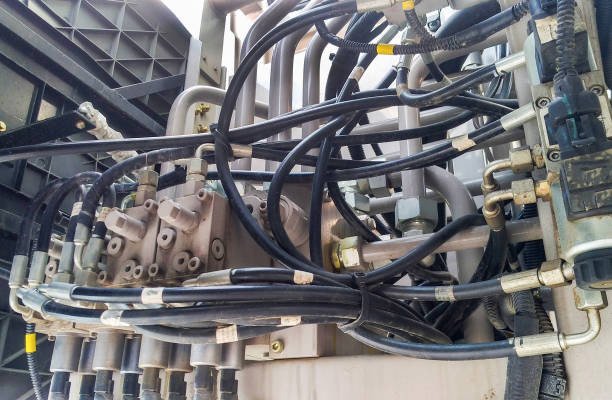
What Are High Pressure Hoses?
High pressure hoses are specially engineered flexible tubes designed to transport fluids under high pressure. These hoses are essential in applications where standard hoses would fail due to extreme pressure levels, abrasion, or temperature fluctuations. They play a critical role in the efficient operation of hydraulic systems, industrial machinery, automotive components, and more.
The main components of a high pressure hose typically include an inner tube that carries the fluid, one or more reinforcement layers for strength, and an outer cover that resists environmental damage. The inner tube is often made from synthetic rubber or thermoplastics, while reinforcement layers might consist of braided or spiral steel wires to withstand immense internal pressure.
Common Applications of High Pressure Hoses
High pressure hoses are incredibly versatile and find application in a broad range of industries. Below are some of the most common uses:
Industrial Use Cases
In manufacturing and construction, high pressure hoses are used to operate hydraulic machinery, pneumatic tools, and spray equipment. Their durability and ability to handle high PSI ratings make them indispensable for heavy-duty environments like mining and oil drilling.
Automotive and Hydraulic Systems
Vehicles, especially those with hydraulic systems like power steering and brake lines, rely on high pressure hoses for fluid transmission. These hoses ensure safe and reliable vehicle operation by handling high-temperature, high-pressure fluids without leaking or collapsing.
Residential and Commercial Cleaning Equipment
Pressure washers and other high-performance cleaning devices utilize high pressure hoses to deliver water or detergents at extremely high velocities. This enables efficient removal of dirt, grime, and grease from surfaces, even in commercial or industrial cleaning settings.
Materials Used in High Pressure Hose Construction
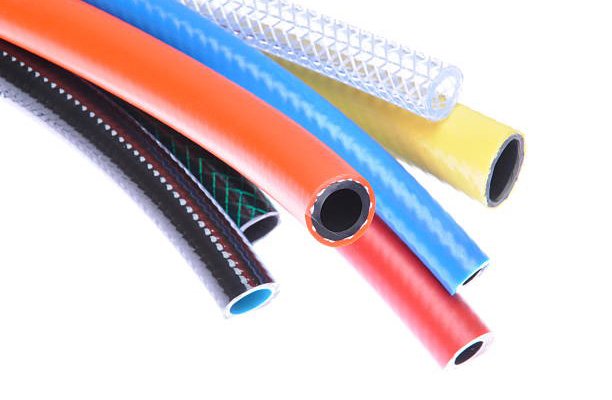

The performance and durability of high pressure hoses largely depend on the materials used in their construction. Below are the primary types:
Rubber Hoses
Rubber hoses are highly flexible and resistant to abrasion, making them ideal for dynamic environments. They are typically reinforced with steel wire braiding for added strength. However, they may degrade under exposure to UV light or certain chemicals.
Thermoplastic Hoses
Thermoplastic hoses are lighter and more resistant to chemical exposure than rubber. They offer excellent flexibility and can operate effectively in both low and high temperature ranges. These hoses are often used in industrial and mobile equipment.
