Introduction
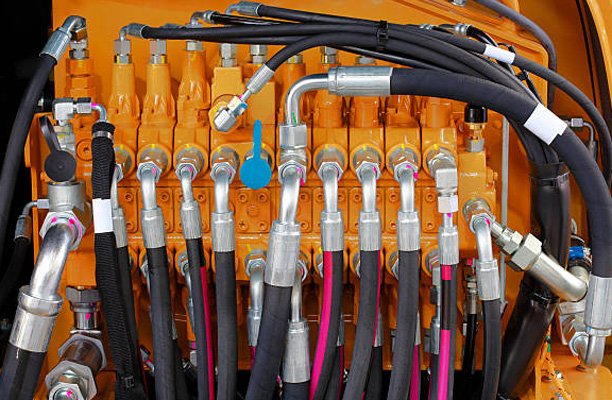
Hydraulic systems are widely used in various industries, from construction and agriculture to automotive and manufacturing. One of the most critical components of these systems is the hose ferrule, which ensures a secure connection between the hose and the fitting. Choosing the right ferrule is essential for maintaining hydraulic efficiency, preventing leaks, and ensuring safety.
In this guide, we will explore everything you need to know about selecting the perfect hose ferrule, including the different types available, key selection factors, and industry best practices.
Understanding Hose Ferrules
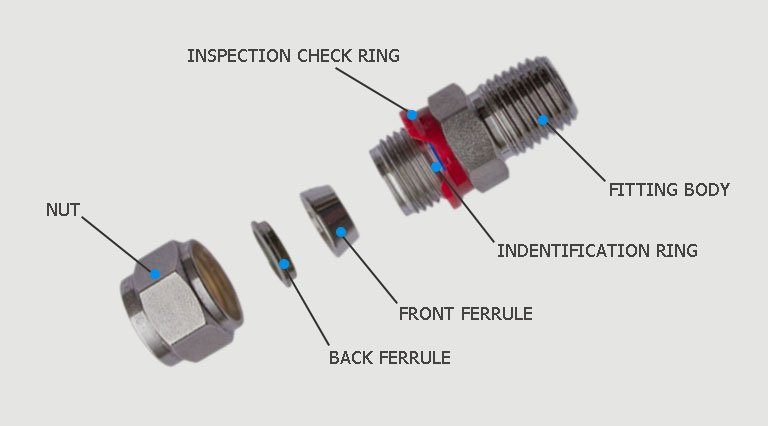
A hose ferrule is a metal sleeve that is crimped or swaged around the end of a hydraulic hose to provide a secure connection between the hose and its fitting. It plays a crucial role in sealing and reinforcing the hose assembly, preventing leaks and maintaining the structural integrity of the system.
Ferrules are typically made from durable materials such as:
- Stainless Steel: Offers high corrosion resistance, ideal for harsh environments.
- Brass: Suitable for low-pressure applications, resistant to rust.
- Aluminum: Lightweight but not as strong as stainless steel.
Proper selection of a ferrule is vital to ensure a long-lasting and reliable hydraulic system.
Types of Hose Ferrules
There are various types of hose ferrules, each designed for specific applications and installation methods. The most common types include:
1. Crimped Ferrules
These ferrules are permanently attached to the hose using a hydraulic crimping machine. They provide a strong, leak-proof connection and are widely used in high-pressure applications.
2. Swaged Ferrules
Similar to crimped ferrules, swaged ferrules are mechanically compressed onto the hose. This method also ensures a secure attachment but may require specialized swaging equipment.
3. Push-On Ferrules
Push-on ferrules are designed for low-pressure applications and do not require crimping. They are easy to install and remove but may not be suitable for high-pressure environments.
4. Reusable vs. Permanent Ferrules
- Reusable Ferrules: Can be removed and reinstalled multiple times, often used in field repairs.
- Permanent Ferrules: Crimped or swaged tightly and cannot be reused once installed.
Understanding the differences between these ferrule types will help in choosing the right one for your hydraulic system’s needs.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Hose Ferrule
Selecting the right hose ferrule requires careful consideration of several key factors. Using an incompatible ferrule can lead to system failure, leaks, and safety hazards. Below are the essential elements to keep in mind:
1. Hose Type Compatibility
Different hydraulic hoses are made from materials like rubber, thermoplastic, or PTFE (Teflon). The ferrule must match the hose type to ensure a proper seal and long-term durability. Using the wrong ferrule can cause fitting failures and fluid leaks.
