automated robotics.
Aerospace and Automotive
Aerospace engineers use metal hydraulic hoses in fuel lines, hydraulic flight control systems, and cooling systems because of their lightweight durability and ability to operate under extreme altitude and temperature conditions. Similarly, in high-performance automotive applications, they serve in braking systems, turbochargers, and exhaust systems.
Oil and Gas Industry
Drilling platforms and refineries rely heavily on metal hoses to transport high-pressure fluids and gases. Their resistance to corrosive chemicals and high temperatures makes them vital in offshore and onshore oil exploration and processing environments.
Power Generation and Chemical Plants
In environments where exposure to chemicals and high heat is frequent, such as nuclear power plants or chemical processing facilities, metal hoses provide secure, leak-proof transfer of fluids. Their design supports both static and dynamic applications across complex piping networks.
Benefits of Metal Hydraulic Hoses
The numerous advantages of metal hydraulic hoses contribute to their widespread use in critical operations. Below are the core benefits that set them apart from other hose types:
Durability and Lifespan
Metal hoses have a long operational lifespan due to their ability to resist abrasion, high temperatures, UV radiation, and corrosive environments. This durability reduces replacement frequency and minimizes system downtime.
High-Pressure Performance
These hoses are capable of handling extreme pressure without rupture, especially when equipped with reinforced braiding. This makes them indispensable for hydraulic systems that operate under high loads or frequent pressure surges.
Extreme Environment Suitability
Whether exposed to cryogenic temperatures, superheated steam, or aggressive chemicals, metal hydraulic hoses maintain integrity and performance. They’re suited for mission-critical environments where hose failure can result in catastrophic damage or safety hazards.
Limitations to Consider
Despite their many advantages, metal hydraulic hoses are not universally suitable. Understanding their limitations is essential for appropriate system design and cost-efficiency:
Weight and Handling
Metal hoses are heavier than rubber or thermoplastic alternatives. This added weight can be a disadvantage in applications where mobility and ease of handling are critical. It can also increase load on support structures and machinery.
Cost Implications
The initial purchase cost of metal hoses is typically higher due to the materials and manufacturing processes involved. While they offer long-term value, the upfront investment can be a barrier for smaller operations or less demanding applications.
Maintenance Needs
Although durable, metal hoses still require regular inspection for signs of fatigue, especially in high-vibration or flexing scenarios. Improper routing, overbending, or corrosive build-up can compromise their performance and lead to premature failure.
Installation Guidelines
Proper installation of metal hydraulic hoses is essential for optimizing performance, extending lifespan, and ensuring safety. Incorrect routing or handling can result in premature hose failure or system inefficiencies. Below are key best practices for installation:
Correct Sizing and Routing
Choose the hose diameter that matches the required flow rate and system pressure. Undersized hoses can lead to pressure drops and overheating. Routing should minimize bends and avoid tight angles. Use gentle curves and appropriate bend radii to reduce stress and improve flow dynamics.
Avoiding Overbending and Stress Points
Metal hoses have a minimum bend radius that must be respected. Bending a hose below this threshold causes fatigue and cracking. Additionally, installers should avoid torsional stress by ensuring they do not twist the hose during installation. They should use support brackets or clamps to secure the hoses and prevent unnecessary movement.
End Connection Integrity
Use compatible fittings and secure them according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Inspectors should check welded ends for leaks, and technicians must properly torque threaded connections to prevent them from loosening under vibration. Always check for leaks after initial pressurization.
Maintenance and Inspection
Routine maintenance and inspection are critical to ensure the long-term reliability and safety of metal hydraulic hoses. Even the most robust hoses can suffer from wear and environmental degradation over time.
Regular Checks and Lifecycle Considerations
Conduct visual inspections regularly to detect surface wear, corrosion, or fraying of braiding. Use non-destructive testing techniques for internal flaws in critical applications. Maintenance schedules should be aligned with operational hours and environmental exposure levels.
Signs of Wear or Failure
Early signs of degradation include kinking, bulging, corrosion, and unusual vibration or noise. A decrease in system pressure or an increase in temperature at the hose site may indicate internal obstruction or leakage. Replace any hose showing these signs immediately to prevent system failure.
Safety Considerations
Using metal hydraulic hoses in high-pressure systems necessitates adherence to strict safety protocols to prevent injury and equipment damage. Safety begins with design and extends through installation, operation, and maintenance.