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) Hoses
PTFE hoses provide superior chemical resistance and are ideal for transporting aggressive fluids. They can also withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for aerospace and pharmaceutical applications.
Reinforcement Layers
High pressure hoses are often reinforced with steel wire braids or spirals, textile fibers, or a combination of both. The choice of reinforcement impacts the hose’s pressure rating, flexibility, and overall lifespan. Multi-layered hoses are preferred for ultra-high pressure applications.
Understanding Pressure Ratings and Hose Standards
When selecting or using high pressure hoses, understanding pressure ratings and industry standards is essential for both performance and safety. The pressure rating defines the maximum pressure a hose can handle safely and is usually expressed in PSI (pounds per square inch) or bar.
PSI Ratings and What They Mean
Each high pressure hose comes with a specific PSI rating, indicating its maximum operating pressure. For example, light-duty hoses may be rated up to 3,000 PSI, while heavy-duty hydraulic hoses can exceed 10,000 PSI. Exceeding the pressure rating can cause the hose to burst, leading to equipment damage or personal injury.
SAE and ISO Standards Explained
Two major organizations that govern hose standards are the SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) and ISO (International Organization for Standardization). These standards provide guidelines on hose construction, testing methods, and performance criteria.
- SAE Standards: Common in North America, SAE standards such as SAE 100R1 and 100R2 define specifications for hydraulic hoses.
- ISO Standards: ISO 1436 and ISO 18752 are widely used internationally, ensuring consistency in quality and performance.
Following these standards ensures compatibility, durability, and safety across various applications.
What Are High Pressure Hose Fittings?
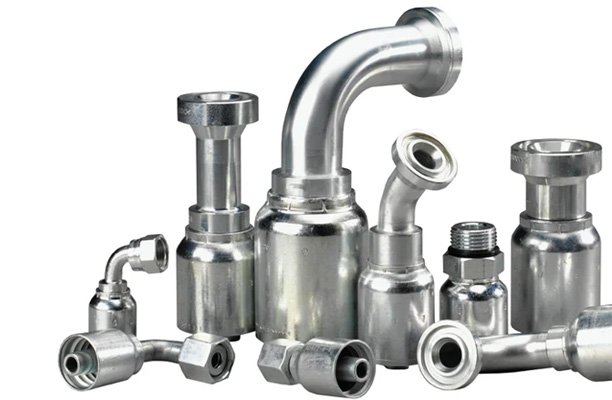

High pressure hose fittings are components used to connect hoses to machines, valves, or other hoses. Their purpose is to create a secure, leak-free connection capable of withstanding the same high pressure as the hose itself. Choosing the right fitting is crucial to system integrity and functionality.
Overview and Purpose
Fittings are designed to facilitate easy installation, replacement, and maintenance of hose systems. They are typically made to match the material and pressure rating of the hose to ensure a perfect seal and long-term durability.
Types of Fittings
- Crimp Fittings: Attached to hoses using specialized crimping tools, these provide a permanent and secure connection ideal for high-pressure environments.
- Push-to-Connect Fittings: These offer quick installation without tools and are commonly used in pneumatic systems. However, they are generally limited to lower pressure applications.
- Threaded Fittings: Available in various thread types (NPT, BSP, JIC), threaded fittings are versatile and often used in both hydraulic and industrial settings.
Common Materials Used in Fittings
The material of a hose fitting directly impacts its resistance to corrosion, durability, and pressure handling. Selecting the appropriate material is crucial based on the type of fluid, pressure levels, and environmental conditions.
Stainless Steel
Known for its exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, stainless steel fittings are ideal for harsh environments such as chemical processing, marine, and offshore applications. They offer longevity and superior sealing capability.
Brass
Brass is commonly used in lower-pressure applications due to its excellent corrosion resistance and ease of machining. It is suitable for air, water, and non-corrosive fluid applications, especially in residential or light industrial settings.
Carbon Steel
Carbon steel fittings are strong and economical, making them suitable for many hydraulic systems. However, they are prone to corrosion and typically require protective coatings when used in moist or corrosive environments.