2. Operating Pressure and Temperature
Hydraulic systems operate under varying pressures and temperatures. The ferrule must be rated for the specific pressure and temperature conditions of the system. High-pressure applications require robust, crimped ferrules made from durable materials like stainless steel.
3. Material Selection for Corrosion Resistance
Hydraulic hoses are exposed to various environmental conditions, including moisture, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. Choosing a corrosion-resistant ferrule material (such as stainless steel) is crucial for long-term performance in harsh environments.
4. Industry Standards and Certifications
To ensure safety and reliability, hose ferrules should meet industry standards like:
- SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) – Sets guidelines for hydraulic hose fittings.
- ISO (International Organization for Standardization) – Ensures global compliance.
- DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung) – Common in European applications.
Verifying compliance with these standards helps maintain system integrity and avoid costly failures.
5. Crimping vs. Swaging Requirements
Some hydraulic applications require crimped ferrules, while others may use swaged ferrules. Understanding the installation process and equipment needed is essential when selecting a ferrule. Crimped ferrules require a hydraulic crimping machine, while swaged ferrules need specialized swaging tools.
Selecting the Right Size and Fit
Choosing the correct ferrule size is critical for maintaining a secure hydraulic connection. An improperly sized ferrule can lead to fluid leakage or hose blowouts.
1. Measuring Hose Diameter
Before selecting a ferrule, measure the hose’s inside and outside diameter. Most manufacturers provide sizing charts to match ferrules with hose dimensions.
2. Tolerance and Fitting Snugness
The ferrule should fit snugly around the hose without excessive force. Too tight, and it may damage the hose; too loose, and it won’t provide a secure seal.
3. Avoiding Common Sizing Mistakes
- Using an oversized ferrule can cause leaks.
- Choosing an undersized ferrule may crush the hose and restrict fluid flow.
- Failing to verify manufacturer recommendations can result in improper installations.
Ferrule Installation Best Practices
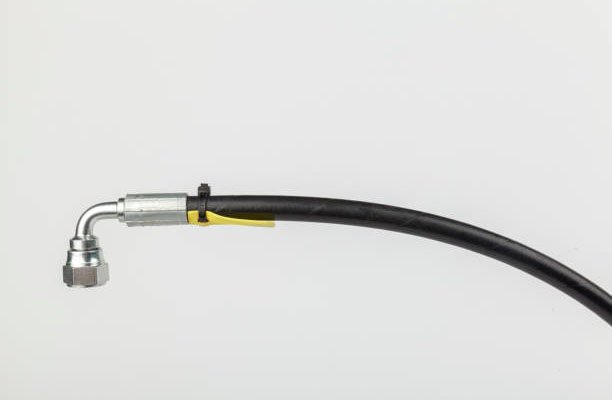

Proper installation of a hose ferrule is crucial for hydraulic system efficiency and safety. Below are best practices to follow during installation.
1. Proper Crimping Techniques
Use a high-quality hydraulic crimping machine to attach crimped ferrules. Follow manufacturer specifications for crimping pressure and dimensions to avoid under- or over-crimping.
2. Using the Right Crimping Tools and Machines
Ensure you use a compatible crimping tool for the ferrule type. Hand crimpers, hydraulic crimping machines, and automated crimping stations provide different levels of precision.
3. Inspection and Testing for Secure Attachment
- After crimping, inspect the ferrule visually for cracks or deformities.
- Perform a pressure test to confirm the connection’s integrity.
- Regularly check for signs of wear or corrosion to ensure long-term reliability.
By following these best practices, you can extend the life of your hydraulic hoses and prevent unexpected failures.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even with careful selection, errors during installation or use can compromise the performance of hydraulic systems. Here are some common mistakes to watch out for when choosing and installing hose ferrules.
1. Using an Incompatible Ferrule
One of the biggest mistakes is selecting a ferrule that doesn’t match the hose type. Different hoses—such as rubber, thermoplastic, or PTFE—require specific ferrules to ensure a secure and leak-proof connection. Always refer to manufacturer guidelines before purchasing.
2. Over-Crimping or Under-Crimping
Applying too much force when crimping can damage the hose, while insufficient crimping can lead to leaks. Use the correct crimping pressure as specified by the ferrule and hose manufacturer.
