Hydraulic systems are vital in various industries like construction and aerospace, making the selection of the right fittings and adapters essential for reliable performance. Two prominent standards, SAE J514 and ISO 8434-2, lead the market. While both offer high-quality hydraulic fittings, they differ significantly in regional usage, material choices, and performance. SAE J514 is primarily used in North America, whereas ISO 8434-2 is prevalent in Europe and beyond. This article explores these differences to help you make informed decisions when choosing hydraulic fittings.
Overview of SAE J514 vs. ISO 8434-2
SAE J514 Standard
What are SAE J514 Fittings?
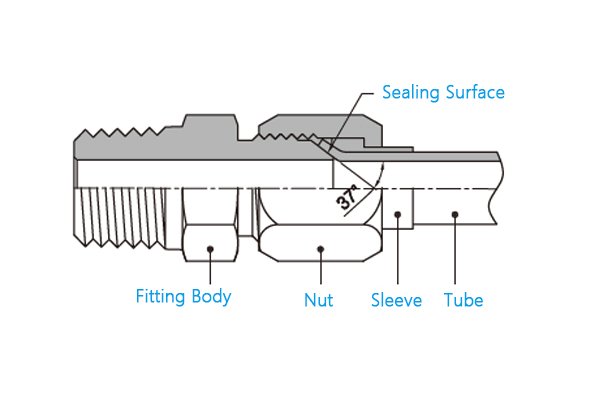
Developed by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the SAE J514 standard serves North American industries by ensuring the safety and reliability of hydraulic systems through established performance and dimensional specifications for hose fittings and adapters.
Common Industries Using SAE J514:
Industries such as automotive, industrial hydraulics, construction, agriculture, and aerospace commonly utilize SAE J514 fittings. These industries rely on hydraulic systems operating under high pressure, making standardization essential to prevent leaks and ensure long-lasting performance.
Types of Fittings:
The SAE J514 standard encompasses various fitting types, including:
- 37° Flare Fittings: Designed for high-pressure applications, these fittings provide a secure seal.
- Straight-thread O-ring fittings
- Tapered pipe-thread fittings
These fittings thrive in high-pressure environments and have gained widespread adoption due to their reliability and ease of installation.
ISO 8434-2 Standard
What are ISO 8434-2 Fittings?
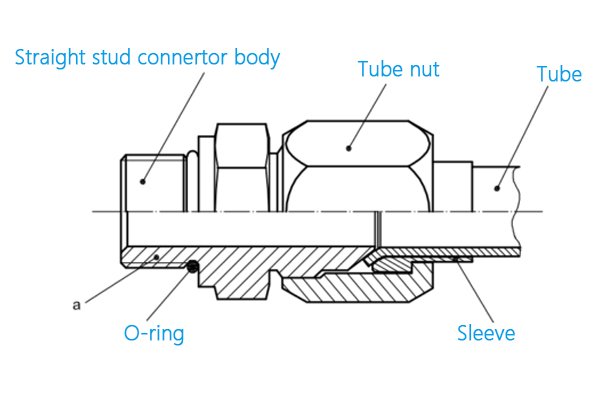
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) developed ISO 8434-2 to provide global standards for hydraulic fittings, particularly those that use metric measurements. This standard emphasizes material specifications, pressure ratings, and compatibility for international applications.
Common Industries Using ISO 8434-2:
ISO 8434-2 fittings are commonly found in manufacturing, heavy equipment, marine, agriculture, and oil & gas industries. These sectors often operate globally, making a unified international standard critical for ensuring system compatibility across borders.
Types of Fittings:
ISO 8434-2 focuses on metric compression fittings, which provide strong sealing in high-pressure conditions. These fittings are known for their reliability in environments requiring frequent maintenance and reconnection.
Why Compare SAE J514 and ISO 8434-2 Hydraulic Fittings?
Regional Usage: SAE J514 vs. ISO 8434-2
The first major difference between SAE J514 and ISO 8434-2 lies in their regional focus. SAE J514 fittings are predominantly used in North America, while ISO 8434-2 is widely adopted in Europe and other global markets. This means the two standards are generally not interchangeable due to differences in fitting designs, such as thread types.
- SAE J514: Primarily relies on 37° flare-type fittings and NPT (National Pipe Taper) threads, common in North America.
- ISO 8434-2: Uses metric compression fittings and ISO threads, more prevalent internationally, especially in Europe.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for engineers working in different regions or designing systems for global markets to avoid compatibility issues.
Design and Material Differences in Hydraulic Fittings
Material Specifications
Both standards specify high-performance materials, but preferences differ:
- SAE J514 Materials:
- Steel: Commonly used for its high strength and ability to handle high-pressure systems.
- Brass: Valued for corrosion resistance but typically suited for lower-pressure systems.
- Stainless Steel: Ideal for high temperatures or corrosive environments, such as marine applications.
- ISO 8434-2 Materials:
- Stainless Steel and Carbon Steel: ISO tends to focus more on corrosion-resistant materials, suitable for international industries facing harsh environmental conditions.
- Nickel-Plated Brass: Frequently used for its enhanced corrosion resistance.
Comparison of Strengths and Weaknesses:
- Steel (SAE J514): Excellent for high-pressure applications but may require additional corrosion protection.
- Brass (Both Standards): Great for resisting corrosion but not ideal for high-pressure environments.
- Stainless Steel (Both Standards): Top choice for durability in extreme conditions, though typically more expensive.
- Nickel-Plated Brass (ISO 8434-2): Balances strength and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for marine and oil & gas industries.
Design Differences in Fittings
The design of fittings varies between the two standards:
- SAE J514: Includes mostly 37° flare fittings with NPT threads. The flare design creates a secure seal by deforming the tube, effective for high-pressure applications.