Compatibility Between Hoses and Fittings
Ensuring compatibility between hoses and fittings is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of high pressure systems. Mismatched sizes or thread types can lead to leaks, equipment failure, and safety hazards.
Matching Sizes and Thread Types
Each hose and fitting must be matched based on internal diameter (ID), external diameter (OD), and thread type. Common thread types include:
- NPT (National Pipe Thread): Tapered threads commonly used in North America for hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
- BSP (British Standard Pipe): Widely used in Europe and Asia, includes both parallel (BSPP) and tapered (BSPT) threads.
- JIC (Joint Industry Council): Flare fittings with a 37-degree angle, ideal for high-pressure applications.
Using the wrong thread type can result in poor sealing and cross-threading, causing long-term system damage.
Importance of Proper Installation
Even the best hose and fitting combinations can fail if not installed correctly. Proper crimping, torque settings, and alignment must be ensured to maintain system integrity. Always use calibrated tools and follow manufacturer guidelines for installation.
Selecting the Right Hose and Fitting for Your Application
Choosing the correct high pressure hose and fitting requires careful evaluation of several factors to ensure safety, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
Pressure, Temperature, and Fluid Compatibility
Consider the maximum working pressure and temperature range the hose will be exposed to. Additionally, ensure that the hose material is chemically compatible with the fluid being transported, whether it’s oil, water, chemicals, or gases.
Environmental Factors and Safety Requirements
Hose and fitting materials must also be chosen based on the external environment. For example:
- UV-resistant covers for outdoor use
- Fire-resistant sleeves for high-heat areas
- Anti-static and non-conductive materials for explosive environments
Also, ensure that the selection meets any industry-specific safety regulations, such as OSHA or MSHA standards.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity and Safety
Regular maintenance of high pressure hoses and fittings can significantly extend their service life and prevent costly failures. An effective maintenance routine includes inspection, cleaning, and proper storage.
Routine Inspection Checklist
- Check for visible signs of wear, such as cracks, abrasions, or bulges
- Inspect fittings for corrosion, leaks, or looseness
- Verify that crimped connections are secure and undamaged
- Monitor for signs of fluid seepage or pressure drops during operation
Cleaning and Storage Best Practices
Clean hoses with appropriate solvents compatible with their internal materials. Store hoses in a dry, shaded area away from direct sunlight, chemicals, or extreme temperatures. Use hose reels or racks to avoid unnecessary kinks and bends.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with High Pressure Hoses and Fittings
Even the most durable high pressure hoses and fittings can encounter performance issues over time. Identifying and resolving these problems early can prevent equipment failure, minimize downtime, and enhance safety.
Leaks, Bursts, and Connection Failures
Leaks are often caused by loose fittings, worn seals, or improper installation. Regularly check all connections and seals for signs of fluid seepage. Bursts typically result from exceeding pressure ratings, kinking, or internal abrasion. Always operate within the hose’s PSI limits and avoid sharp bends.
Diagnosing Wear and Tear
Visible wear indicators include:
- Surface abrasions or blisters on the hose body
- Cracks or fraying near fittings
- Rust or deformation on metal fittings
Unusual sounds during operation—such as whistling or popping—may also indicate internal damage. Replace any damaged hoses immediately to avoid failure under pressure.
Safety Precautions When Using High Pressure Systems
Working with high pressure hoses involves inherent risks. Following proper safety protocols can mitigate hazards and ensure a safe working environment.
Proper Handling Techniques
Never exceed the rated pressure or temperature of a hose. Avoid pulling, twisting, or dragging hoses over abrasive surfaces. Always depressurize the system before disconnecting fittings. Use proper tools and avoid makeshift solutions that compromise integrity.
