What is NPSM Thread?
NPSM stands for National Pipe Straight Mechanical thread. It is a standardized thread used primarily in the United States for mechanical applications involving piping systems. Unlike tapered threads, which get tighter as they are screwed in, NPSM threads are straight (parallel) and do not taper. This means they require a gasket or sealing ring to prevent leakage, as the thread itself does not provide a seal.
In simpler terms, NPSM threads focus on connecting pipes or fittings without relying on the threads for sealing. They’re often used in low-pressure systems where tight seals are not crucial, or where the sealing is done by an O-ring, gasket, or similar component.
Key Features of NPSM Threads
NPSM threads come with specific features that set them apart from other types of pipe threads. Let’s break them down:
- Parallel (Straight) Thread: The threads run parallel to each other, unlike tapered threads like NPT (National Pipe Taper), which tighten and create a seal as they are screwed in.
- Sealing Mechanism: Since the threads are straight, an external seal (like a gasket or O-ring) is required to prevent leakage.
- Thread Standards: NPSM threads conform to ANSI/ASME B1.20.1 standards in the United States, ensuring compatibility with other standardized mechanical parts.
- Size Range: NPSM threads come in a variety of sizes, typically ranging from 1/8 inch to 12 inches in diameter.
- Pressure Rating: These threads typically suit lower-pressure applications, making them ideal for environments where a perfect thread seal isn’t necessary, such as plumbing or certain mechanical applications.
Applications
Now that we understand the basics, let’s explore where NPSM threads are actually used. Due to their characteristics, these threads are popular in several industries, including:
- Hydraulic Systems: NPSM threads frequently connect pipes or hoses in hydraulic systems without requiring tapered sealing threads. The threads rely on O-rings to make sure everything stays leak-free.
- Plumbing: Many low-pressure plumbing systems use NPSM fittings for water or other fluid connections. The straight thread makes them easier to work with in applications where a watertight seal is created by a separate gasket.
- HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning): HVAC systems often utilize NPSM threads in the connection of pipes carrying refrigerants or coolants. In these cases, gaskets or sealing washers are employed to ensure leak prevention.
- Gas and Fuel Lines: In certain fuel delivery systems, they are used when the sealing is handled by gaskets or other mechanical seals.
- Manufacturing and Industrial Machinery: Many types of industrial equipment use NPSM-threaded fittings due to their reliability and compatibility with gasketed seals.
NPSM vs. NPT Threads: What’s the Difference?
Although both are standardized in the U.S., they serve different purposes:
| Feature | NPSM (National Pipe Straight Mechanical) | NPT (National Pipe Taper) |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Type | Straight (parallel) | Tapered |
| Sealing Method | Requires a gasket or O-ring | Threads provide the seal |
| Primary Use | Mechanical joints | Pressure-tight pipe fittings |
| Thread Angle | 60 degrees | 60 degrees |
| Leakage Prevention | External gasket/seal needed | Tapered thread forms a seal |
The key takeaway here is that NPT threads provide a seal through the tightening of the threads themselves, making them ideal for high-pressure systems like gas or water supply lines. On the other hand, NPSM threads need an additional sealing component, which makes them more suitable for mechanical or low-pressure systems.
NPSM vs. MPT Threads: What’s the Difference?
