In industrial operations, valves might seem like small players in a big game, but their role is absolutely critical. These devices regulate the flow of fluids and gases, maintain system pressure, and ensure processes run smoothly and safely.
However, without proper standards to guide their design and use, valves could easily become weak links in complex systems, leading to leaks, malfunctions, or even catastrophic failures. That’s where valve standards come into play. They establish the benchmarks for performance, safety, and reliability that industries like oil & gas, pharmaceuticals, and water treatment depend on.
In this blog, we’ll walk through what valve standards are, why they matter, who sets these standards, and the trends shaping their future. If you’re a professional in the field or a curious learner, this post will give you all the insights you need!
What Are Valve Standards?
At their core, valve standards are a set of detailed guidelines and requirements that dictate how valves are designed, manufactured, tested, and maintained. These standards ensure that valves meet stringent criteria for safety, reliability, and functionality.
Imagine you’re running a high-pressure oil pipeline. Would you trust a valve that hasn’t been tested to withstand the required pressure? Of course not! Valve standards ensure that every valve in the system can handle the job it’s designed for.
Key Characteristics of Valve Standards
- Material Specifications: Define which materials (like stainless steel, carbon steel, or plastic) are suitable for various applications to ensure durability and compatibility.
- Pressure and Temperature Ratings: Ensure valves can operate safely under specific pressure and temperature ranges.
- Leakage Limits: Standards define acceptable levels of leakage, ensuring tight seals and preventing wastage or environmental contamination.
- Testing Requirements: Include hydrostatic, pneumatic, and performance testing to validate a valve’s functionality under real-world conditions.
How They’re Used
Valve standards guide manufacturers in creating products that meet the expectations of different industries. For end-users, these standards provide confidence that the valves they install are up to the task.
Why Are Valve Standards Important?
Valve standards are the unsung heroes that prevent disasters, improve efficiency, and save costs. Here’s a deeper dive into their importance:
1. Enhanced Safety
Valves are often the first line of defense against dangerous leaks or system failures. In industries like nuclear power or petrochemicals, a faulty valve could lead to catastrophic outcomes. It ensure valves can handle high pressure, extreme temperatures, and hazardous materials without failing.
- Example: API 607, which tests valves for fire safety, ensures they remain operational even during fires.
2. Operational Efficiency
Standards streamline manufacturing and installation processes by promoting uniformity. When valves meet a common set of guidelines, industries can avoid compatibility issues, reducing downtime and improving overall productivity.
- Imagine a power plant that uses valves from different manufacturers. Standards ensure these valves work together seamlessly.
3. Cost-Effective Maintenance
Valves designed to meet stringent standards require less maintenance and are less prone to failure. This saves industries millions in repair and replacement costs.
- Example: ISO 15848 focuses on fugitive emissions, reducing long-term environmental fines and maintenance expenses.
4. Sustainability
Many modern standards include environmental protection measures, such as limiting fugitive emissions from valves in chemical plants or oil refineries. By following these standards, companies can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to global sustainability goals.
Who Establishes Valve Standards?
Valve standards are established by globally recognized organizations, each with its area of expertise. Here’s an in-depth look at the major players:
1. American Petroleum Institute (API)
The API creates standards primarily for the oil and gas industry. Their guidelines are widely recognized for their emphasis on safety, performance, and quality.
- Examples of API Standards:
- API 600: Specifies design, materials, and testing requirements for gate valves used in petroleum and natural gas industries.
- API 624: Focuses on valves with low fugitive emissions to reduce environmental impact.
2. International Organization for Standardization (ISO)

ISO is an independent, non-governmental body that develops standards across multiple industries. Their valve standards are designed for global application, ensuring consistency worldwide.
- Examples of ISO Standards:
- ISO 5208: Defines pressure testing requirements for metallic valves.
- ISO 10497: Specifies fire-testing procedures to ensure valve safety in fire-prone environments.
3. American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME)
ASME focuses on mechanical engineering, including pressure equipment and valves. These are essential for ensuring the structural integrity of valves in high-pressure applications.
- Key ASME Standard:
- ASME B16.34: Covers pressure-temperature ratings, dimensions, and testing of valves.
