Swage fittings play a critical role in ensuring secure, reliable connections in high-pressure systems. Whether in industrial settings, oil rigs, or aerospace applications, these fittings are designed to withstand extreme conditions. In this guide, we’ll dive deep into what swage fittings are, how they work, and their importance in high-pressure applications. You’ll also learn about the various types of swage fittings available and how to choose the right one for your system.
What Are Swage Fittings?
Manufacturers design swage fittings as mechanical connectors to provide a reliable, leak-proof seal for pipes and tubes, especially in high-pressure systems. They typically use swage fittings in systems where welded connections aren’t feasible or where ease of installation is crucial. Swage fittings are unique because they use a process known as “swaging” to deform the fitting, creating a tight seal between the fitting and the pipe or tubing.
Unlike compression fittings, which rely on a mechanical compression to seal, swage fittings rely on a cold working process that deforms the material around the pipe to create a tight, permanent connection. This makes swage fittings ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications where leakage is a critical concern.
Manufacturers make swage fittings from materials like stainless steel, carbon steel, and brass, ensuring they offer high durability and resistance to wear, corrosion, and extreme environmental conditions.
How Do Swage Fittings Work?
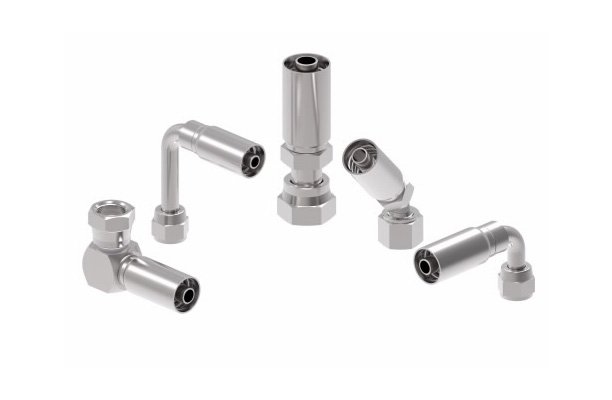

The swaging process is what differentiates swage fittings from other types of connectors. During installation, a special tool is used to deform the fitting around the tubing or pipe, ensuring a secure and permanent bond. This deformation creates a tight seal that prevents any fluid or gas from leaking, even under high pressure.
The primary advantage of swage fittings over other types of fittings, such as compression fittings, is the ability to create a seal without requiring an additional sealing component like an O-ring. Instead, the fitting itself forms the seal when it is compressed around the tube or pipe.
Once installed, swage fittings are resistant to high pressure, temperature fluctuations, and corrosive environments, making them ideal for a wide range of industries, including aerospace, oil and gas, and hydraulic systems.
Types of Swage Fittings
Single-Ferrule vs. Double-Ferrule Swage Fittings
Swage fittings are typically classified into two types: single-ferrule and double-ferrule. A single-ferrule fitting uses one ferrule to create a seal, while a double-ferrule fitting uses two ferrules to ensure a more secure connection. Double-ferrule swage fittings are preferred in systems where extra reliability and safety are necessary.
Straight, Elbow, and Tee Swage Fittings
Swage fittings come in different shapes, including straight connectors, elbows, and tees. Straight swage fittings connect two straight sections of tubing, while elbows and tees redirect the flow of fluids or gases in a system. These fittings are critical for ensuring smooth transitions and reliable connections within high-pressure systems.
Male and Female Swage Connectors
Swage connectors come in male and female types, designed to join pipes and tubing with complementary threads or connectors. A male connector features external threads, while a female connector has internal threads. These fittings play a crucial role in ensuring strong, leak-proof connections within a system.
Advantages of Using Swage Fittings in High-Pressure Systems
Swage fittings stand out in high-pressure systems due to their numerous advantages, making them the preferred choice for industries like aerospace, oil and gas, and automotive. These fittings provide strong, reliable connections that resist leaks, even under extreme pressure and temperature conditions.
- Enhanced Leak-Proof Performance: Swage fittings create a permanent, leak-proof seal by securely gripping the tubing. Their design prevents loosening over time, ensuring a long-lasting, reliable connection.
