JIC threads are a crucial component in hydraulic systems, known for their reliable sealing and ability to handle high pressures. Whether you’re involved in design, maintenance, or repair, understanding the fundamentals of JIC threads is essential. This guide will walk you through everything from the basics of JIC threads to their installation, material selection, and common issues, ensuring you have the knowledge to work with these fittings effectively.
What is a JIC Thread?
A JIC (Joint Industry Council) thread is a type of hydraulic fitting with a 37-degree flare that ensures a tight, leak-proof connection. These threads use Unified National Fine (UNF) threads, making them ideal for high-pressure environments. JIC fittings are widely used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and industrial machinery, where reliable sealing is critical.
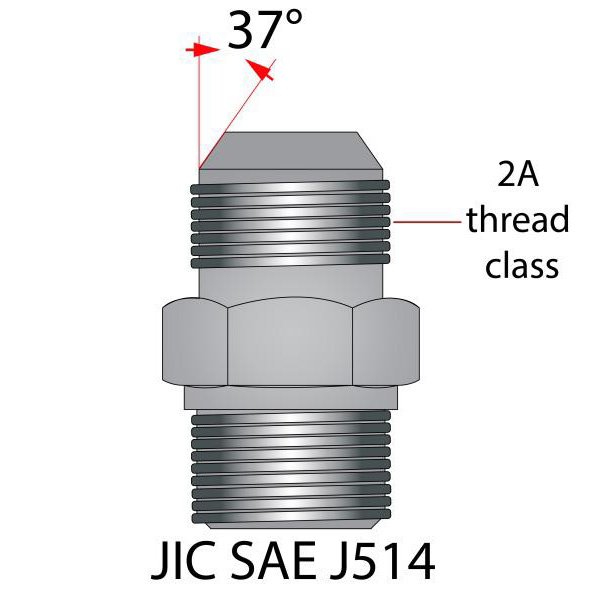
Key Features of JIC Threads
JIC threads are known for several key features that make them ideal for high-pressure applications:
- 37-Degree Flare: Provides a strong metal-to-metal seal.
- High-Pressure Tolerance: Suitable for environments with significant pressure levels.
- Versatility: Compatible with a wide range of tubing and fittings.
- Ease of Installation: Simple assembly and disassembly process, beneficial for maintenance and repairs.
These features make JIC threads a preferred choice in various industrial applications.
JIC Thread Standards and Certification
Specific standards govern JIC threads to ensure their quality and compatibility across different applications. The key standards include:
- SAE J514: This standard specifies the design, dimensions, and performance requirements for JIC fittings.
- ISO 8434-2: This international standard ensures that JIC fittings meet global safety and performance criteria.
- ASME B1.1: Defines the Unified Inch Screw Threads (UNF/UNC) used in JIC fittings, ensuring consistent quality.
Adhering to these standards guarantees that manufacturers produce JIC fittings to high-quality specifications, providing dependable performance in demanding environments.
JIC Thread Chart: Understanding Sizes and Specifications
A JIC thread chart is a vital tool for selecting the correct fitting size and ensuring accurate installation. Here’s a detailed JIC thread chart:
| JIC Size | Thread Size (inches) | Threads Per Inch (TPI) | Dash Size | Tap Drill Size (inches) | Flare Diameter (inches) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/8″ | 5/16-24 UNF | 24 | -2 | 0.272 | 0.184 |
| 3/16″ | 3/8-24 UNF | 24 | -3 | 0.332 | 0.250 |
| 1/4″ | 7/16-20 UNF | 20 | -4 | 0.391 | 0.313 |
| 5/16″ | 1/2-20 UNF | 20 | -5 | 0.453 | 0.391 |
| 3/8″ | 9/16-18 UNF | 18 | -6 | 0.510 | 0.469 |
| 1/2″ | 3/4-16 UNF | 16 | -8 | 0.682 | 0.625 |
| 5/8″ | 7/8-14 UNF | 14 | -10 | 0.810 | 0.750 |
| 3/4″ | 1 1/16-12 UNF | 12 | -12 | 0.955 | 0.938 |
| 1″ | 1 5/16-12 UNF | 12 | -16 | 1.195 | 1.188 |
| 1 1/4″ | 1 5/8-12 UNF | 12 | -20 | 1.535 | 1.469 |
| 1 1/2″ | 1 7/8-12 UNF | 12 | -24 | 1.776 | 1.750 |
| 2″ | 2 1/2-12 UNF | 12 | -32 | 2.276 | 2.406 |
How to Use the JIC Thread Chart
When examining a JIC thread chart, you need to carefully consider key parameters such as thread size, threads per inch (TPI), dash size, and tap drill size.These parameters determine the thread’s outer diameter, inner diameter, and thread pitch. Ensuring that the thread matches the fitting is critical because even a small discrepancy can lead to loose connections or leaks.