Best Practices for Safe Usage
- Always use hoses that meet or exceed the system’s maximum pressure rating.
- Install safety guards or sleeves in areas where hose failure could pose a hazard to personnel.
- Depressurize the system before inspecting or replacing any hoses.
Industry Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that hoses and fittings conform to industry standards such as SAE, ISO, and ASME. Certification not only guarantees performance but also satisfies legal and insurance requirements. Work with suppliers who provide traceable quality documentation and testing reports.
Innovations in Metal Hydraulic Hose Technology
Advancements in engineering and materials science have significantly improved the performance and versatility of metal hydraulic hoses. These innovations aim to enhance safety, durability, and real-time performance monitoring.
Advances in Metallurgy and Design
New alloy formulations have increased corrosion resistance and tensile strength, allowing hoses to perform under even more extreme conditions. Innovations such as laser-welded seams and tighter braiding patterns have improved leak resistance and reduced weight, enabling more compact installations.
Smart Monitoring Systems
Integrated sensors and smart fittings now allow real-time monitoring of pressure, temperature, and hose integrity. These systems can alert operators to potential issues before they become critical, reducing downtime and enhancing safety through predictive maintenance.
Choosing the Right Metal Hydraulic Hose
Selecting the right hose is essential for system efficiency and reliability. The ideal choice depends on multiple operational factors and the specific application environment.
Based on Pressure, Temperature, and Medium
Analyze the maximum operating pressure, temperature range, and chemical compatibility required. For instance, stainless steel is ideal for corrosive environments, while braided configurations are better suited for high dynamic loads.
Supplier and Manufacturer Credibility
Partner with reputable manufacturers who provide technical support, certifications, and customization options. Ensure they follow industry standards and offer products tested for your application environment. Customer reviews and case studies can also provide valuable insights.
Environmental Impact
While metal hoses offer longevity and performance, their environmental footprint should also be considered, especially in sustainability-focused industries.
Recyclability of Metal Hoses
One of the ecological advantages of metal hydraulic hoses is that they are largely recyclable. At the end of their service life, the stainless steel or galvanized materials can be melted down and reused in new products, reducing landfill waste.
Sustainable Manufacturing Trends
Many manufacturers are adopting greener processes such as water-based coolants, low-emission production techniques, and the use of recycled materials in non-critical components. Supporting such suppliers contributes to overall sustainability efforts.
Conclusion
Metal hydraulic hoses represent a critical solution for high-performance fluid power systems. Their unmatched durability, pressure-handling capacity, and resistance to harsh environments make them indispensable in industries such as aerospace, oil and gas, and heavy manufacturing.
While they come with higher initial costs and handling considerations, the long-term benefits—reduced downtime, fewer replacements, and enhanced safety—often outweigh the drawbacks. By choosing the right type, ensuring proper installation, and adhering to a regular maintenance schedule, organizations can maximize the performance and reliability of their hydraulic systems.
FAQs
1. What is a metal hydraulic hose used for?
Metal hydraulic hoses are used to transport high-pressure fluids in extreme conditions, such as in chemical plants, oil rigs, aerospace systems, and heavy industrial machinery. Their construction makes them ideal for resisting heat, vibration, and corrosive substances.
2. How do metal hydraulic hoses differ from rubber hoses?
Metal hoses offer higher resistance to pressure, temperature, and abrasion, making them suitable for harsh environments. In contrast, rubber hoses are more flexible and cost-effective for less demanding applications. The choice depends on the specific requirements of your hydraulic system.
3. Can metal hydraulic hoses be reused?
While metal hoses are durable, they are typically not reused in high-pressure systems due to safety and performance standards. However, in some non-critical applications, a thoroughly inspected and undamaged hose may be reused with new fittings.
4. How long do metal hydraulic hoses last?
The lifespan of a metal hydraulic hose varies based on usage, environment, and maintenance. In well-maintained systems, they can last several years, often outlasting rubber hoses by a significant margin due to their robust construction.
5. Are metal hydraulic hoses environmentally friendly?
Yes, metal hydraulic hoses are largely recyclable and often manufactured using environmentally conscious processes. Choosing recyclable materials and working with sustainable manufacturers can reduce your operation’s overall environmental impact.