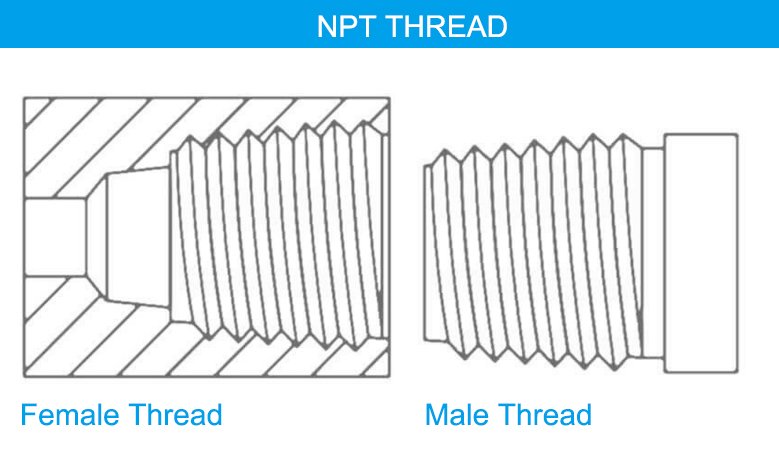
NPT threads, or National Pipe Tapered threads, play a crucial role in piping systems across many industries. Specifically, these threads are essential for creating leak-proof connections that ensure the safe and efficient transfer of liquids, gases, and other materials. Throughout this comprehensive guide, we will explore the specifications, applications, and standards of NPT threads, thereby providing valuable insights into their use and importance.
What is an NPT Thread?
The American National Standard Pipe Thread (NPT) standards are U.S. technical standards for screw threads on threaded pipes and fittings. Specifically, the “T” denotes “tapered,” indicating that the thread diameter gradually decreases along its length. This tapering is crucial because it forms a tight seal, which is essential for preventing leaks in systems that handle fluids and gases under pressure. Consequently, this design ensures the secure and efficient functioning of piping systems in various industrial applications.
History and Evolution of NPT Threads
William Sellers, an American engineer, standardized NPT threads in the 19th century, playing a crucial role in developing a unified system for thread dimensions. His work laid the foundation for NPT threads, which industries have widely adopted since. Over time, the design and application of NPT threads have evolved to meet the growing demands of modern piping systems, but their fundamental principles remain unchanged.
Specifications of NPT Thread
NPT threads are defined by several specifications that ensure their performance and compatibility:
- Thread Angle: NPT threads have a 60-degree thread angle, crucial for creating a strong connection.
- Taper Angle: The taper angle of 1 degree 47 minutes ensures a gradual reduction in diameter, enhancing the sealing capability.
- Pitch Diameter and Pitch: These measurements vary depending on the thread size, with the pitch being the distance between threads.
ANSI/ASME B1.20.1 standardizes these specifications, ensuring consistency and reliability across different manufacturers and applications.
NPT Thread Sizes and Dimensions
NPT thread sizes range from 1/16 inch to 12 inches, with each size corresponding to a nominal pipe size (NPS). The threads’ actual outside diameter slightly exceeds the nominal size, ensuring a tight fit when the threads engage. Understanding these dimensions is crucial for selecting the right thread size for your specific application, as an improper fit can lead to leaks and system failures.