PPE and Workplace Safety Guidelines
Operators should wear appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) such as:
- Safety goggles or face shields
- Gloves resistant to chemicals and abrasion
- Steel-toed boots for heavy-duty environments
Ensure that emergency shut-off valves and pressure relief systems are in place and operational. Train personnel on emergency response procedures and routine inspections.
Innovations in High Pressure Hose Technology
Recent advancements in materials science and smart technology are reshaping the future of high pressure hoses and fittings. These innovations improve safety, performance, and environmental sustainability.
Recent Advancements in Materials and Design
New composite materials offer higher pressure tolerance, better chemical resistance, and lighter weight. Multi-layer thermoplastic designs and nano-engineered reinforcements provide longer service life and greater flexibility under stress.
Smart Hoses and Monitoring Systems
Emerging technologies include “smart” hoses equipped with embedded sensors that monitor temperature, pressure, and wear in real-time. These systems can alert operators to potential failures before they occur, reducing maintenance costs and improving reliability in mission-critical applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
As industries push toward greener practices, sustainability in high pressure hose manufacturing and use is gaining attention. Modern hoses are increasingly designed with environmental impact in mind, from materials sourcing to end-of-life disposal.
Eco-Friendly Materials and Recycling Options
Many manufacturers now offer hoses made from recyclable or biodegradable materials. Rubber and thermoplastic hoses can be processed and reused in new products. Metal fittings, especially those made from stainless steel or brass, are also highly recyclable.
Reducing Waste through Durable Design
Longer-lasting hose designs not only lower replacement frequency but also reduce landfill waste. Innovations like abrasion-resistant outer layers and self-sealing features help extend the lifecycle of high pressure hoses in demanding environments.
Leading Manufacturers and Brands to Know
Choosing a reputable brand ensures that your high pressure hoses and fittings meet or exceed industry standards. The following manufacturers are recognized globally for quality, innovation, and reliability:
- Gates Corporation: Known for a wide range of hydraulic and industrial hose solutions, including heavy-duty applications.
- Parker Hannifin: Offers precision-engineered hoses and fittings with a focus on performance and sustainability.
- Ryco Hydraulics: An Australian-based company respected for robust hydraulic hose systems and international certifications.
- Eaton: Delivers high-quality hose products for aerospace, agriculture, and industrial sectors.
- Manuli Hydraulics: Specializes in ultra-high-pressure hose assemblies for oil and gas and mining industries.
Always look for certifications such as ISO, SAE, and MSHA to validate product quality and compliance.
Final Thoughts: Choosing Quality for Performance and Safety
High pressure hoses and fittings are foundational components across industries—from construction and automotive to cleaning systems and chemical processing. Investing in the right equipment ensures not only optimal performance but also workplace safety and environmental compliance.
To summarize:
- Understand your system’s pressure, temperature, and fluid requirements
- Choose hoses and fittings that meet industry standards
- Maintain them through regular inspection and proper handling
- Opt for sustainable and durable options to minimize long-term costs and environmental impact
By prioritizing quality and safety, businesses can maximize efficiency, reduce downtime, and protect both personnel and the planet.
FAQs
1. What is the maximum pressure a high pressure hose can handle?
The maximum pressure varies by design and application. While standard hoses operate up to 3,000 PSI, specialized ultra-high pressure hoses can handle over 10,000 PSI.
2. How do I know if my hose fitting is compatible?
Check for matching thread types, pressure ratings, and material compatibility. Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications or use a thread gauge for accurate matching.
3. Can high pressure hoses be repaired or should they be replaced?
Minor issues like leaks near fittings may be repaired using proper crimping tools. However, for severe damage or degradation, full replacement is recommended to ensure safety.
4. Are there hoses suitable for both hot and cold temperatures?
Yes, thermoplastic and PTFE hoses offer wide temperature tolerance, making them suitable for both extreme heat and cold environments.
5. What certifications should I look for in a high pressure hose?
Key certifications include SAE, ISO, and MSHA. These ensure the hose meets global safety, quality, and performance standards.