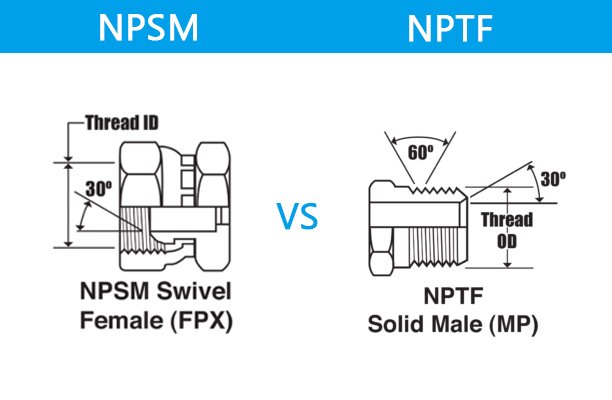
Here’s a quick and simple comparison of NPSM (National Pipe Straight Mechanical) and MPT (Male Pipe Taper) threads to help you understand their key differences:
| Feature | NPSM (National Pipe Straight Mechanical) | MPT (Male Pipe Taper) |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Type | Straight (Parallel) | Tapered |
| Sealing Method | Requires a gasket, O-ring, or external seal | Self-sealing via taper, may use thread sealant (e.g., Teflon tape) |
| Primary Use | Low-pressure systems, mechanical joints | High-pressure systems (e.g., gas, water) |
| Thread Angle | 60 degrees | 60 degrees |
| Pressure Sealing | No pressure-tight seal from the thread itself | Provides a pressure-tight seal as threads tighten |
| Applications | Hydraulics, industrial machinery, plumbing | Gas lines, water supply, compressed air systems |
| Compatibility | Compatible with NPSM female threads | Compatible with FPT (Female Pipe Taper) threads |
| Typical Sizes | Various sizes, typically 1/8″ to 12″ | Various sizes, typically 1/8″ to 12″ |
How to Properly Install
This section would provide a step-by-step guide for installing NPSM-threaded fittings. While many readers might already have some experience, a detailed walkthrough would be helpful for beginners. It could include tips on preparing the pipes, selecting the right gasket or O-ring, and tightening the fittings properly without damaging them.
Suggested Steps:
- Prepare the Pipes: Ensure that both the male and female threads are clean and free from debris. Dirt or particles can affect the fit or cause leaks.
- Choose the Right Sealing Material: Depending on the application, choose the correct gasket or O-ring. This could vary based on pressure, temperature, or the type of fluid being transported.
- Lubricate if Necessary: Some installations may benefit from a thread lubricant to make tightening easier.
- Tighten Carefully: Hand-tighten the fitting first, then use a wrench to make it snug. Avoid overtightening, which can damage the threads or crush the sealing component.
- Test for Leaks: After installation, test the system by introducing the appropriate fluid or pressure to check for leaks. Adjust or tighten as needed.
Sealing Materials
Discussing the best sealing materials used with NPSM threads could be highly beneficial. Since NPSM threads rely on external seals (like O-rings or gaskets), explaining the various materials available, and their ideal use cases, would be very informative.
For example:
- Nitrile O-Rings: Great for general-purpose use with petroleum oils and fluids.
- PTFE Gaskets: Ideal for high-temperature applications or where chemical resistance is needed.
- Silicone Gaskets: Used for high-temperature applications in the food and medical industries.
- EPDM O-Rings: Perfect for water, steam, and some chemicals but unsuitable for petroleum-based fluids.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
A section on common mistakes or “pitfalls” people often face when working with NPSM threads would offer additional value. Highlight errors like:
- Using the Wrong Sealing Material: Discuss how using the wrong type of gasket or O-ring can lead to leaks or failure of the system.
- Overtightening the Fittings: Many people make the mistake of overtightening, thinking it will create a better seal. In fact, overtightening can damage the threads or crush the seal.
- Mismatching Threads: Accidentally pairing NPSM threads with NPT threads, which leads to poor fit and leaks.
- Skipping Leak Tests: Not testing for leaks after installation is a common mistake that can lead to problems later on.
Industry Standards and Certifications for NPSM Threads
Add a section detailing industry standards or certifications that relate to NPSM threads. This is important for professionals who want to ensure they are using fittings and components that meet safety and regulatory standards. You could cover:
- ANSI/ASME B1.20.1: The primary standard for NPSM threads in the U.S.
- ISO Standards: Discuss any relevant ISO standards for international applications.
- Certifications to Look For: If you’re purchasing fittings or piping, look for parts that meet relevant standards to ensure compatibility and performance.
Alternatives to NPSM Threads
You could include a section discussing alternatives to NPSM threads. Some users might not be aware of other options available, so explaining when NPSM might not be ideal and presenting alternatives could be beneficial. Consider discussing:
- NPT (National Pipe Tapered) Threads: The most common alternative to NPSM, ideal for high-pressure, fluid-tight seals.
- BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel) Threads: Often used in Europe and other parts of the world, similar to NPSM but with different standards.
- JIC (Joint Industry Council) Fittings: Another type of connection that uses a tapered seat to create a seal, often used in hydraulic applications.