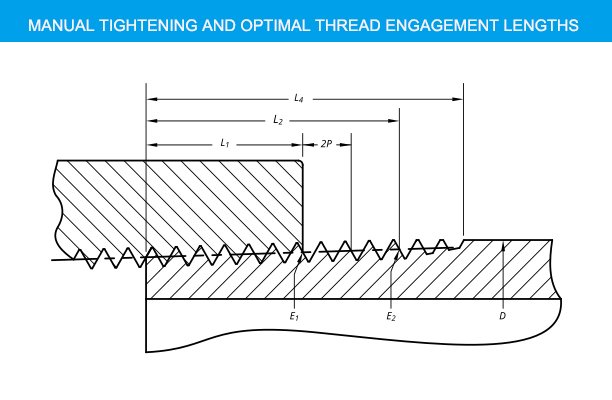
Standard sizes chart
| Nominal pipe size | Thread density | Thread pitch P | Hand-tight engagement | Effective thread | Overall length L4 | Actual outside diameter D | Tap drill | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length L1 | Turns | Diameter E1 | Length L2 | Turns | Diameter E2 | |||||||||
| inch | inch−1 | inch | mm | inch | inch | inch | inch | inch | inch | mm | inch | mm | ||
| 1⁄16 | 27 | 0.03703704 | 0.9407 | 0.1600 | 4.32 | 0.28118 | 0.2611 | 7.05 | 0.2875 | 0.3896 | 0.313 | 7.950 | ||
| 1⁄8 | 27 | 0.03703704 | 0.9407 | 0.1615 | 4.36 | 0.37360 | 0.2639 | 7.13 | 0.38000 | 0.3924 | 0.405 | 10.287 | 0.339 | 8.6106 |
| 1⁄4 | 18 | 0.05555555 | 1.4111 | 0.2278 | 4.10 | 0.49163 | 0.4018 | 7.23 | 0.50250 | 0.5946 | 0.540 | 13.716 | 7⁄16 | 11.113 |
| 3⁄8 | 18 | 0.05555555 | 1.4111 | 0.2400 | 4.32 | 0.62701 | 0.4078 | 7.34 | 0.63750 | 0.6006 | 0.675 | 17.145 | 37⁄64 | 14.684 |
| 1⁄2 | 14 | 0.07142857 | 1.8143 | 0.3200 | 4.48 | 0.77843 | 0.5337 | 7.47 | 0.79178 | 0.7815 | 0.840 | 21.3360 | 23⁄32 | 18.2563 |
| 3⁄4 | 14 | 0.07142857 | 1.8143 | 0.3390 | 4.75 | 0.98887 | 0.5457 | 7.64 | 1.00178 | 0.7935 | 1.050 | 26.6700 | 59⁄64 | 23.4156 |
| 1 | 11+1⁄2 | 0.08695652 | 2.2087 | 0.4000 | 4.60 | 1.23863 | 0.6828 | 7.85 | 1.25631 | 0.9845 | 1.315 | 33.4010 | 1+5⁄32 | 29.3688 |
| 1+1⁄4 | 11+1⁄2 | 0.08695652 | 2.2087 | 0.4200 | 4.83 | 1.58338 | 0.7068 | 8.13 | 1.60131 | 1.0085 | 1.660 | 42.1640 | 1+1⁄2 | 38.1000 |
| 1+1⁄2 | 11+1⁄2 | 0.08695652 | 2.2087 | 0.4200 | 4.83 | 1.82234 | 0.7235 | 8.32 | 1.84131 | 1.0252 | 1.900 | 48.2600 | 1+47⁄64 | 44.0531 |
| 2 | 11+1⁄2 | 0.08695652 | 2.2087 | 0.4360 | 5.01 | 2.29627 | 0.7565 | 8.70 | 2.31630 | 1.0582 | 2.375 | 60.3250 | 2+7⁄32 | 56.3563 |
| 2+1⁄2 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 0.6820 | 5.46 | 2.76216 | 1.1375 | 9.10 | 2.79063 | 1.5712 | 2.875 | 73.0250 | 2+5⁄8 | 66.6750 |
| 3 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 0.7660 | 6.13 | 3.38850 | 1.2000 | 9.60 | 3.41563 | 1.6337 | 3.500 | 88.9000 | 3+1⁄4 | 82.5500 |
| 3+1⁄2 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 0.8210 | 6.57 | 3.88881 | 1.2500 | 10.00 | 3.91563 | 1.6837 | 4.000 | 101.6000 | 3+3⁄4 | 95.2500 |
| 4 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 0.8440 | 6.75 | 4.38713 | 1.3000 | 10.40 | 4.41563 | 1.7337 | 4.500 | 114.3000 | 4+1⁄4 | 107.9500 |
| 4+1⁄2 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 5.000 | 127.0000 | 4+3⁄4 | 120.6500 | |||||||
| 5 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 0.9370 | 7.50 | 5.44929 | 1.4063 | 11.25 | 5.47863 | 1.8400 | 5.563 | 141.3002 | 5+9⁄32 | 134.1438 |
| 6 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 0.9580 | 7.66 | 6.50597 | 1.5125 | 12.10 | 6.54063 | 1.9462 | 6.625 | 168.2750 | 6+11⁄32 | 161.1313 |
| 8 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 1.0630 | 8.50 | 8.50003 | 1.7125 | 13.70 | 8.54063 | 2.1462 | 8.625 | 219.0750 | ||
| 10 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 1.2100 | 9.68 | 10.62094 | 1.9250 | 15.40 | 10.66563 | 2.3587 | 10.750 | 273.0500 | ||
| 12 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 1.3600 | 10.88 | 12.61781 | 2.1250 | 17.00 | 12.66563 | 2.5587 | 12.750 | 323.8500 | ||
