Introduction: Small Parts, Massive Impact
In hydraulic systems, power moves through fluid under pressure—but it’s the fittings that hold everything together. Hydraulic fitting choice plays a crucial role in system efficiency, uptime, and safety. One wrongly selected or poorly installed fitting can mean the difference between smooth operation and catastrophic failure. From mining sites to manufacturing lines, these small components have a big impact—and ignoring their importance can be a costly mistake.
In this article, we’ll explore why hydraulic fitting selection deserves more attention, how it impacts key areas like uptime and safety, and what your business can do to optimize both costs and performance.
Understanding Hydraulic Fittings
Types of Hydraulic Fittings
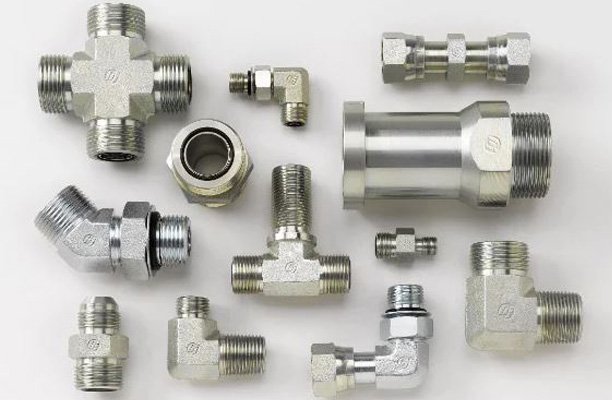

There are several fitting styles in hydraulic applications. Each type aligns with specific thread patterns and pressure ratings:
- NPT (National Pipe Thread): Widely used in North America; requires sealants.
- JIC (Joint Industry Council): Metal-to-metal seal, common in high-pressure systems.
- BSP (British Standard Pipe): Common in European systems.
- SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers): Standardized fittings for automotive and industrial uses.
- ORFS (O-Ring Face Seal): Excellent for leak resistance in high-vibration environments.
Material Considerations
Choosing the right material improves corrosion resistance, pressure tolerance, and service life:
- Carbon Steel: Durable and cost-effective, but prone to corrosion.
- Stainless Steel: Corrosion-resistant; ideal for marine or chemical exposure.
- Brass: Used in low-pressure systems; good for vibration absorption.
- Thermoplastics/Composites: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, for specialized low-pressure systems.
Compatibility Is Critical
A mismatch in fitting type, thread pattern, or pressure rating can cause leakage, failure, or injury. The right combination ensures seamless integration with hoses, valves, and cylinders.
Efficiency & Uptime Optimization
Downtime is the enemy of productivity. And while pumps and motors often get blamed, fittings are frequently the root cause.
Prevent Leaks That Halt Operations
Leaking hydraulic fittings not only waste fluid—they compromise pressure stability and contaminate the environment. A single worn fitting can drop system pressure by 10–15%, reducing machine efficiency and creating delays.
Avoid Costly Downtime
Unexpected failure of hydraulic systems costs companies an average of $700 to $1,100 per hour in downtime. Properly installed, high-quality fittings can extend maintenance intervals, reducing both planned and unplanned halts.
Design for Reliability
The most efficient systems use fittings engineered for precise tolerances and pressure ratings. Investing in compatible, crimped fittings reduces micro-leaks, boosts overall power transmission, and prevents cascading equipment failure.
Safety First: Fitting Failures Can Be Dangerous
Hydraulic systems operate under pressures up to 6,000 PSI. A fitting failure at that level doesn’t just stop work—it can seriously injure workers or destroy nearby equipment.
Injury Risks from High-Pressure Leaks
Pinhole leaks in a high-pressure system can inject fluid through skin—a serious injury known as fluid injection. Left untreated, it can lead to amputation or death.
Compliance with Industry Standards
Selecting fittings certified by SAE, ISO, or other relevant bodies helps ensure they meet safety and performance thresholds. It also supports your regulatory compliance efforts, avoiding costly fines and shutdowns.
Built-In Safety Features
Newer fittings include burst sleeves, pressure relief indicators, and reinforced seals designed to minimize catastrophic failure risks. These features are critical in hazardous industries like oil & gas or mining.