- Durability and Longevity: With their robust construction, swage fittings excel in resisting high pressures, temperature fluctuations, and vibration. They stand up to harsh operating environments, delivering a long service life without significant wear or degradation.
- Minimal Maintenance Needs: Once installed, swage fittings require minimal maintenance. They provide a maintenance-free solution that reduces the need for ongoing adjustments or inspections, unlike compression or threaded fittings that may require periodic tightening.
- Ease of Installation: Swage fittings simplify installation due to their user-friendly design. Technicians can install them quickly using swaging tools, which saves time and reduces the complexity associated with other fitting types.
- Space Efficiency: The compact design of swage fittings makes them ideal for tight spaces, which is often a challenge in high-pressure systems. Their small footprint allows for more flexible system layouts and optimizes available space.
- Excellent Vibration Resistance: Swage fittings perform exceptionally well under vibrations and other mechanical stresses. Their secure fit prevents loosening, ensuring the integrity of the high-pressure system remains intact, even in dynamic environments.
By choosing swage fittings, industries can enhance the reliability, efficiency, and safety of their high-pressure systems, all while minimizing the risk of leaks and system failures.
Applications of Swage Fittings in High-Pressure Environments
Swage fittings play a critical role in various high-pressure applications, ensuring durable, leak-proof connections. Their robust design makes them essential for industries where system integrity and safety are top priorities. Below are the key sectors that rely on swage fittings:
1. Oil and Gas Industry
Swage fittings ensure secure and leak-proof connections in pipelines transporting oil, gas, and other high-pressure fluids. Their durability makes them ideal for:
- Onshore and offshore pipelines – Preventing leaks in high-pressure oil and gas transport.
- Refineries and processing plants – Ensuring system reliability under extreme temperature and pressure conditions.
- Compliance with API and ISO standards – Meeting industry regulations for safety and performance.
2. Aerospace and Aviation
In aircraft and spacecraft, swage fittings provide reliable connections in critical systems:
- Fuel lines – Preventing fuel leakage at high altitudes and extreme temperatures.
- Hydraulic systems – Withstanding high-pressure fluctuations in landing gear and control mechanisms.
- Air supply lines – Ensuring consistent airflow for cabin pressure regulation.
Their ability to handle extreme pressure changes and vibrations enhances flight safety and efficiency.
3. Automotive Manufacturing
Swage fittings play a vital role in ensuring strong, secure connections in high-performance vehicle systems:
- High-pressure fuel systems – Preventing leaks in fuel injection components.
- Braking systems – Providing reliable hydraulic pressure transmission.
- Hydraulic lines – Enhancing durability and vibration resistance in power steering and suspension systems.
These fittings contribute to the longevity and performance of automotive components.
4. Hydraulic Systems
Swage fittings are widely used in industrial hydraulic applications due to their leak-proof sealing:
- Heavy machinery and construction equipment – Providing secure high-pressure connections.
- Industrial manufacturing – Ensuring efficient fluid power transmission.
- Safety-critical applications – Preventing fluid leakage that could lead to system failure.
Their high-pressure resistance makes them indispensable in fluid power systems.
5. Chemical Processing Industry
Chemical plants require fittings that can safely contain aggressive substances under high pressure:
- High-pressure chemical transport lines – Preventing leaks of hazardous materials.
- Corrosion-resistant applications – Suitable for handling acidic or caustic fluids.
- Dynamic processing environments – Withstanding extreme temperature and pressure fluctuations.
Swage fittings ensure the integrity of fluid transfer systems in corrosive and volatile environments.
6. Marine Industry
The marine industry depends on swage fittings for their high-pressure resistance and durability in harsh conditions:
- Offshore oil rigs – Withstanding high-pressure operations in deep-sea environments.
- Ships and marine vessels – Ensuring leak-proof hydraulic and fuel line connections.
- Saltwater-resistant applications – Preventing corrosion in marine environments.
These fittings play a crucial role in maintaining safe and efficient marine operations.
Choosing the Right Swage Fittings for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate swage fittings for a high-pressure system involves considering several important factors. Choosing the right fitting ensures that your system remains leak-free, safe, and efficient. Here are some key aspects to keep in mind when selecting swage fittings:
Pressure Rating
The pressure rating plays a crucial role when choosing swage fittings. Select fittings that can handle the maximum pressure your system will encounter. Since swage fittings have specific pressure ratings, choose ones that safely accommodate your system’s pressures to prevent failures.