| 14 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 1.5620 | 12.50 | 13.87263 | 2.2500 | 18.00 | 13.91563 | 2.6837 | 14.000 | 355.6000 | ||
| 16 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 1.8120 | 14.50 | 15.87575 | 2.4500 | 19.60 | 15.91563 | 2.8837 | 16.000 | 406.4000 | ||
| 18 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 2.0000 | 16.00 | 17.87500 | 2.6500 | 21.20 | 17.91563 | 3.0837 | 18.000 | 457.2000 | ||
| 20 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 2.1250 | 17.00 | 19.87031 | 2.8500 | 22.80 | 19.91563 | 3.2837 | 20.000 | 508.0000 | ||
| 24 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 2.3750 | 19.00 | 23.86094 | 3.2500 | 26.00 | 23.91563 | 3.6837 | 24.000 | 609.6000 | ||
Types of NPT Threads
Various variations of NPT threads are used in different applications:
| Type | Description | Application | Sealant Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| NPT | Tapered threads (1° 47′ taper) designed for tight, leak-proof seals. | General-purpose use where leak-proof connections are essential. | Requires thread sealant (e.g., PTFE tape). |
| NPTF | Tapered threads (Dryseal) that create a metal-to-metal seal without deformation. | Critical applications like fuel or hydraulic systems. | Typically does not require additional sealant. |
| NPS | Straight threads used for mechanical joints, not for sealing. | Applications where alignment is critical, not pressure-tight. | May require a gasket or O-ring to seal. |
| NPSM | Straight threads used in mechanical and low-pressure systems. | Common in hydraulic and pneumatic systems with cone seating. | Generally sealed with an O-ring or metal contact. |
| NPSC | Straight threads designed for coupling without taper. | Used in non-pressure or mechanical joint applications. | Sealing typically achieved through a gasket or O-ring. |
Each type has specific applications and performance characteristics, making them suitable for different industrial needs.
Applications of NPT Threads
NPT threads are widely used in various industries due to their reliability and ease of use:
- Plumbing: Commonly used in residential and commercial plumbing for connecting pipes and fittings.
- Oil and Gas: Essential in high-pressure systems transporting petroleum, natural gas, and other fluids.
- HVAC Systems: Used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to ensure secure connections in duct-work and piping.
- Industrial Manufacturing: NPT threads are used in systems that require the secure transfer of liquids and gases in manufacturing processes.
- Automotive Industry: Applied in fuel lines, brake systems, and hydraulic connections in vehicles.
The versatility of NPT threads makes them indispensable across these varied applications.
How NPT Threads Work
NPT threads function by creating an interference fit between the male and female threads. As the threads are screwed together, the tapering causes the threads to compress against each other, forming a tight, leak-proof seal. This design is particularly effective in high-pressure systems where the integrity of the seal is critical. To enhance the seal, a thread sealant such as Teflon tape is often used to fill any microscopic gaps between the threads.