Cost-Saving Strategies
One of the most underestimated benefits of choosing the right hydraulic fittings is long-term cost reduction. While high-quality fittings may seem more expensive initially, they yield significant returns in reduced maintenance, extended lifespan, and fewer emergency repairs.
Invest in Quality Over Quantity
Low-grade fittings are more likely to corrode, crack, or fail under pressure. While they may lower upfront costs, they often lead to more frequent replacements and downtime. Investing in quality, brand-tested fittings ensures longer service intervals and fewer system interruptions.
Prevent Expensive Repairs with Leak-Free Designs
Advanced fittings with O-ring face seals (ORFS) or flareless compression ends help eliminate common leak points. Leak-free operation not only conserves expensive hydraulic fluid but also prevents component wear, avoiding repair costs of cylinders, valves, and pumps.
Avoid Emergency Downtime Charges
Emergency service calls can cost 2–3 times more than regular maintenance. Preventive measures—like choosing fittings rated well above your system’s peak pressure—are far cheaper than a sudden shutdown caused by fitting failure.
Maintenance Best Practices
Even the best fittings require proper installation and regular checks. Establishing a strong maintenance routine is essential to ensure hydraulic system reliability and safety.
Schedule Regular Inspections
Check all hydraulic connections for:
- Surface corrosion or discoloration
- Moisture accumulation or slow leaks
- Signs of over-tightening, cracks, or misalignment
Regular visual inspections and scheduled torque checks reduce undetected failures.
Follow Correct Assembly Techniques
Improper assembly—over-tightening, under-crimping, or poor alignment—can weaken the entire system. Use manufacturer-specified torque levels and crimping equipment for each fitting type. Never mix thread types or force mismatched parts together.
Utilize Mobile Maintenance Kits
On-site fitting kits stocked with the correct sizes, threads, and sealing elements reduce repair time. Tools like hose tagging and mobile crimping units help streamline field maintenance for faster turnaround.
Future Trends & Innovations
The hydraulic fitting market is rapidly evolving, driven by demand for smarter systems, better safety, and environmental compliance.
Smart Fittings for Predictive Maintenance
Sensor-enabled fittings now detect early signs of pressure loss, wear, or leakage—alerting technicians before problems occur. These predictive systems help reduce unplanned outages and optimize part replacement schedules.
Eco-Friendly Materials & Designs
Sustainable alternatives, like biodegradable hydraulic fluids and recyclable thermoplastic fittings, are becoming standard in industries focused on green compliance. New coatings also enhance corrosion resistance without toxic chemicals.
Modular & Quick-Connect Systems
Quick-connect and modular fittings speed up assembly and reduce error. These innovations are especially valuable in mobile equipment, rental fleets, and systems requiring regular configuration changes.
Conclusion
Choosing the right hydraulic fitting is more than a technical decision—it’s a strategic move that influences the reliability, safety, and cost-efficiency of your entire operation. By selecting fittings that are properly matched to your system’s pressure, material, and sealing needs, you can dramatically reduce downtime, enhance worker safety, and stretch maintenance budgets further.
In today’s high-demand environments, a $10 fitting could be the reason you avoid a $10,000 breakdown. Now is the time to assess your inventory, upgrade outdated components, and build a hydraulic system designed for maximum uptime and minimal risk.
FAQs
1. How do I choose the correct hydraulic fitting thread type?
Identify whether your equipment uses NPT, BSP, JIC, or another standard. Match the thread profile visually or use a thread gauge, and always refer to manufacturer specs for compatibility.
2. What pressure rating should I look for in hydraulic fittings?
Select a fitting with a pressure rating higher than your system’s maximum operating pressure. Add a 25%–50% safety margin to accommodate spikes and dynamic loads.
3. What are the early signs of hydraulic fitting failure?
Common signs include visible leaks, pressure drops, moisture build-up, odd noises, or a gradual loss in machine efficiency. Inspect fittings for rust, loose connections, or damaged seals.
4. Are smart hydraulic fittings worth the investment?
Yes. In high-value or mission-critical systems, sensor-enabled fittings help detect failures early, reducing unplanned downtime and minimizing the cost of large-scale damage.
5. How often should hydraulic fittings be inspected or replaced?
Visual inspections should occur monthly or as part of regular maintenance. Replacement should follow OEM guidelines or immediately after detecting damage, excessive wear, or leaks.