Introduction to Ferrule Fittings
What Are Ferrule Fittings?
Ferrule fittings are a type of compression fitting used to connect tubing in a leak-proof and pressure-tight manner. These fittings are widely used in fluid and gas systems, particularly where precision and reliability are critical. A typical ferrule fitting consists of a nut, a ferrule (or ferrules), and a fitting body. When tightened, the ferrule(s) deform to grip the tubing and create a seal between the tube and the fitting body. This design eliminates the need for welding or soldering, offering a versatile and easy-to-install solution for many industrial applications.
Importance in Industrial Applications
Ferrule fittings are essential in industries where leak-proof performance, durability, and corrosion resistance are non-negotiable. In sectors like oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, and food processing, ferrule fittings ensure secure connections that can withstand high pressures and temperatures. Their reusability and easy maintenance make them cost-effective, while their design supports compliance with stringent safety and cleanliness standards. The reliability of ferrule fittings reduces downtime and operational risks, making them a critical component in mission-critical fluid and gas transfer systems.
Key Components of a Ferrule Fitting
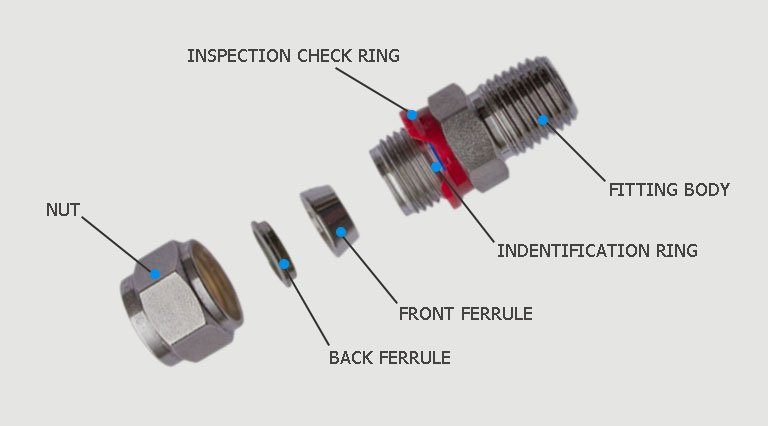
A ferrule fitting typically includes three key components:
- Nut: Tightens the fitting and drives the ferrule forward to compress it against the tube and fitting body.
- Ferrule: The metallic or plastic ring that deforms to create a seal. In double ferrule fittings, two ferrules are used for added grip and sealing.
- Fitting Body: The main component that houses the tubing and ferrule, connecting to other piping or systems.
Understanding these components helps in choosing the right fitting configuration and ensures correct installation, directly impacting performance and longevity.
Main Types of Ferrule Fittings
Single Ferrule Fittings
Single ferrule fittings use one ferrule to create the seal and grip on the tubing. These fittings are commonly used in applications where moderate sealing is sufficient. They are simpler in design and are typically easier to install than double ferrule systems. However, they may not offer the same level of mechanical strength or sealing integrity under high pressure or vibration conditions. Single ferrule designs are cost-effective and suited for general-purpose instrumentation and light industrial use.
Double Ferrule Fittings
Double ferrule fittings are the industry standard for high-performance sealing and mechanical grip. These fittings utilize two ferrules: the front ferrule provides the sealing mechanism, while the back ferrule grips the tube and prevents it from slipping. This dual-action design ensures high pressure handling, superior vibration resistance, and consistent reusability. Double ferrule fittings are widely used in critical industries like oil & gas, pharmaceuticals, and chemical processing where safety and reliability are paramount.
Compression Ferrule Fittings
Compression ferrule fittings include both single and double ferrule designs and are named for their method of sealing—compression. These fittings are popular due to their leak-proof capabilities without the need for soldering or welding. Compression fittings work by tightening the nut, which compresses the ferrule(s) onto the tubing to form a strong seal. They are used across a range of industries for gas, liquid, and hydraulic systems where dependable connections are necessary.