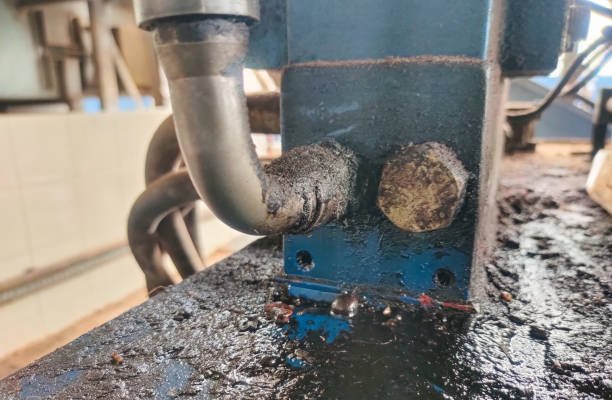
3. Ignoring Environmental Factors
Exposure to chemicals, UV rays, and extreme temperatures can degrade ferrules over time. Stainless steel ferrules are best for corrosive environments, while brass or aluminum ferrules may be suitable for lower-stress applications.
4. Failing to Perform Regular Inspections
Skipping routine inspections can lead to unnoticed wear, which may cause sudden hydraulic failures. Regularly check ferrules for cracks, corrosion, and leaks to ensure long-term reliability.
Industry-Specific Applications
Different industries have unique hydraulic system requirements. Choosing the right hose ferrule depends on the specific environment and operational demands.
1. Automotive
Hydraulic hoses in vehicles require high-performance ferrules that can withstand heat and pressure fluctuations. Stainless steel ferrules are commonly used in power steering and braking systems.
2. Agriculture
Tractors and farming equipment rely on hydraulic systems for lifting, plowing, and irrigation. Ferrules for agricultural applications should be resistant to dirt, moisture, and chemicals commonly found in fertilizers.
3. Construction & Heavy Machinery
Excavators, bulldozers, and cranes use hydraulic hoses to operate heavy loads. Ferrules must be durable and able to handle extreme pressures without failure.
4. Industrial Manufacturing
Factories use hydraulic hoses for automation, material handling, and production lines. Ferrules in manufacturing environments need to withstand continuous operation and exposure to lubricants or coolants.
Maintenance and Replacement Considerations
Even the best ferrules wear out over time. Proper maintenance and timely replacement are essential for preventing hydraulic failures.
1. Signs of Ferrule Wear and Failure
Look for the following warning signs that indicate a ferrule needs replacement:
- Cracks or visible deformation in the ferrule
- Rust or corrosion, especially in wet environments
- Leaks at the hose connection point
- Loss of pressure in the hydraulic system
2. When to Replace Ferrules and Hoses
Ferrules should be replaced whenever hoses are changed or when there are visible signs of damage. Waiting too long can result in system failure and costly repairs.
3. Importance of Routine Inspections
Regularly inspect hoses and ferrules to identify early signs of wear. Preventative maintenance can extend the life of hydraulic components and improve overall efficiency.
Conclusion
Choosing the right hose ferrule for hydraulic applications is essential for system efficiency, safety, and longevity. A well-matched ferrule prevents leaks, withstands pressure, and ensures a secure connection between the hose and fitting.
By considering factors such as hose type compatibility, pressure and temperature ratings, material selection, and industry standards, you can make an informed decision. Additionally, following best practices for installation and maintenance will help prevent costly failures.
Investing in quality ferrules and conducting regular inspections ensures that your hydraulic system operates reliably in any application, whether in automotive, agriculture, construction, or industrial manufacturing.
FAQs
1. How do I know if my hose ferrule is the right fit?
The correct ferrule should match the hose diameter and type. Always check the manufacturer’s sizing chart and ensure a snug fit without excessive force.
2. Can I reuse hydraulic hose ferrules?
Reusable ferrules are available, but most ferrules are crimped or swaged permanently. If a ferrule has been deformed or damaged during removal, it should not be reused.
3. What happens if I use the wrong ferrule material?
Using the wrong material can lead to corrosion, leaks, or hose damage. For example, brass ferrules may not withstand high pressures, while stainless steel offers better corrosion resistance in harsh environments.
4. How do I prevent hydraulic leaks caused by ferrules?
Proper crimping, selecting the right ferrule size, and conducting regular inspections can help prevent leaks. Always follow manufacturer guidelines for installation.
5. What tools do I need for ferrule installation?
Common tools include hydraulic crimping machines, hand crimpers, and swaging tools. The choice of tool depends on the type of ferrule and hose assembly.