Temperature Resistance
Choose swage fittings based on the temperature conditions they will encounter. Some fittings withstand extreme heat, while others perform better in low temperatures. For applications involving high heat, such as steam systems, or cryogenic conditions, such as in aerospace or gas liquefaction, be sure to select fittings that can withstand the temperature extremes without compromising the integrity of the connection.
Material Compatibility
Swage fittings come in various materials, such as stainless steel, carbon steel, and brass. The material chosen should be compatible with the fluid or gas being transported in the system. For instance, if your system handles corrosive chemicals, you may need to select swage fittings made from corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel, to avoid degradation over time.
Compliance with Industry Standards
It’s crucial to ensure that your swage fittings comply with industry standards such as ASTM, ASME, and ISO. These standards ensure that the fittings meet the necessary safety and performance requirements for high-pressure applications. Checking for certifications and markings on fittings will give you confidence that they meet the regulatory requirements of your industry.
Installation Guide for Swage Fittings
Proper installation of swage fittings is essential to ensure they function as designed and provide a reliable, leak-free connection. Here’s a step-by-step guide to installing swage fittings in high-pressure systems:
Step 1: Prepare the Tubing or Pipe
Before installing the swage fitting, make sure the tubing or pipe is properly cleaned and cut to the correct length. It’s important to remove any burrs or sharp edges from the pipe to ensure a smooth surface for the fitting. Deburring tools or a file can be used to smooth out any imperfections in the pipe ends.
Step 2: Select the Correct Fitting Size
Choose the appropriate swage fitting size based on the diameter of your tubing or pipe. It’s crucial that the fitting is compatible with the tubing to ensure a proper seal. Check that the fitting’s inner diameter matches the outer diameter of the pipe.
Step 3: Insert the Pipe into the Fitting
Insert the pipe or tube into the swage fitting, ensuring it is properly aligned. The tube should fit snugly into the fitting, with the pipe’s end resting against the internal shoulder of the fitting. The fit should be tight, but be careful not to force the pipe into the fitting, as this could damage both the fitting and the pipe.
Step 4: Swage the Fitting
Using a swaging tool, apply the appropriate pressure to the fitting. The tool will deform the fitting around the tube, creating a tight, permanent seal. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the proper swaging process to avoid over-compressing or under-compressing the fitting. It’s important to ensure the fitting is properly deformed for a secure connection.
Step 5: Inspect the Connection
After swaging the fitting, inspect the connection carefully. Look for any signs of deformation, improper fit, or potential leaks. Ensure the fitting is firmly connected and the seal is leak-proof. If you detect any issues, replace the fitting and reinstall it.
Common Issues with Swage Fittings and How to Avoid Them
While swage fittings are known for their durability and reliability, there are some common issues that can arise during their use. Understanding these potential problems and how to avoid them will help ensure a smooth operation and increase the lifespan of your fittings.
Leakage Due to Improper Installation
Leakage is one of the most common issues with swage fittings and often results from improper installation. Misaligned pipes, over-tightening, or incorrect swaging can cause leaks. To prevent this, follow the proper installation procedure and ensure correct pipe alignment before swaging. Additionally, it’s essential to use the appropriate tools and ensure they are in good condition.
Corrosion Over Time
Corrosion can affect swage fittings over time, especially when exposed to moisture, chemicals, or extreme temperatures. This deterioration can weaken the fitting, increasing the risk of failure. Proper material selection and protective coatings help extend the fitting’s lifespan. To prevent corrosion, choose swage fittings made from corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel, when used in environments with exposure to harsh conditions. Regular inspection and maintenance can also help detect signs of corrosion before it leads to failure.
Improper Pressure Rating
Using a swage fitting with an inadequate pressure rating is another common issue. If the fitting is not rated to withstand the system’s operating pressure, it may fail under stress. To avoid this, always check the pressure rating of the swage fitting and ensure it meets or exceeds the maximum pressure of the system. Be mindful that swage fittings come in different pressure ratings, so choosing the right one is critical for safety and performance.
