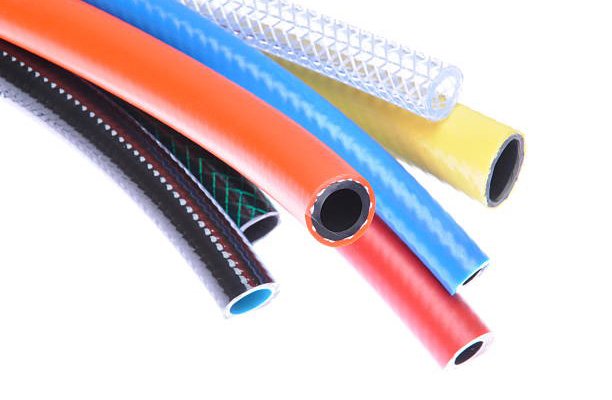
In the world of hydraulic and pneumatic systems, hoses are critical components that help transfer fluids or gases with precision and safety. However, even the smallest mistake in hose fabrication or installation can lead to catastrophic failures, causing system downtime, safety hazards, and unnecessary costs. This comprehensive guide aims to help you understand how to avoid the common pitfalls associated with hose fabrication and installation, ensuring a longer lifespan and optimal performance of your hose assemblies.
Introduction
Hose assemblies are often treated as secondary components in a hydraulic or pneumatic system, yet they play an indispensable role in its overall functionality. Poorly fabricated or improperly installed hoses can lead to leaks, pressure drops, or even sudden failures. Whether you are a seasoned professional or a novice installer, understanding the nuances of hose fabrication and installation is essential for ensuring efficiency, safety, and durability in your operations.
Understanding Hose Fabrication and Installation
Before diving into the common mistakes to avoid, it is important to clarify the two critical stages of working with hoses: fabrication and installation. Hose fabrication involves selecting the right materials, measuring, cutting, and assembling hoses with appropriate fittings. On the other hand, hose installation is the process of correctly positioning and securing the hose within the system to ensure it can operate under specific conditions without failure.
In both stages, small errors can lead to significant issues. Therefore, it is essential to be familiar with both the materials and techniques used in each step to prevent unnecessary risks.
Selecting the Right Hose for the Job

One of the first and most common mistakes in hose fabrication is failing to select the right hose for the specific application. Hoses come in a variety of materials and designs, each intended for a specific type of fluid, temperature, and pressure.
- Material Compatibility: Always ensure the hose material is compatible with the fluid it will transport. For instance, rubber hoses may degrade when exposed to certain chemicals, while metal hoses can withstand extreme temperatures.
- Pressure Rating: Overlooking the pressure requirements can lead to bursting hoses. Every hose has a maximum pressure rating that should never be exceeded.
- Temperature Tolerance: Operating a hose beyond its temperature limit can cause material breakdown and failure.
- Application-Specific Design: Hoses designed for hydraulic systems are different from those used in pneumatic applications. Ensure the hose is designed for the system’s needs.
Failing to Measure Accurately
Accurate measurement is crucial in hose fabrication. Incorrect hose length or diameter can lead to performance inefficiencies and premature wear.
- Hose Length: A hose that is too short will experience excessive strain, while a hose that is too long can sag, creating flow restrictions or unnecessary wear. Always account for the hose’s flexibility and movement during operation.
- Diameter Selection: Using a hose with an incorrect inner diameter can lead to flow restriction, pressure loss, or increased energy consumption. Always match the hose diameter with the system’s requirements.
Improper Cutting Techniques
Cutting hoses may seem like a straightforward task, but improper techniques can lead to fraying, contamination, or irregular edges, all of which can compromise hose performance.
- Fraying: Hoses that are not cut cleanly may fray, leaving small particles that can contaminate the system.
- Straight Edges: Always ensure a clean, straight cut. Angled or jagged edges can prevent proper sealing and increase the risk of leakage.
- Proper Tools: Always use the appropriate cutting tools, such as hose saws or specialized cutters, to ensure precision.
Incorrect Fitting Assembly
Fittings are critical to the integrity of the hose assembly. Incorrectly assembled fittings are a common cause of leaks, which can lead to system failure or safety hazards.
- Fitting Selection: Ensure that the fitting material is compatible with the hose and the fluid it will transport.
- Crimping Errors: Over-crimping can damage the hose, while under-crimping can lead to leaks. Always follow manufacturer specifications when crimping fittings.
- Thread Mismatch: Be cautious of thread types, especially in hydraulic applications. Mixing metric and imperial threads can result in improper sealing and damage.