Instrumentation Ferrule Fittings
Precision and Performance
Engineers specifically design instrumentation ferrule fittings for high-precision applications that require accuracy, stability, and leak-tight performance. Industries predominantly use these fittings in analytical instruments, control panels, flow measurement systems, and other critical process equipment. Designed with tight tolerances, they support high-purity applications and ensure minimal dead space, which reduces the risk of contamination and flow disruption.
Material Compatibility
To ensure reliability in sensitive environments, instrumentation ferrule fittings are typically manufactured from high-grade stainless steel (like SS316), and sometimes from Monel, Hastelloy, or other corrosion-resistant alloys. This ensures long-lasting performance even under extreme temperatures or aggressive chemical exposure.
Common Configurations
These fittings are available in multiple configurations, including tees, elbows, unions, and bulkhead fittings, making them adaptable to complex system architectures. Their modular nature allows for easy integration into existing setups, making them a top choice for engineers and instrumentation specialists.
Material Classification of Ferrule Fittings
Stainless Steel Ferrule Fittings
Engineers most commonly choose stainless steel for ferrule fittings because it offers exceptional mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and temperature tolerance. Many industries—such as pharmaceuticals, oil & gas, and food processing—prefer SS316 for its non-reactive and hygienic properties. Stainless steel ferrule fittings offer excellent resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking—ideal for high-pressure and harsh environments.
Brass Ferrule Fittings
Engineers frequently use brass ferrule fittings in applications that don’t require high-pressure resistance or exposure to corrosive media. Because brass is cost-effective and easy to machine, it makes these fittings ideal for water, air, and non-aggressive gases. As a result, many HVAC systems, pneumatic controls, and general plumbing setups rely on them.
Polymer and Plastic Ferrule Fittings
Engineers frequently use brass ferrule fittings in applications that don’t require high-pressure resistance or exposure to corrosive media. Because brass is cost-effective and easy to machine, it makes these fittings ideal for handling water, air, and non-aggressive gases. As a result, HVAC systems, pneumatic controls, and general plumbing often rely on them.
Similarly, designers choose plastic ferrule fittings—typically made from PTFE, nylon, or polypropylene—for situations where metal contamination must be avoided or chemical inertness is essential. These fittings play a key role in laboratory setups, semiconductor processing, and low-pressure chemical dosing systems. Although lightweight and corrosion-resistant, they are not suitable for high-temperature or high-pressure conditions.
Exotic Alloy Ferrule Fittings (Hastelloy, Inconel, etc.)
Specialty Materials for Extreme Conditions
Manufacturers design exotic alloy ferrule fittings—such as those made from Hastelloy, Inconel, Monel, or Titanium—for extreme operating conditions involving aggressive chemicals, high temperatures, and corrosive environments. These alloys offer unique properties like resistance to acid attack, stress corrosion, and oxidation, making them indispensable in high-end applications such as offshore oil rigs, nuclear power plants, and aerospace systems.
Advantages of Using Exotic Alloys
- Enhanced Corrosion Resistance: Superior to standard stainless steel, especially in acidic or chloride-rich environments.
- High Temperature Stability: Capable of maintaining integrity in extreme heat.
- Extended Service Life: Reduces maintenance and replacement frequency.
Cost Considerations
While more expensive than conventional materials, exotic alloy ferrule fittings offer value through extended durability, reduced downtime, and superior safety margins. Selecting the right alloy based on the application environment is crucial to achieving optimal performance and cost efficiency.
Design Features and Functionality

How Ferrule Fittings Work
The core functionality of ferrule fittings lies in their mechanical grip and sealing action. When the nut of the fitting is tightened, the ferrule (or ferrules) are compressed between the nut and the fitting body. This compression causes the ferrule to grip the outside diameter of the tube while simultaneously creating a tight seal between the tube and the fitting body. This unique sealing method eliminates the need for threads on the tube itself, reducing leak paths and enhancing safety.
Leak-Proof Sealing Mechanism
One of the primary benefits of ferrule fittings is their ability to provide a leak-tight seal under extreme conditions. The front ferrule forms a primary seal against both the tube and the fitting body, while the back ferrule provides a secondary seal and strong tube grip. This double sealing system in double ferrule fittings ensures high performance even under vibrations, temperature fluctuations, and pressure surges. Engineers especially value the robust design in applications that require zero tolerance for leaks, such as gas chromatography or high-purity fluid systems.
