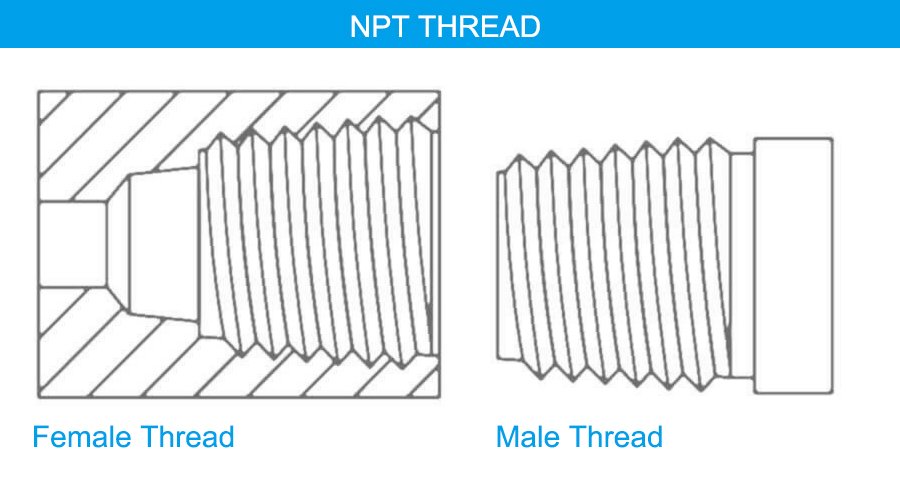
What Does NPT Mean in Threads?
NPT, or National Pipe Tapered threads, is a widely recognized standard for threading used in plumbing, construction, manufacturing, and beyond. Known for its tapered design, NPT threads provide a reliable, leak-proof connection that has made them indispensable in systems requiring the safe and efficient transfer of fluids and gases.
Introduction
Threaded connections are the unsung heroes of plumbing and industrial piping systems because they provide the structural integrity and sealing required for fluid and gas transport. Moreover, among the various threading standards, NPT (National Pipe Tapered) threads stand out as one of the most commonly used, not only in the United States but also internationally.
But what makes NPT threads so effective? Their unique tapered design creates a wedging action when joined, forming a tight seal that prevents leaks. This feature, combined with their ease of use and versatility, has ensured their dominance in industries where precision and reliability are paramount.
Let’s explore what NPT means in threads, its key characteristics, and why it remains a preferred standard across diverse applications.
What Is NPT?

What Does NPT Stand For?
NPT stands for National Pipe Tapered threads, a U.S. standard for tapered threads used in pipes and fittings. These threads were established by the American National Standard Institute (ANSI) to provide a reliable and leak-resistant connection for systems requiring tight seals.
How Tapered Threads Work
The key to NPT’s effectiveness lies in its taper. The threads decrease in diameter at a rate of 1/16 inch per inch of thread length. This gradual reduction forces the mating threads into tighter contact as they are screwed together, creating both a mechanical and a sealing function.
Key Specifications of NPT Threads:
- Taper Rate: 1/16 inch per inch
- Thread Angle: 60 degrees
- Standards: Governed by ANSI/ASME B1.20.1
How Do NPT Threads Work?
Sealing Mechanism
NPT threads rely on a mechanical seal created by tightening the male and female threads together. Consequently, the tapered design increases surface contact, which helps reduce gaps that could allow leaks.
Tapered Design
The taper angle of 1° 47′ (1.7899°) helps achieve a secure fit. This design causes the threads to compress against each other as they are tightened.
Applications of NPT Threads
NPT threads are ubiquitous in industries requiring leak-proof connections. Here are some of their most prominent applications:
Plumbing Systems
NPT threads are a staple in residential and commercial plumbing because they are widely used for water supply lines, drainage systems, and fixtures. Furthermore, their tapered design ensures reliable seals, which significantly reduces the risk of leaks, even under high water pressure.
Oil and Gas Industry
In pipelines and equipment for transporting pressurized fluids and gases, NPT threads ensure safety and reliability. Their ability to handle extreme pressures makes them ideal for this sector.
HVAC Systems
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems use NPT threads to secure connections in refrigerant lines, ducts, and other components. This ensures energy efficiency and system performance.
Industrial Manufacturing
NPT threads play a critical role in pneumatic and hydraulic systems used in manufacturing and automation. Their precision and reliability ensure optimal machine performance.