How to Measure JIC Thread Size
To accurately select a JIC thread, it’s important to correctly measure the thread size. Typically, a thread pitch gauge and calipers are used to measure the outer diameter and the pitch of the thread. The thread pitch gauge helps determine the TPI, while calipers can precisely measure the outer diameter of the thread.
- Measuring the Outer Diameter: Use calipers to measure the maximum outer diameter of the thread and record this measurement.
- Determining the Thread Pitch: Use a thread pitch gauge to find the number of threads per inch (TPI) by fitting the gauge into the threads and matching the correct pitch.
- Cross-Referencing with the Chart: Once you have the outer diameter and TPI, cross-reference these measurements with the JIC thread chart to identify the exact fitting size.
Understanding these measurements and using the JIC thread chart correctly ensures that you select the right fitting, preventing issues like mismatched threads or leaks.
Common Mistakes in Measuring JIC Threads
- Misidentifying Thread Size: It’s easy to confuse similar thread sizes, especially when working with fittings of close dimensions. Always double-check your measurements against the chart.
- Incorrectly Using Tools: Misuse of measurement tools like calipers or thread gauges can lead to inaccurate readings. Ensure that tools are used properly and that the gauge fits snugly into the thread.
- Overlooking TPI Variations: Even slight variations in TPI can cause fitting issues. Carefully match the TPI with the chart to avoid selecting the wrong fitting.
These steps and considerations are essential to accurately identifying and using JIC threads in any hydraulic system.
JIC Thread Size: The Importance of Precision
Selecting the correct JIC thread size is essential for achieving a secure connection. Specifically, a dash number represents JIC thread sizes, corresponding to the nominal size of the tubing they fit. Therefore, precision in selecting the correct size ensures that the fittings provide a tight seal, preventing leaks and, consequently, maintaining the integrity of the hydraulic system.
Understanding JIC Thread Pitch
Thread pitch refers to the number of threads per inch (TPI) on a fitting. In JIC threads, pitch is crucial for creating a tight seal. A higher TPI means finer threads, which can create a more precise seal. Understanding the pitch helps in selecting the correct fitting for your application, ensuring a secure and leak-free connection.
JIC Thread Tap: Achieving the Perfect Fit
Tapping is the process of creating threads inside a hole to allow a fitting to be screwed in. For JIC threads, tapping requires creating the exact thread pattern specified by the thread size and pitch. This ensures a perfect fit and a secure, leak-free connection. The tap drill size is also critical to match the fitting’s threads correctly.
JIC Thread Material Selection: Choosing the Right Material
Choosing the right material for JIC threads is a critical decision that impacts the performance, durability, and longevity of hydraulic systems. You must select the material based on the specific environmental conditions, fluid types, and pressure requirements of the application.
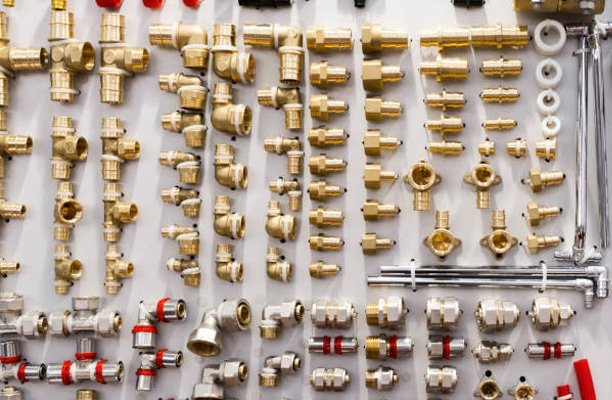

Common Materials for JIC Fittings
- Stainless Steel:
- Properties: Stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion and can withstand harsh environmental conditions, such as those found in marine or chemical processing applications. It also offers excellent durability and strength, making it ideal for high-pressure applications.
- Applications: This material is commonly used in industries where the fittings are exposed to corrosive substances, such as offshore drilling, marine, and chemical industries, because it offers excellent resistance to corrosion.
- Carbon Steel:
- Properties: Carbon steel is known for its strength and cost-effectiveness. It is suitable for high-pressure applications but does not have the same level of corrosion resistance as stainless steel.
- Applications: Industries such as industrial machinery, construction equipment, and agricultural machinery use carbon steel JIC threads widely in less corrosive environments where high strength is still required.
- Brass:
- Properties: Brass offers good corrosion resistance and is easy to machine, which makes it suitable for precision applications. It also has good thermal conductivity and is resistant to many chemicals.
- Applications: Plumbing, automotive, and refrigeration applications often use brass fittings where resistance to water, coolants, and mild chemicals is necessary.