Advantages of Double Ferrule Systems
Double ferrule fittings offer several technical advantages:
- Enhanced Grip: The rear ferrule provides a firm hold on the tube, preventing slippage or pull-out under stress.
- Consistent Sealing: The front ferrule creates a consistent seal regardless of operator variation during installation.
- Reusability: These fittings can be disassembled and reassembled multiple times without compromising seal integrity.
- Minimized Galling: The absence of metal-to-metal threading on the tube reduces wear and galling during maintenance.
This makes double ferrule systems ideal for critical applications where performance and safety are top priorities.
Applications Across Industries
Oil & Gas Industry
Ferrule fittings play a vital role in upstream and downstream oil and gas operations. They are used extensively in control panels, offshore platforms, refinery instrumentation, and hydraulic systems. These fittings withstand corrosive media, pressure cycling, and temperature variations typical in oilfield conditions. Stainless steel and exotic alloy ferrule fittings are especially preferred for their ability to resist hydrogen sulfide, saltwater, and other harsh chemicals commonly found in oil and gas processes.
Pharmaceutical and Biotech
In pharmaceutical and biotech industries, maintaining high standards of purity and sterility is critical. Ferrule fittings used in these sectors must comply with stringent regulations such as ASME BPE and FDA standards. Manufacturers often use electropolished stainless steel to make these fittings, preventing microbial growth. They design the fittings with minimal crevices to eliminate the risk of contamination. Clean-in-place (CIP) and steam-in-place (SIP) systems commonly employ them to ensure reliable fluid transfer in drug manufacturing and laboratory processes.
Food and Beverage Industry
Ferrule fittings in the food and beverage sector help maintain sanitary conditions while providing durable, leak-proof connections. These fittings are typically constructed from food-grade stainless steel and are compliant with hygienic design principles. Used in processing lines, bottling systems, and CIP setups, ferrule fittings must endure frequent cleaning, high temperatures, and exposure to acidic or sugary fluids without degradation or corrosion. Smooth internal surfaces and secure connections help preserve product quality and safety.
Petrochemical and Power Generation
Ferrule Fittings in Chemical Plants
In the petrochemical sector, ferrule fittings are crucial for safe and efficient transport of corrosive chemicals, high-temperature steam, and pressurized gases. They are used in reactors, condensers, pressure vessels, and pipeline networks. The fittings’ leak-tight design prevents the escape of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and enhances operational safety. Double ferrule systems, often made from Inconel or Hastelloy, are especially favored in reactors and high-risk zones.
Power Plants and Utilities
In power generation—whether nuclear, thermal, or hydroelectric—ferrule fittings ensure the integrity of control and instrumentation tubing systems. Their vibration-resistant and high-temperature tolerant properties make them ideal for monitoring systems, boiler tubing, turbine controls, and feedwater loops. Their quick installation and minimal maintenance also reduce downtime, which is essential for maximizing plant efficiency.
Environmental and Safety Benefits
Using high-quality ferrule fittings reduces environmental hazards by minimizing the risk of leaks and emissions. In regulated industries, this contributes to compliance with EPA, OSHA, and international safety standards. Their robust construction and adaptability also improve system reliability, thereby protecting both personnel and the environment.
Installation and Maintenance
Best Practices for Installation
Proper installation of ferrule fittings is critical to ensure optimal performance and safety. Here are some industry-recommended best practices:
- Cut the Tubing Square: Use a tube cutter to make a clean, perpendicular cut to ensure an even seal surface.
- Deburr the Tube: Remove internal and external burrs to prevent damage to the ferrule and ensure proper seating.
- Use Correct Assembly Tools: Use a calibrated torque wrench or spanner to avoid over-tightening or under-tightening.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Different brands may have specific torque ratings or installation sequences—always follow the recommended guidelines.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Improper installation can compromise the integrity of the fitting and lead to leaks or system failure. Common mistakes include:
- Reusing Old Ferrules: Once compressed, ferrules should not be reused as they lose their sealing properties.