NPT vs. NPS: Key Differences
| Feature | NPT (National Pipe Tapered) | NPS (National Pipe Straight) |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Type | Tapered | Straight |
| Sealing Method | Thread interference | Requires a gasket/seal |
| Applications | High-pressure systems | Low-pressure systems |
Is BSP Better Than NPT?
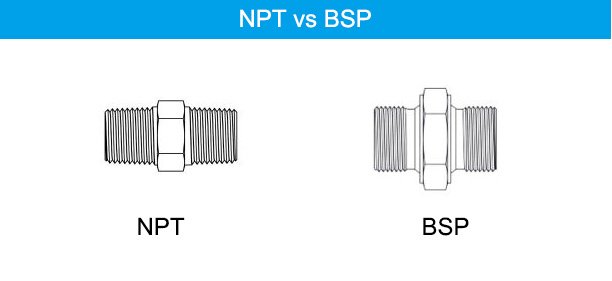
Understanding BSP Threads
BSP (British Standard Pipe) threads are another widely used threading system, particularly in Europe, Asia, and Australia. BSP threads come in two types:
- BSPT (British Standard Pipe Tapered)
- BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel)
Key Differences Between BSP and NPT
- Thread Angle: NPT threads have a 60-degree angle, while BSP threads have a 55-degree angle. This slight difference affects how the threads engage and seal.
- Sealing Mechanism: BSPP requires additional sealing materials like O-rings, while BSPT functions similarly to NPT by relying on a taper to create a seal.
Which Is Better?
The choice between BSP and NPT depends on the application and region. NPT threads are more common in North America, while BSP threads dominate in Europe and Asia. Both systems are equally reliable when used within their intended contexts. Adapters can be used to bridge compatibility gaps when necessary.
NPT Thread Types
Understanding the various types of NPT threads helps in selecting the right fit for specific applications.
1. Standard NPT Threads
These are the most common and are used for general-purpose plumbing and piping systems.
2. NPTF (National Pipe Tapered for Fuel)
Known as Dryseal NPT threads, NPTF threads achieve a seal without the need for additional sealants. As a result, they are particularly ideal for high-pressure and fuel systems.
3. MNPT and FNPT
These terms refer to male and female NPT threads, which must be paired to form a connection. MNPT (male) and FNPT (female) are common in plumbing and HVAC systems.
4. NPS (National Pipe Straight)
NPS threads are straight, not tapered, and rely on additional components like gaskets to achieve a seal. They are used in applications where alignment is critical.
Materials Used for NPT Threads
NPT threads are manufactured from materials compatible with their application environment, including:
- Stainless steel
- Brass
- Carbon steel
- Plastic (e.g., PVC)
Measuring NPT Threads
Thread Pitch
The distance between the peaks of adjacent threads. This is measured in threads per inch (TPI).
Taper Angle
The 1° 47′ taper ensures a tight, leak-proof fit. Tools such as thread gauges and calipers are used for accurate measurement.
Common Sizes of NPT Threads
NPT threads come in standard sizes ranging from 1/16 inch to 6 inches. Popular sizes include:
- 1/2 inch
- 3/4 inch
- 1 inch
These sizes are defined by ANSI/ASME standards.
Advantages of NPT Threads
- Leak-Proof Design: Their tapered shape naturally creates a seal, reducing the need for additional materials.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of fluids and gases across industries.
- Ease of Use: Simple installation with standard tools.
Conclusion
NPT threads are a cornerstone of fluid and gas transport systems because their tapered design and reliability have made them a go-to choice across industries. Moreover, by understanding what NPT threads are, their types, and how they compare to alternatives like BSP, you can make more informed decisions for your piping projects. Whether you’re working on plumbing, HVAC, or industrial systems, NPT threads offer a dependable solution.
FAQs
What does NPT stand for?
NPT stands for National Pipe Tapered threads, a standard used for threaded connections in plumbing and industrial systems.
Are BSP threads compatible with NPT threads?
No, due to differences in thread angle and pitch, BSP and NPT threads are not directly compatible without adapters.
What is the difference between NPT and NPTF threads?
NPTF threads are manufactured to stricter tolerances, creating a seal without the need for additional sealants.
Why do NPT threads taper?
The taper creates a wedging action when tightened, forming a secure and leak-proof seal.