- ISO 8434-2: Emphasizes metric compression fittings with ISO threads. These fittings offer high precision in sealing, especially useful in systems where minimal leaks are critical.
Sealing Methods
Both standards aim for leak-proof connections but use different methods:
- SAE J514: Utilizes flare fittings where the end of the tube flares to create a seal. It also commonly uses O-ring boss (ORB) fittings for tighter seals.
- ISO 8434-2: Primarily employs compression fittings, where a ferrule compresses the tube to form a seal, allowing for easier reconnection and disconnection during maintenance.
Pressure Ratings and Performance
Pressure Ratings
Both SAE J514 and ISO 8434-2 fittings design for high-pressure systems, but they have slight differences in testing and performance ratings:
- SAE J514: Typically rated for pressures up to 6,000 psi (depending on the material and fitting type). Flare and O-ring fittings are reliable in high-pressure environments.
- ISO 8434-2: Handles similar pressure ratings, often up to 450 bar (6,500 psi). ISO fittings focus on metric measurements and often provide more precise sealing for specific applications.
Corrosion Resistance
- SAE J514: Utilizes materials like plated steel and stainless steel, but some fittings (like brass) may degrade faster in highly corrosive environments.
- ISO 8434-2: Prioritizes materials like stainless steel and nickel-plated brass, which offer enhanced protection against corrosion, especially in marine and chemical processing industries.
Temperature Range and Compatibility
- SAE J514: Generally operates in temperature ranges from -65°F to 400°F (-54°C to 204°C), suitable for both high- and low-temperature applications.
- ISO 8434-2: Designed for similar temperature ranges, focusing on materials that can handle extreme fluctuations, particularly in oil & gas or marine systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Pros and Cons of SAE J514
Advantages:
- Widespread Acceptance: SAE J514 fittings are widely recognized in North America, making them a common choice in various industries. This standardization helps ensure compatibility across different equipment and systems.
- Robust Performance: These fittings are designed to handle high-pressure applications effectively. Their ability to maintain integrity under pressure makes them suitable for hydraulic systems, where reliability is paramount.
- Material Versatility: SAE J514 fittings can be manufactured from various materials, including steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. This versatility allows for their use in diverse environments, including corrosive settings.
- Ease of Assembly: The design of SAE J514 fittings typically allows for straightforward assembly and disassembly. This feature benefits maintenance scenarios where technicians require quick access to components.
Disadvantages:
- Limited International Usage: While SAE J514 is popular in North America, its usage may be limited in other regions. This can pose challenges for companies operating globally, leading to potential compatibility issues.
- Higher Cost for Specialized Variants: Some specialized variants of SAE J514 fittings can be more expensive than standard options, which might not be ideal for projects with tight budgets.
Pros and Cons of ISO 8434-2
Advantages:
- International Standardization: ISO 8434-2 fittings promote compatibility and interoperability across international borders, earning recognition worldwide. This is particularly advantageous for multinational companies.
- Precision Engineering: Manufacturers produce ISO fittings to precise tolerances, enhancing their performance in high-demand applications. This precision can contribute to reduced leakage and improved system efficiency.
- Broad Range of Options: The ISO standard encompasses various types and sizes of fittings, allowing engineers to choose the most appropriate option for their specific applications.
- Enhanced Safety Features: Many ISO 8434-2 fittings incorporate safety features, such as locking mechanisms, which help prevent accidental disconnections in critical applications.
Disadvantages:
- Complex Installation: Installing some ISO 8434-2 fittings can be more complex than installing SAE J514 fittings. This complexity may require specialized training or tools, increasing installation time and costs.
- Potential Availability Issues: Depending on the region, ISO 8434-2 fittings may not be as readily available as SAE J514 fittings, potentially leading to longer lead times for sourcing.
Choosing Between SAE J514 and ISO 8434-2 Hydraulic Fittings

Which Hydraulic Fittings Standard is Right for Your Industry?
Choosing between SAE J514 and ISO 8434-2 depends on several factors, including location, industry requirements, and system design. Consider the following:
- North American Applications: Automotive, industrial, and construction systems in North America commonly use SAE J514.
- International Applications: Global industries, especially in Europe’s marine, oil & gas, and heavy equipment sectors, often require ISO 8434-2.
- High-Pressure Systems: Both standards provide reliable solutions for high-pressure systems, with users particularly favoring ISO 8434-2’s compression fittings for precision sealing in leak-free operations.
Conclusion
Selecting between SAE J514 and ISO 8434-2 fittings hinges on regional focus, industry needs, and specific application requirements. While both standards offer reliable solutions for hydraulic systems, SAE J514 is the go-to in North America, whereas ISO 8434-2 is more prevalent in Europe and globally. Understanding these differences helps ensure system compatibility, performance, and compliance with regional standards.
FAQ
What is the SAE J514 standard?
SAE J514 is a North American standard governing hydraulic fittings, primarily used in automotive and industrial applications.
What is ISO 8434-2?
ISO 8434-2 is an international standard for hydraulic fittings that focuses on metric compression fittings, widely used in Europe.
Can SAE J514 and ISO 8434-2 fittings be used interchangeably?
No, they are generally not interchangeable due to differences in thread types and design specifications.
Which standard is better for high-pressure systems?
Both standards support high-pressure systems, but ISO 8434-2 offers more precise sealing, especially in marine and chemical processing industries.
What materials are used in SAE J514 fittings?
Common materials include steel, brass, and stainless steel, each suited for different pressure and environmental conditions.
Where is ISO 8434-2 commonly used?
ISO 8434-2 is widely utilized in global industries, particularly in Europe, and sectors like marine and heavy equipment.