- Using Damaged Tubing: Scratched or oval tubing can prevent proper sealing and should be replaced.
- Incorrect Tube Insertion: The tube must bottom out in the fitting to ensure correct ferrule compression.
- Over-Tightening: Applying excessive torque can deform the ferrule, leading to leaks or stress fractures.
Inspection and Replacement Tips
Regular inspection of ferrule fittings is essential for preventing failures, especially in high-pressure systems. Key inspection practices include:
- Visual Checks: Look for signs of corrosion, deformation, or discoloration on fittings and surrounding tubing.
- Leak Testing: Periodically perform hydrostatic or pneumatic leak tests to verify sealing integrity.
- Replacement Schedule: Replace ferrules and fittings based on hours of operation, pressure cycles, or manufacturer guidelines—even if no visible damage is present.
Comparing Ferrule Fittings with Other Fittings
Ferrule vs Flare Fittings
Flare fittings use a flared end on the tube, usually formed by a tool, to create a seal against a conical surface in the fitting. While they are reliable and widely used in gas and refrigeration systems, they require precise flaring tools and more preparation. In contrast, ferrule fittings are easier to install and provide excellent sealing without modifying the tubing end. They also tend to have better performance in high-vibration and high-pressure environments.
Ferrule vs Push-to-Connect Fittings
Push-to-connect (or push-fit) fittings offer extremely fast installation, often without tools, making them ideal for low-pressure pneumatic or water systems. However, their sealing integrity and pressure tolerance are significantly lower than those of ferrule fittings. Ferrule fittings are more robust, reusable, and suitable for industrial environments where safety and reliability are paramount.
Ferrule vs Welded Connections
Welded connections offer permanent, leak-proof joints and are common in systems where long-term integrity is critical. However, welding requires skilled labor, expensive equipment, and downtime. Ferrule fittings offer flexibility and ease of maintenance while still delivering high-pressure and leak-free performance. They are ideal when modularity, reusability, and rapid installation are important considerations.
Standards and Compliance
ASME and ASTM Standards
Ferrule fittings often adhere to rigorous industry standards set by organizations like ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) and ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials). These standards govern dimensions, pressure ratings, materials, and manufacturing processes to ensure consistency and safety. For example, ASTM A276 and ASTM A479 specify the quality of stainless steel bars used in ferrule fittings.
ISO Certifications for Ferrule Fittings
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 8434 for metallic tube connections ensure that ferrule fittings meet global benchmarks. These certifications indicate a manufacturer’s commitment to quality, traceability, and continuous improvement, which is crucial for industries with strict regulatory oversight.
Industry-Specific Regulations
Certain sectors have their own compliance frameworks. For example:
- Pharmaceuticals: Must comply with FDA and ASME BPE standards for hygienic design and material traceability.
- Oil & Gas: API and NACE standards address material performance under corrosive and high-pressure environments.
- Food & Beverage: Requires compliance with NSF/ANSI standards to ensure food safety and cleanability.
Adherence to these standards ensures product safety, environmental protection, and operational efficiency.
Choosing the Right Ferrule Fitting
Factors to Consider
Selecting the correct ferrule fitting for your application requires careful evaluation of system parameters and environmental conditions. Critical considerations include:
- Media Type: Compatibility with gases, liquids, corrosive chemicals, or hygienic fluids.
- System Pressure and Temperature: Ensure the fitting’s rated limits match or exceed system requirements.
- Installation Environment: Consider vibration, corrosion, and accessibility for maintenance.
Making the right choice not only ensures operational efficiency but also minimizes long-term maintenance costs and safety risks.
Working Pressure and Temperature
Ferrule fittings come with manufacturer-rated pressure and temperature thresholds. These ratings vary by material and design. For instance, stainless steel ferrule fittings may handle pressures up to 6,000 psi and temperatures ranging from -425°F to 1200°F, while plastic variants are suitable only for lower pressure and moderate temperatures. Always reference the datasheet or consult with the supplier when designing a high-stress system.