NPT Thread Standards and Compliance
NPT threads adhere to strict standards to ensure their compatibility and performance:
- ANSI/ASME B1.20.1: Defines the dimensions and tolerances for NPT threads, ensuring that they are standardized across different manufacturers.
- ISO 7-1: The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides an equivalent standard for pipe threads, including both tapered and parallel threads.
- ASTM F1387: Specifies the performance requirements for mechanical fittings, including NPT threads, used in piping systems.
Compliance with these standards ensures that NPT threads meet the necessary safety and performance criteria.
Advantages of Using NPT Threads
NPT threads offer several advantages:
- Leak-Proof Seal: The tapered design ensures a tight, leak-proof seal, critical in applications involving fluids and gases.
- Versatility: They come in various sizes and materials, making them suitable for diverse applications across industries.
- Ease of Installation: NPT threads are simple to install, needing only basic tools and knowledge.
- Standardization: Widely used, NPT threads are easy to find and compatible with many components, simplifying maintenance and replacement.
These advantages make NPT threads a preferred choice in many industrial applications.
Challenges and Considerations with NPT Threads
While NPT threads are highly effective, they present certain challenges:
- Proper Alignment: Ensuring proper thread alignment is crucial to avoid cross-threading, which can damage the threads and compromise the seal.
- Over-Tightening: Over-tightening can deform the threads, leading to potential leaks. It is important to follow recommended torque specifications.
- Material Compatibility: Moreover, ensuring the material of the NPT threads is compatible with the piping components and the fluids being transported is essential to prevent corrosion and ensure durability.
By addressing these challenges, you can ensure the reliable performance of NPT threads in your applications.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with NPT Threads
To avoid installation failures or leaks, it’s important to avoid common mistakes:
- Using the Wrong Size: Selecting the wrong NPT thread size can result in a poor fit and potential leaks.
- Neglecting Sealing Compounds: While NPTF threads may not require sealants, standard NPT threads benefit from the use of Teflon tape or pipe dope to enhance the seal.
- Ignoring Torque Specifications: Proper torque application is crucial to prevent over-tightening or under-tightening, both of which can lead to leaks or component failure.
Avoiding these mistakes will help ensure the long-term reliability of your NPT-threaded connections.
NPT Thread Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance and inspection are crucial for ensuring the longevity of NPT threads:
- Visual Inspection: Regularly check National Pipe Tapered threads for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
- Leak Testing: Periodically test the system for leaks by applying pressure and observing for any fluid or gas escaping from the joints.
- Re-Tightening: If leaks are detected, carefully re-tighten the threads to the recommended torque specifications.
Proper maintenance will help extend the life of your NPT-threaded systems and prevent costly failures.
NPT Thread vs. Other Thread Types
NPT threads are just one of many thread types used in piping systems. Understanding how they compare to other thread types is important for making informed decisions:
- BSP (British Standard Pipe): BSP threads are similar to NPT but have a different thread angle and pitch, commonly used in Europe and Asia.
- Metric Threads: Metric threads are used in mechanical and automotive applications and are not tapered like NPT threads.
- UNF (Unified National Fine): Additionally, UNF threads have a finer thread pitch for more secure connections, commonly used in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Choosing the Right NPT Thread for Your Application
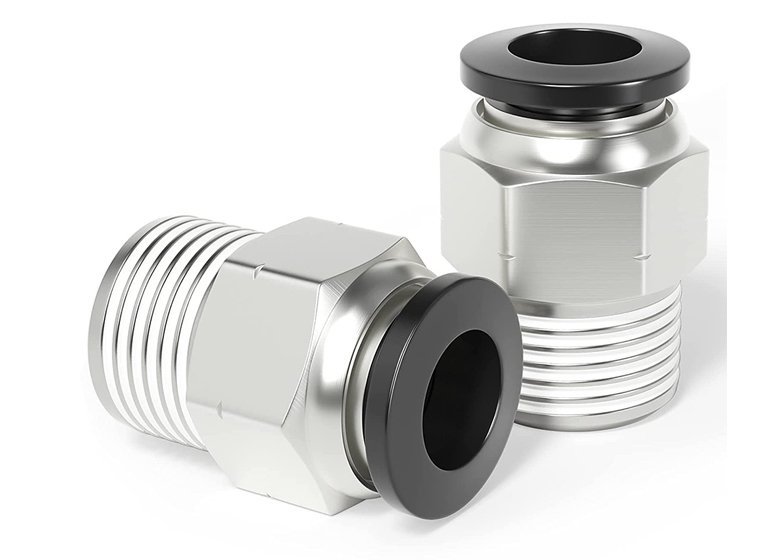

Selecting the right NPT thread involves considering several factors:
- Material: Choose a material that is compatible with the fluid or gas being transported and the surrounding environmental conditions.