Comparison Between NPSM, BSPP, and BSPT Threads
You could further expand the NPSM vs NPT comparison section by adding information about BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel) and BSPT (British Standard Pipe Tapered) threads. These are common in international settings, and readers dealing with international projects would find the comparison helpful.
| Feature | NPSM | BSPP | BSPT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thread Type | Straight (parallel) | Straight (parallel) | Tapered |
| Primary Use | Mechanical joints | Mechanical joints | Pressure-tight seals |
| Sealing Method | Gasket or O-ring | Gasket or O-ring | Threads form the seal |
| International Use | Primarily U.S. | Common in Europe | Common in Europe and other regions |
| Thread Angle | 60 degrees | 55 degrees | 55 degrees |
NPSM Thread Compatibility
Understanding the compatibility of NPSM threads is crucial, especially when working in mechanical, hydraulic, or plumbing systems. Since they are straight (parallel) and don’t rely on the thread for sealing, it’s essential to ensure you’re pairing them with the correct fittings and sealing components.
When are NPSM Threads Compatible?
- Fittings with Gaskets or O-Rings: NPSM threads are often paired with female fittings that have internal seats for O-rings or gaskets. This is what provides the actual seal in the connection, making NPSM threads suitable for mechanical or low-pressure systems.
- NPSM Male with NPSM Female: These threads work together when you use the correct sealing component, such as a gasket or O-ring. Both threads are straight, and the sealing mechanism creates the seal externally.
- NPSM Male with NPT Female (Limited Use): Although it’s not ideal, you can sometimes pair an NPSM male thread with an NPT female thread for non-critical, low-pressure applications. However, avoid this pairing for high-pressure systems because the threads do not form a natural seal like NPT threads do.
- ISO or BSPP Threads (Not Directly Compatible): They are not directly interchangeable with BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel) or ISO parallel threads, even though all are straight threads. Each follows a different standard, making precise fitment and sealing difficult without the use of adapters.
Adapter Use for Compatibility
If you need to connect NPSM threads to other thread types like NPT, BSPP, or BSPT, specialized adapters are required to ensure proper fitment. Always make sure to use adapters that account for the difference in thread taper and ensure you add the necessary sealing mechanisms (gaskets, O-rings, or thread sealant) when transitioning between thread types.
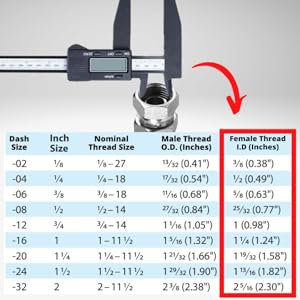
NPSM Thread Chart
Using a thread chart is important when determining the correct size and dimensions of NPSM threads. This helps ensure proper fitment and compatibility between male and female fittings. Below is a standard chart with common straight threads sizes, along with their dimensions and threads per inch (TPI).