Material Compatibility and Corrosion Resistance
Material compatibility is essential for the long-term performance of ferrule fittings. Mismatched materials can result in galvanic corrosion or degradation of seals. In applications involving acids, chlorides, or seawater, exotic alloys such as Hastelloy or Titanium may be necessary. For general-purpose uses, SS316 typically offers a strong balance between durability and cost-effectiveness. A corrosion failure not only causes leaks but can also contaminate the process media or trigger hazardous reactions.
Top Manufacturers and Suppliers
Global Leaders in Ferrule Fitting Production
Several manufacturers are recognized globally for producing high-quality ferrule fittings. Some of the most trusted brands include:
- Swagelok: Known for precision, durability, and an expansive product line.
- Parker Hannifin: Offers a wide range of fittings for instrumentation and fluid systems.
- Hy-Lok: Renowned for cost-effective solutions and interchangeability with other brands.
- DK-Lok: Gaining popularity for its high-performance fittings in global markets.
Criteria for Selecting Reliable Suppliers
Choosing a reliable supplier is just as important as selecting the right fitting. Look for suppliers that provide:
- ISO or ASME Certification
- Technical Support and Customization
- Transparent Quality Control Processes
- Proven Track Record in Your Industry
Online vs Offline Purchasing
Online platforms offer convenience, broader selection, and often better pricing. However, offline purchasing may be preferable when personalized service, immediate availability, or detailed consultation is needed. Reputable distributors often offer hybrid services, combining online catalogs with in-person technical support and local stock availability.
Future Trends in Ferrule Fittings
Advancements in Material Science
Innovations in material engineering are introducing new alloys and coatings that improve corrosion resistance, reduce weight, and enhance performance. Expect to see a broader use of composite materials, smart alloys, and antimicrobial coatings in the future, especially for biotech and cleanroom environments.
Automation and Smart Assembly
The integration of IoT and smart tools in fitting assembly is revolutionizing how installations are managed. Automated torque tools, digital assembly validation, and sensor-embedded fittings will enhance reliability and provide traceable installation records—ideal for regulated industries.
Sustainability and Environmental Compliance
Environmental regulations are pushing industries toward sustainable practices. Future ferrule fittings will likely emphasize recyclability, reduced carbon footprint in production, and the use of eco-friendly materials. Manufacturers are also working on minimizing fugitive emissions and optimizing designs for longer service life to support global sustainability goals.
Conclusion
Ferrule fittings are indispensable in creating secure, leak-proof, and high-performance connections in a wide variety of industrial applications. From simple single ferrule fittings to advanced double ferrule systems made of exotic alloys, each type is designed for specific environments and requirements.
Whether you’re an engineer designing high-pressure instrumentation or a procurement specialist sourcing fittings for critical infrastructure, understanding the types, materials, and applications of ferrule fittings empowers you to make informed decisions. Prioritize quality, compliance, and proper installation to ensure long-term success in your operations.
FAQs
What is the difference between single and double ferrule fittings?
Single ferrule fittings use one ferrule to seal and grip the tubing, while double ferrule fittings use two: the front ferrule for sealing and the back ferrule for tube grip. Double ferrule designs offer higher reliability and are preferred for high-pressure and vibration-prone applications.
Are ferrule fittings reusable?
While the fitting body and nut can often be reused, ferrules are generally not reusable after they’ve been compressed during installation, as their shape changes to form a seal. Reusing ferrules may compromise sealing integrity.
Which industries benefit the most from ferrule fittings?
Industries such as oil & gas, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, petrochemicals, and power generation heavily rely on ferrule fittings due to their leak-proof performance, corrosion resistance, and ease of maintenance.
How do I know which ferrule material to choose?
Select the material based on media compatibility, pressure/temperature requirements, and environmental conditions. Stainless steel is a general-purpose choice, while exotic alloys like Hastelloy are best for aggressive chemicals or extreme environments.
What are the signs of a failing ferrule fitting?
Signs include visible leaks, corrosion, discoloration, deformation of the fitting or tubing, and pressure drop in the system. Regular inspections and testing can help identify these early and prevent system failure.