4. MSS (Manufacturers Standardization Society)
MSS develops technical guidelines for valve components like fittings, flanges, and piping systems.
- Example:
- MSS SP-61: Specifies pressure testing procedures for valves.
5. European Standards (EN)
The EN standards apply to industries within the European Union. They often align with ISO standards but include additional regional requirements.
- Example:
- EN 593: Covers butterfly valves used in industrial applications.
Types of Valves and Their Standards
Each valve type is tailored to specific applications, and corresponding standards ensure their performance:
1. Gate Valves
- Purpose: Provide an on/off function by lifting or lowering a gate inside the valve body.
- Standards: API 600, ISO 10434
2. Ball Valves
- Purpose: Use a rotating ball to control flow, offering quick shutoff.
- Standards: API 608, ISO 17292
3. Globe Valves
- Purpose: Regulate fluid flow with precision, ideal for throttling.
- Standards: ASME B16.34
4. Butterfly Valves
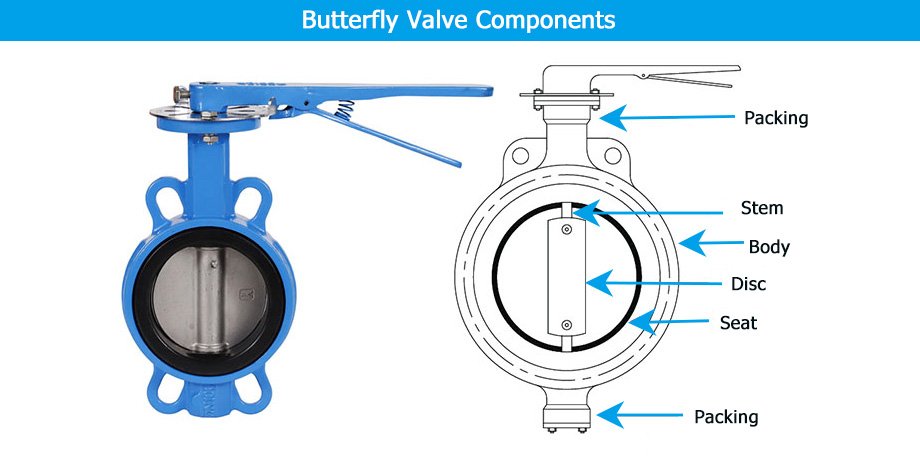
- Purpose: Compact, lightweight valves used for isolating or regulating flow in large pipes.
- Standards: EN 593, API 609
5. Check Valves
- Purpose: Prevent backflow in pipelines, essential for system safety.
- Standards: API 6D, ISO 14313
Future Trends
Valve standards continue to evolve with new technologies and global challenges. Here are a few trends to watch:
- Smart Valves
With the rise of IoT, valve standards are incorporating guidelines for smart sensors, remote monitoring, and automation to enhance system performance. - Stricter Emission Standards
As industries move toward sustainability, expect tougher regulations on fugitive emissions. For instance, API 624 is likely to be expanded to include additional emission-reducing technologies. - Advanced Materials
New materials like carbon composites and 3D-printed metals are becoming common in valve manufacturing. Future standards will include guidelines for testing and certifying these materials.
Conclusion
Valve standards are critical to industrial safety, reliability, and sustainability. Whether you’re designing systems or sourcing valves for your operation, understanding these standards is key to making informed decisions. They’re not just guidelines—they’re lifesavers, cost-cutters, and problem-solvers.
FAQs
1. What’s the difference between API and ISO valve standards?
API standards are often industry-specific (e.g., oil & gas), while ISO standards are designed for broader global application.
2. How do I ensure a valve meets international standards?
Check for manufacturer certifications, testing documentation, and compliance markings (e.g., API, ISO, or ASME).
3. Are valve standards mandatory?
In most cases, yes. Many industries require compliance with specific standards to ensure safety and legal adherence.
4. What is the most commonly used valve standard?
API 600 is one of the most widely used standards for gate valves in the oil and gas industry.
2. How do I know if a valve meets the required standard?
Look for certifications and markings from recognized organizations like API, ASME, or ISO on the valve or its documentation.
3. Why do standards vary between regions?
Regional standards often reflect local regulations, market demands, and environmental conditions.