- Aluminum:
- Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in aerospace. However, it is not as strong as steel and may not be suitable for high-pressure applications.
- Applications: Aluminum JIC threads are used
How to Properly Install JIC Fittings
Proper installation of JIC fittings is essential for preventing leaks and ensuring reliable performance. Follow these steps:
- Clean the Components: Ensure all parts are free from debris.
- Align the Fitting: Hand-tighten to ensure correct alignment.
- Use the Right Tools: Use a flare nut wrench to avoid damaging the fitting.
- Apply Correct Torque: Use a torque wrench to tighten according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Inspect the Connection: Check for proper alignment and test for leaks.
These steps help ensure a secure and effective installation of JIC fittings.
JIC Threads vs. Other Thread Standards
When choosing the right thread standard for a specific application, it’s important to understand how JIC threads compare to other common thread types:
- NPT Threads: Tapered and often require sealants for a leak-proof connection.
- BSP Threads: Similar to NPT but not interchangeable, used in hydraulic systems.
JIC threads are often preferred for their ease of use and reliable sealing in high-pressure environments.
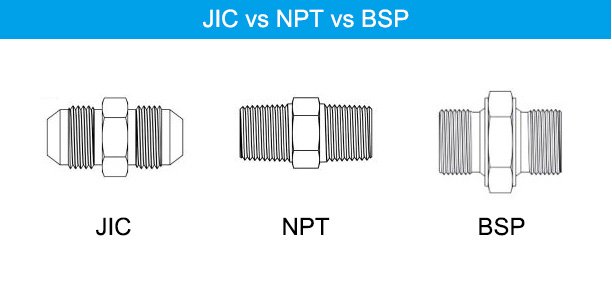
JIC Threads vs. NPT Threads: Understanding the Differences
JIC and NPT threads serve similar purposes but have key differences:
- Thread Type: JIC threads are straight, while NPT threads are tapered.
- Sealing Mechanism: JIC uses a 37-degree flare for sealing, while NPT relies on thread interference.
- Applications: JIC threads are reusable and easier to assemble, while NPT threads are often used in permanent connections.
Common Problems with JIC Threads and How to Avoid Them
Despite their reliability, issues can arise with JIC threads if not handled properly. Common problems include:
- Cross-Threading: Occurs when threads are not aligned properly.
- Over-Tightening: Can damage the flare and cause leaks.
- Improper Flare Angle: Mismatched angles can lead to poor seals.
- Corrosion: Can weaken the fitting in harsh environments.
To avoid these problems, follow proper installation procedures, and regularly inspect fittings for wear or damage.
Maintaining JIC Fittings for Long-Term Reliability
Regular maintenance is key to ensuring the long-term reliability of JIC fittings. Tips for maintaining these fittings include:
- Routine Inspections: Check for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
- Leak Checks: Regularly test connections under pressure for leaks.
- System Flushing: Remove contaminants from the system to prevent wear and tear on the fittings.
Maintaining your JIC fittings ensures they remain in good condition and perform reliably over time.
Applications and Benefits of JIC Threads
JIC threads are widely used in industries where reliable sealing and high-pressure performance are crucial. Common applications include:
- Hydraulic Systems: Used in industrial machinery, construction equipment, and aerospace.
- Automotive Industry: Essential in fuel lines, brake systems, and transmission lines.
- Marine Applications: Ideal for hydraulic systems in corrosive environments.
- Agricultural Machinery: Used in tractors and other heavy equipment.
The benefits of using JIC threads include their high-pressure tolerance, ease of installation, and versatility across various applications.
Conclusion
JIC threads play a crucial role in ensuring the integrity and efficiency of hydraulic systems across many industries. By understanding their specifications, including size, pitch, material selection, and installation procedures, you can ensure that your systems remain leak-free and reliable. Whether comparing JIC threads to other standards or addressing common issues, this guide provides the knowledge you need to work confidently with these fittings.
FAQs
What does JIC stand for in JIC thread?
JIC stands for Joint Industry Council, which established the standards for these hydraulic fittings.
How do you measure JIC thread size?
JIC thread size is measured by the outer diameter of the thread and the threads per inch (TPI), typically using a thread gauge.
What is the difference between JIC and NPT threads?
JIC threads create a seal with their straight design and 37-degree flare, while NPT threads require thread sealant for a leak-proof connection due to their tapered design.
Can JIC fittings be reused?
Yes, JIC fittings can be reused if they are in good condition and not damaged. Always inspect them before reuse.
What materials are commonly used for JIC threads?
Common materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, brass, and aluminum, chosen based on the application and environment.
How do you prevent common problems with JIC threads?
Prevent problems by ensuring proper alignment, avoiding over-tightening, selecting the correct flare angle, and regularly inspecting for wear and corrosion.