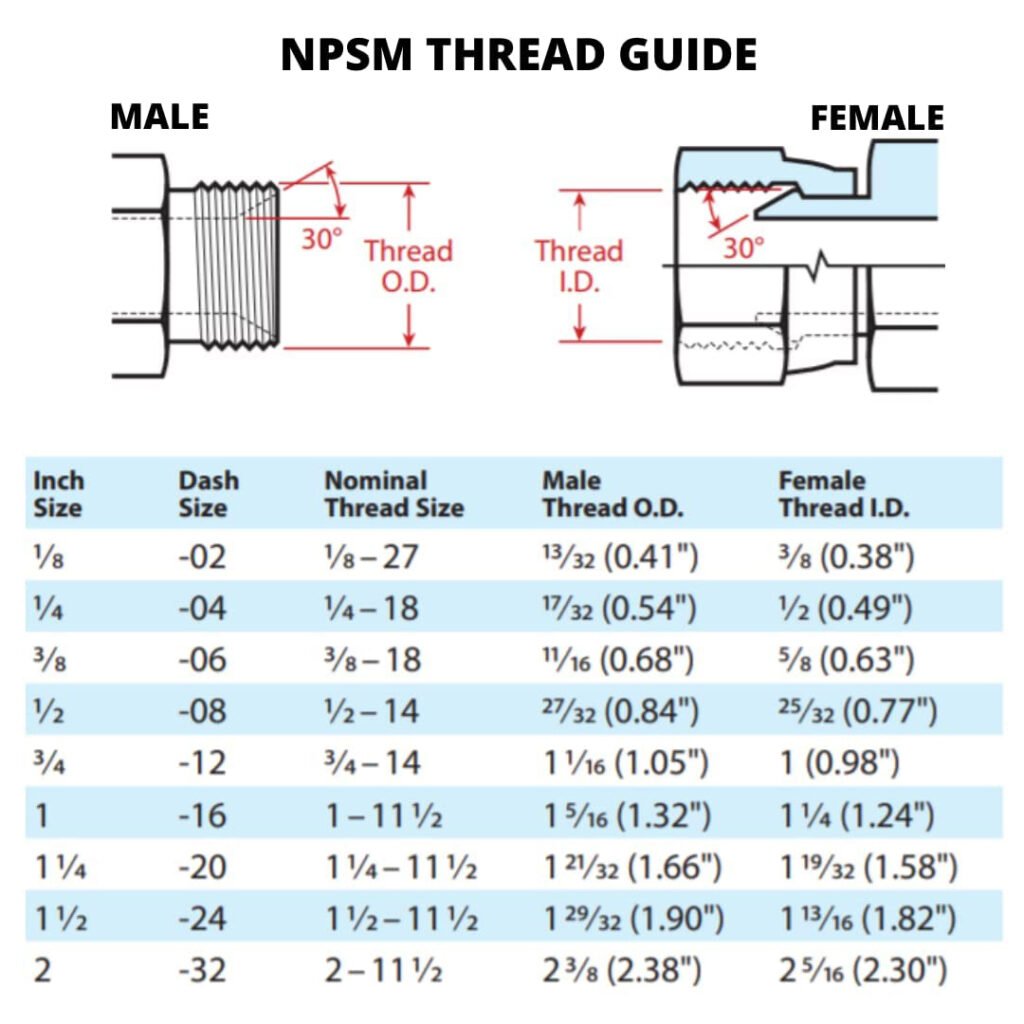
How to Use the NPSM Thread Chart:
- Identify the Pipe Size: Start by measuring the outer diameter of the male thread or inner diameter of the female thread.
- Match TPI (Threads Per Inch): Use a thread gauge to count the threads per inch to match the size in the chart.
- Check the Major/Minor Diameters: Ensure the major (outer) and minor (inner) diameters match your fitting’s measurements for accurate compatibility.
Case Studies Using NPSM Threads
To add more practical, hands-on information, include a section featuring real-world case studies that showcase the use of NPSM threads. For example, you could share:
- Case Study 1: Hydraulic Systems in Construction Equipment:
Discuss how a hydraulic system in construction equipment utilizes NPSM threads, emphasizing their ease of maintenance and installation. - Case Study 2: Plumbing in Commercial Buildings:
Explain how NPSM threads contributed to a reliable low-pressure water supply system, detailing the use of gaskets for leak prevention.
Tools Needed for Working with NPSM Threads
This section would highlight the necessary tools for working with NPSM threads. Readers might appreciate knowing which tools can make their job easier and prevent damage to the threads. You could recommend:
- Thread Gauges: To properly measure NPSM threads and ensure compatibility.
- Caliper: For precisely measuring the diameter of both male and female threads to ensure proper sizing.
- Pipe Wrenches: To tighten the fittings without overtightening.
- Lubricants or Thread Sealants: Only in cases where they might be recommended for easier installation.
- Leak Detection Kits: For testing whether the seal is effective after installation.
Conclusion
NPSM threads play a vital role in many mechanical and plumbing systems, especially when sealing relies on gaskets or O-rings rather than the threads. They are easy to install, maintain, and work best for low-pressure applications. However, they’re not ideal for high-pressure systems unless paired with the right sealing technology. Understanding their characteristics, applications, and differences from NPT threads can help you choose the right type of threading for your next project.
FAQs
Q: Can I use NPSM threads for high-pressure systems?
A: NPSM threads are generally not recommended for high-pressure applications unless paired with a highly reliable sealing mechanism like O-rings or gaskets.
Q: Can NPSM threads be used interchangeably with NPT threads?
A: No, NPSM and NPT threads are not interchangeable due to their differences in thread design. NPT threads are tapered and provide sealing, while NPSM threads are straight and require a gasket to seal.
Q: What is the main benefit of using NPSM threads?
A: The main advantage is their ease of installation and versatility in mechanical applications where the seal is not dependent on the threads but on a separate sealing component.