- Size: Ensure the thread size matches the nominal pipe size and the dimensions of the piping components.
- Pressure Rating: Verify that the NPT threads can withstand the pressure and temperature conditions of the system.
Careful consideration of these factors will help ensure the success of your NPT-threaded connections.
Tools and Equipment for NPT Thread Installation
Installing National Pipe Tapered threads requires specific tools and equipment:
- Pipe Wrench: Used to grip and tighten the pipe and fitting components.
- Thread Sealant: Teflon tape or pipe dope is applied to the threads to enhance the seal.
- Torque Wrench: Used to apply the correct amount of torque to the threads.
NPT Thread Installation Tips and Best Practices
To achieve a successful installation, follow these tips:
- Clean the Threads: Ensure the threads are clean and free from debris, dirt, or rust before installation.
- Apply Sealant Correctly: Apply Teflon tape or pipe dope evenly and in the direction of the threads.
- Hand Tighten First: Start by hand-tightening the threads to ensure proper alignment, then use a pipe wrench to complete the tightening process.
Following these best practices will help you achieve a secure and reliable NNPT Thread Installation Tips and Best Practices
To achieve a successful installation, follow these tips:
- Clean the Threads: Ensure the threads are clean and free from debris, dirt, or rust before installation.
- Apply Sealant Correctly: Apply Teflon tape or pipe dope evenly and in the direction of the threads to enhance the seal and prevent leaks.
- Hand Tighten First: Begin by hand-tightening the threads to ensure proper alignment and to prevent cross-threading. Then, finish tightening with a pipe wrench, applying the correct torque to avoid over-tightening, which can damage the threads.
Following these best practices ensures a secure and reliable NPT-threaded connection that will function effectively in various applications.
Industry Standards for NPT Thread Quality
Maintaining the quality and consistency of NPT threads is essential for ensuring the safety and performance of piping systems. The quality of National Pipe Tapered threads is governed by strict industry standards that manufacturers must adhere to during production. These standards include:
- ANSI/ASME B1.20.1: This standard outlines the dimensional and tolerance requirements for NPT threads, thereby ensuring compatibility and interchangeability across different manufacturers and applications. Furthermore, adherence to this standard guarantees that the threads will not only fit but also perform as expected, providing consistency and reliability in various piping systems. This ensures that components from different sources can work together seamlessly, maintaining the integrity and efficiency of the entire system.
- ISO 7-1: The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides guidelines for pipe threads, including both tapered and parallel threads. This standard is globally recognized, ensuring compatibility and seamless use in international applications without issues.
- ASTM F1387: This standard specifies the performance requirements for mechanical fittings, including NPT threads, used in piping systems. Furthermore, compliance with ASTM F1387 ensures these threads can withstand the pressures and stresses typical of industrial applications.
Environmental Considerations for NPT Threads
Environmental factors play a significant role in the performance and longevity of NPT threads. It is important to consider these factors during the selection and installation process:
- Corrosion Resistance: When selecting NPT threads, opt for materials that resist corrosion, especially if the threads will encounter harsh environments or corrosive substances. Stainless steel and brass are popular choices due to their excellent corrosion resistance, ensuring long-lasting and reliable connections in challenging conditions.