Wear and Tear from Vibration
In some high-pressure systems, particularly those in heavy machinery or vehicles, vibration can cause wear and tear on the fittings, leading to loosened connections or leaks. To mitigate this, consider using vibration-dampening systems or regularly inspecting fittings for signs of loosening. Additionally, proper installation of the fittings with high-quality materials can help reduce the impact of vibration over time.
Advantages of Swage Fittings Over Other Connection Types
| Advantage | Swage Fittings | Compression Fittings | Threaded Connections | Welded Joints |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leak-Proof Seal | Provides a permanent, secure seal with no risk of loosening. | May loosen over time under vibration. | Can leak if not properly sealed. | Provides a strong seal but requires skilled labor. |
| Durability | Highly durable with resistance to vibration and pressure. | Moderate durability, prone to wear under high stress. | Can weaken due to corrosion or mechanical stress. | Very durable but may crack under extreme conditions. |
| Installation Complexity | Easy to install with swaging tools. | Requires precise tightening to avoid leaks. | Easy to install but requires sealing compounds. | Requires skilled labor and welding equipment. |
| Space Requirement | Compact design suitable for tight spaces. | Compact, but may require additional tightening clearance. | Requires extra space for threading tools. | Needs sufficient room for welding. |
| Resistance to Vibration | Excellent resistance; does not loosen over time. | Prone to loosening under vibration. | Threaded connections can loosen with vibration. | Resistant to vibration but can develop stress cracks. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; once installed, it is permanent. | Requires periodic checks and retightening. | May need resealing over time. | Difficult to repair; requires re-welding. |
Maintenance and Inspection of Swage Fittings
To ensure the longevity and functionality of swage fittings, regular maintenance and inspection are essential. By keeping a close eye on these fittings, you can avoid costly failures and extend the life of your high-pressure systems. Here are some best practices for maintaining and inspecting swage fittings:
Routine Visual Inspections
One of the simplest ways to maintain swage fittings is through regular visual inspections. Look for any signs of wear, corrosion, or damage around the fittings, especially at connection points. Pay attention to any leaks or drips, as these could indicate a failure or compromised seal. If any issues are found, it’s important to address them immediately to prevent further damage.
Check for Vibration-Induced Damage
In environments with high vibration levels, swage fittings can gradually loosen or degrade. Regularly check the fittings for signs of wear or loosening, particularly in areas prone to vibration. Tightening and re-sealing the fittings as needed will help maintain their integrity and prevent leaks.
Ensure the Pressure Rating is Still Appropriate
Over time, the pressure rating of the system may change due to modifications or upgrades. Ensure that the swage fittings are still compatible with the new pressure requirements. If your system is subjected to higher pressures than originally designed for, you may need to replace the fittings with those rated for the increased pressure to prevent failure.
Cleaning and Deburring
When performing maintenance, be sure to clean and deburr the ends of the pipes or tubing before reinstalling swage fittings. This ensures that the fittings will seat properly and creates a smooth surface for a tight seal. Cleaning can help prevent contaminants from entering the system, which could cause damage or performance issues.
Conclusion
Swage fittings are vital for high-pressure applications, offering secure, leak-proof connections and durability in extreme environments. With proper material selection and installation, they ensure long-term safety and efficiency across industries like aerospace, oil and gas, and automotive.
As technology advances, swage fittings will continue to evolve, with innovations in materials and monitoring systems. Understanding their benefits and correct usage ensures the reliability of high-pressure systems for years to come.
FAQs
1. What is the maximum pressure rating for swage fittings?
The pressure rating depends on the material and size. Some can handle up to 10,000 PSI or more, but always check the manufacturer’s specifications.
2. Can swage fittings be reused?
No, swage fittings are designed for permanent connections and should not be reused. Use a new fitting for replacements.
3. How do I ensure a leak-proof connection with swage fittings?
Follow proper installation procedures, use the correct tools, and inspect regularly for wear or corrosion.
4. Are swage fittings suitable for cryogenic applications?
Yes, certain swage fittings are designed for low-temperature environments, such as cryogenic applications.
5. Where can I buy high-quality swage fittings?
Swage fittings can be bought from industrial suppliers, online platforms, or manufacturers with certifications like ASTM and ISO.