Neglecting Bend Radius and Hose Routing
Improper hose routing and ignoring the recommended bend radius are frequent mistakes that can lead to premature hose failure.
- Bend Radius: Every hose has a minimum bend radius. Bending a hose too sharply can cause kinks, reduce flow, and increase stress on the material, leading to early failure.
- Routing Errors: Avoid routing hoses through areas with excessive movement, high temperatures, or abrasive surfaces. Ensure hoses are routed to allow for natural movement and avoid tight spaces where friction can occur.
Over-Tightening or Under-Tightening Connections
Tightening connections is a delicate balance. Over-tightening can strip threads or crush the hose, while under-tightening can result in leaks.
- Torque Specifications: Always follow the manufacturer’s recommended torque settings for each connection to ensure optimal sealing without damaging components.
- Thread Sealant: Use appropriate thread sealant or tape as per the application. Overuse or improper application can cause contamination or blockages in the system.
Ignoring Environmental Conditions
The environment in which the hose operates plays a significant role in its lifespan. Failure to consider environmental factors can accelerate wear and tear.
- Temperature Extremes: Ensure that the hose material is suited to the operating temperature. For example, rubber hoses may crack under extreme cold, while certain plastics degrade in high heat.
- UV Exposure: Prolonged exposure to sunlight can degrade hose materials, especially in outdoor applications. Consider using protective sleeves or UV-resistant hoses.
- Abrasive Conditions: If the hose is exposed to abrasive surfaces, it can wear down quickly. Protective coverings or rerouting can extend the hose’s life.
Neglecting Regular Inspections and Maintenance
Even a perfectly fabricated and installed hose assembly can fail without regular inspections and maintenance. Preventive measures can catch small issues before they escalate.
- Routine Inspections: Regularly check hoses for signs of wear, leaks, or damage. Inspect for kinks, cracks, or swelling.
- Preventive Replacement: It’s better to replace hoses on a maintenance schedule rather than waiting for a failure. Sudden hose bursts can cause extensive damage and downtime.
- Cleaning and Flushing: Periodically clean hoses and fittings to remove contaminants that could degrade performance or cause damage.
Common Hose Fabrication and Installation Mistakes
In summary, here are the most common mistakes in hose fabrication and installation to avoid:
- Choosing the Wrong Hose Material or Fitting
- Failing to Measure Accurately
- Improper Cutting Techniques
- Overlooking the Importance of Bend Radius
- Incorrect Crimping and Fitting Assembly
- Neglecting Environmental Factors
- Over-Tightening or Under-Tightening Connections
- Inadequate Routine Maintenance
Best Practices for Hose Fabrication and Installation
To ensure a successful hose fabrication and installation, follow these best practices:
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Always adhere to the manufacturer’s specifications for hose selection, cutting, and fitting assembly.
- Use Proper Tools: Invest in specialized tools for cutting, crimping, and fitting hoses to ensure precision and prevent damage.
- Train Personnel: Ensure that those fabricating and installing hoses are trained and knowledgeable about the specific requirements of your system.
- Regularly Inspect and Maintain: Don’t wait for a hose to fail—inspect regularly and replace as part of preventive maintenance.
FAQs
How can I avoid over-tightening hose fittings?
To avoid over-tightening, always use a torque wrench and follow the manufacturer’s recommended torque settings.
What should I consider when selecting a hose for high-pressure applications?
Ensure the hose has a pressure rating higher than your system’s maximum operating pressure and is compatible with the fluid being transported.
Can I bend a hose to fit into a tight space?
Hoses should not be bent beyond their minimum bend radius. Use elbows or alternative routing methods to avoid kinks and stress.
What causes hose leaks even after proper installation?
Hose leaks can result from incorrect fitting assembly, improper crimping, or using incompatible materials.
Why is hose length important in fabrication?
Too short a hose can cause strain, while too long a hose may sag, both of which can lead to premature wear or damage.
What environmental factors should I consider for hose installations?
Temperature extremes, UV exposure, and abrasive environments are critical factors to consider when selecting and installing hoses.
Conclusion
Hose fabrication and installation may seem straightforward, but it requires careful attention to detail at every step. By avoiding common mistakes such as incorrect material selection, poor measurements, and improper fitting assembly, you can extend the life of your hose assemblies and ensure the safe and efficient operation of your system. Regular maintenance and adhering to best practices are key to preventing costly breakdowns and ensuring reliability in any hydraulic or pneumatic application.
For further information, consider linking to reputable hose manufacturers and fluid system guidelines to expand your knowledge on best practices.