- Temperature Tolerance: They must be able to withstand the temperature conditions of the system. For applications involving extreme temperatures, such as in steam lines or refrigeration systems, selecting threads made from materials designed to handle these conditions is crucial.
- Chemical Compatibility: Ensure the NPT thread material is compatible with the chemicals or fluids in the system to prevent corrosion and maintain a secure connection. Moreover, using incompatible materials can cause them to degrade over time, leading to leaks or system failures. Therefore, selecting the right material is essential for the longevity and safety of the system.
By taking these environmental factors into account, you can extend the life of your NPT-threaded connections and ensure their safe and effective operation in any application.
How to Choose a Hydraulic Adapter Manufacturer?
NPT (National Pipe Tapered) threads often feature in hydraulic adapters, especially in systems requiring high-pressure fluid connections. Their tapered design creates a secure, leak-proof seal, which is essential for preventing leaks in hydraulic systems. This feature makes them a reliable choice for maintaining system integrity. Additionally, NPT threads are compatible with various hydraulic components, making them a standard option in the industry for ensuring secure and dependable connections.
Choosing the right hydraulic adapter manufacturer is crucial for the performance and reliability of your hydraulic systems. When evaluating manufacturers like Taske, consider the following:
- Quality Standards: Ensure the manufacturer adheres to recognized quality certifications like ISO 9001, ensuring product consistency and reliability.
- Product Range: Look for a diverse selection of hydraulic adapters that meet your specific needs.
- Technical Support: Opt for manufacturers who offer strong technical support and guidance.
- Reputation: Choose a manufacturer with a proven track record and positive reviews in the industry.
Conclusion
NPT (National Pipe Tapered) threads play a crucial role in piping systems by offering a standardized and reliable method for creating leak-proof connections across various applications. Moreover, understanding their specifications, types, and best practices is essential for ensuring the safety and efficiency of your systems. Additionally, by mastering these details, you can optimize the performance of piping connections in diverse settings, from plumbing to industrial manufacturing. Whether used in plumbing, industrial manufacturing, or hydraulic systems, NPT threads offer the durability and versatility necessary for secure and effective piping connections. Furthermore, NPT threads provide the reliability and versatility necessary for optimal performance, whether you’re involved in plumbing, industrial manufacturing, or any field requiring secure piping connections.
FAQs
Q1: What does NPT stand for in threading?
NPT stands for National Pipe Tapered thread, a standard for screw threads used on pipes and fittings to create a leak-proof seal. As such, it effectively ensures secure and reliable connections, earning widespread recognition.
Q2: How does an NPT thread differ from other pipe threads?
NPT threads taper along their length, gradually decreasing in diameter. This design compresses the threads together as they are tightened, creating a tight seal. Other threads, like BSP or metric, may have different angles, pitches, or be parallel instead of tapered.
Q3: Can I use Teflon tape on NPT threads?
Yes, you typically use Teflon tape on NPT threads to fill gaps and enhance the seal, thereby preventing leaks. Additionally, ensure you apply it correctly in the direction of the threads for optimal effectiveness.
Q4: What is the purpose of the taper in NPT threads?
The taper in NPT threads compresses the threads, forming a tight, leak-proof seal when screwing the male and female parts together. This feature is crucial for systems handling high-pressure fluids and gases. This feature is essential for systems that handle high-pressure fluids and gases.
Q5: Are NPT threads suitable for high-pressure applications?
Yes, NPT threads are commonly used in high-pressure applications, such as in the oil and gas industry, where they ensure secure and leak-proof connections.
Q6: How do I identify the correct size of NPT thread?
To identify NPT thread size, begin by checking the nominal pipe size (NPS), which refers to the pipe’s inside diameter, not the thread’s outside diameter. Additionally, it’s important to consult size charts and guidelines for accurate identification, ensuring a proper fit and seal. By following these steps, you can avoid mismatches and ensure reliable connections in your piping system.